{{currentView.title}}
February 22, 2022
Ukraine Invasion Updates
This page collects the Critical Threats Project (CTP) and the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) updates on the invasion of Ukraine. In late February 2022, CTP and ISW began publishing daily synthetic products covering key events related to renewed Russian aggression against Ukraine. These Ukraine Conflict Updates replaced the “Indicators and Thresholds for Russian Military Operations in Ukraine and/or Belarus,” which we maintained from November 12, 2021, through February 17, 2022.
This list also includes prominent warning alerts that CTP and ISW launched outside the crisis update structure. These products addressed critical inflection points as they occurred.
Follow the Critical Threats Project on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
- Maps on Assessed Control of Terrain in Ukraine and Main Russian Maneuver Axes
- Recent Updates
- February 2022 - July 2023 Updates
- Related Reads
Maps on Assessed Control of Terrain in Ukraine and Main Russian Maneuver Axes
This interactive map complements the static daily control-of-terrain maps that CTP and ISW produce with high-fidelity and, where possible, street level assessments of the war in Ukraine.
Click here to access the archive of interactive time-lapse maps of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. These maps complement the static control-of-terrain maps that produced daily by showing a dynamic frontline.
The Critical Threats Project and the Institute for the Study of War are publishing a summary of the methodology of our map for those who would like to learn more about the tradecraft for mapping conventional military operations from the open source.
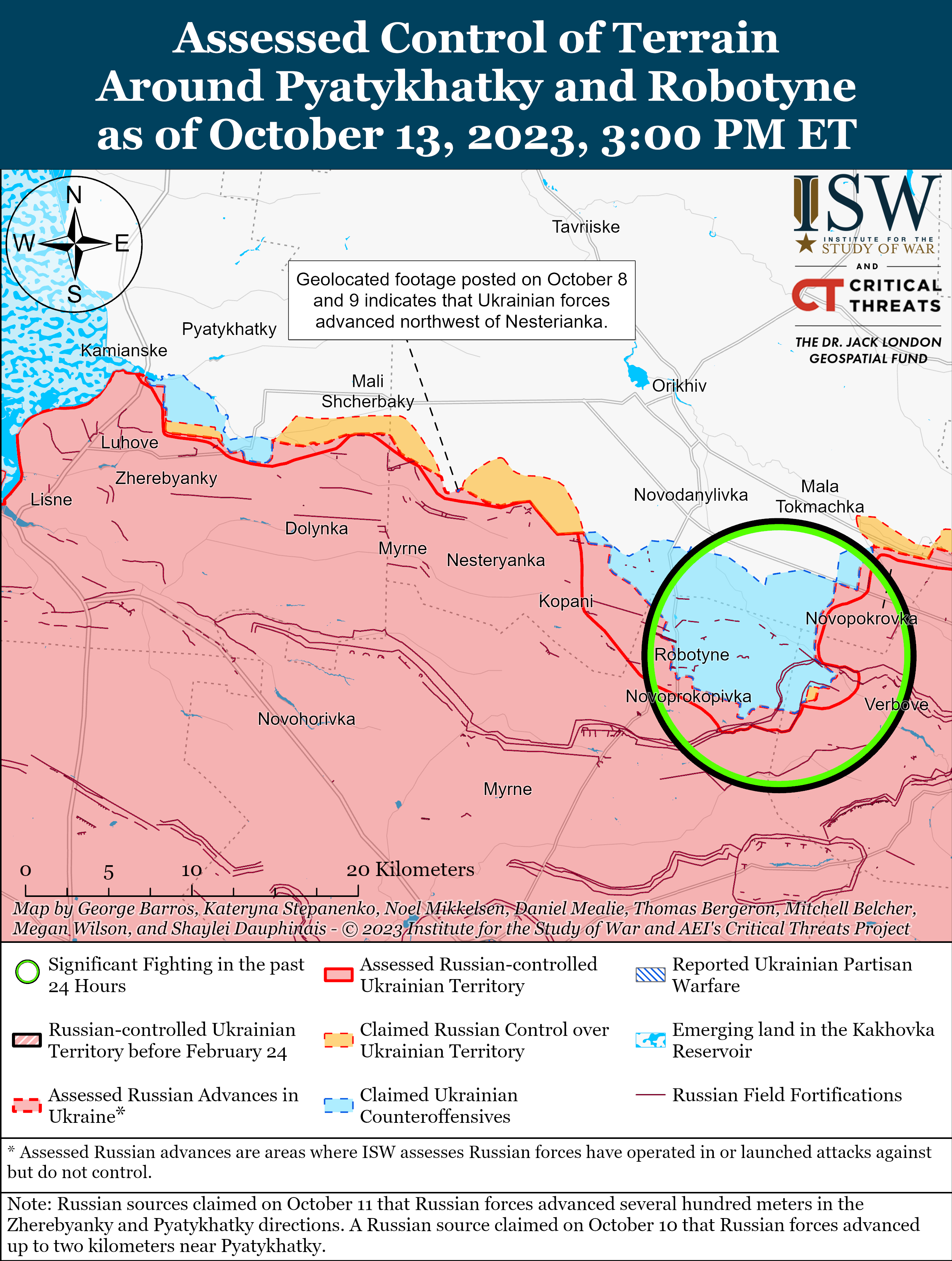
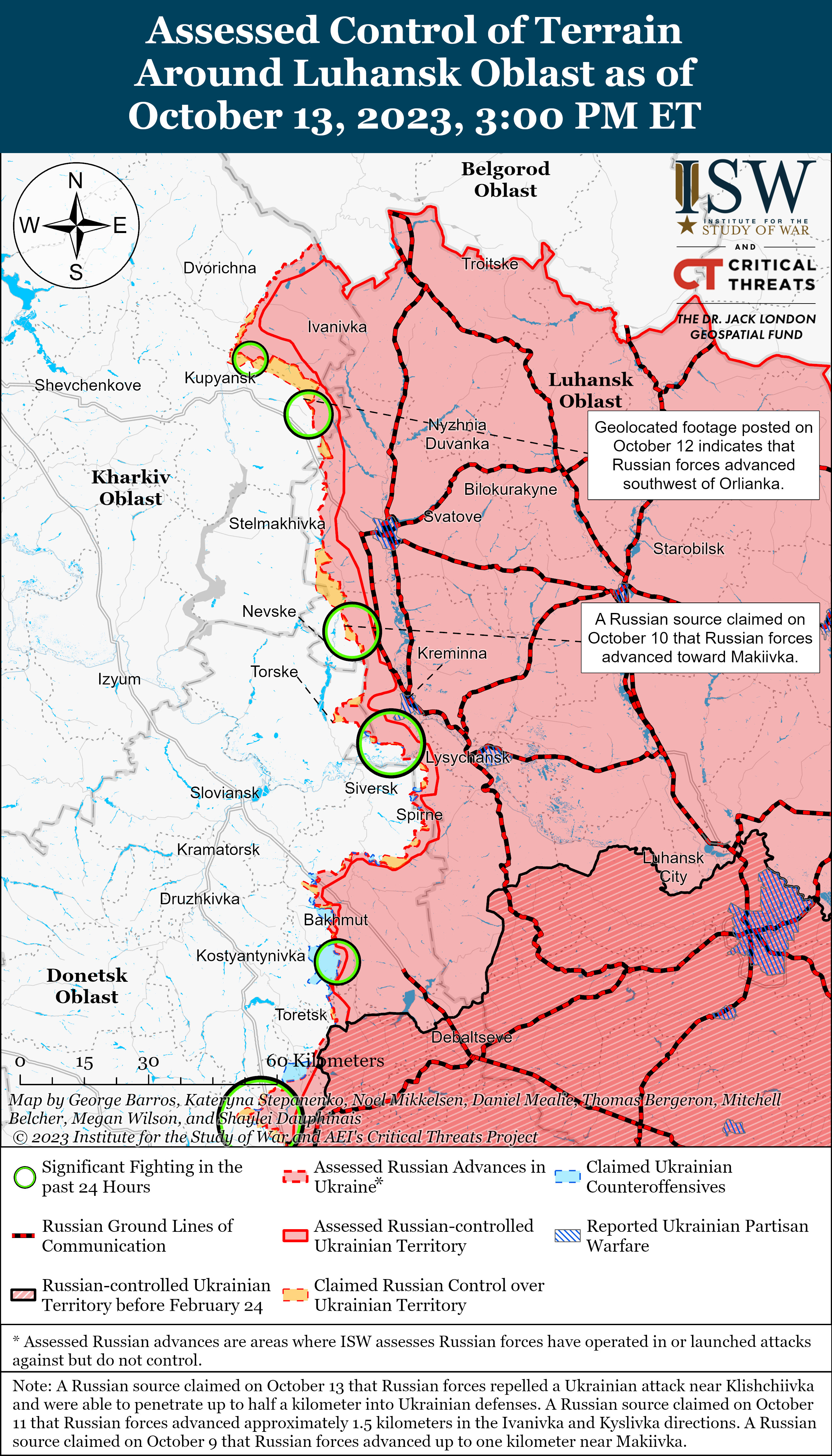
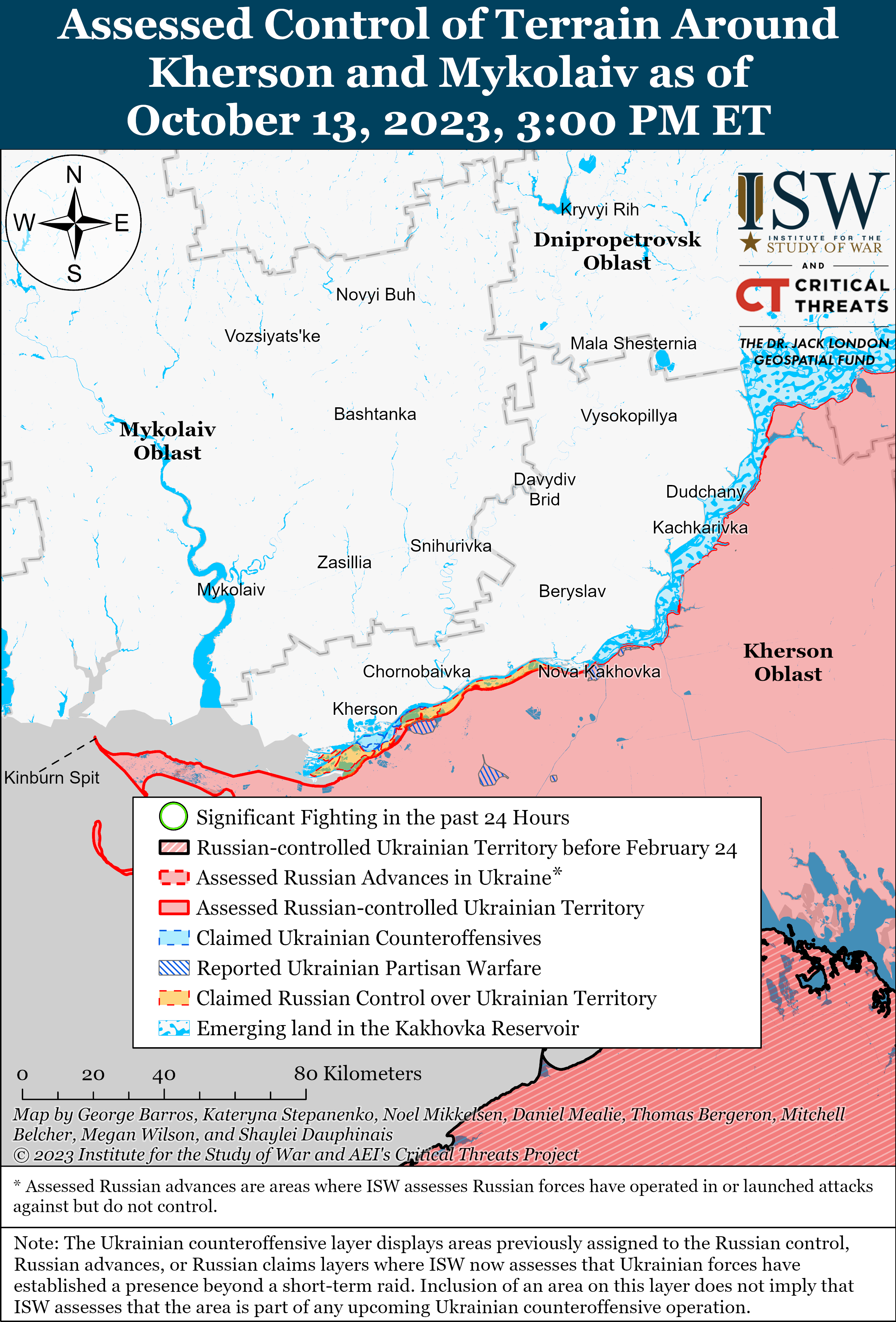
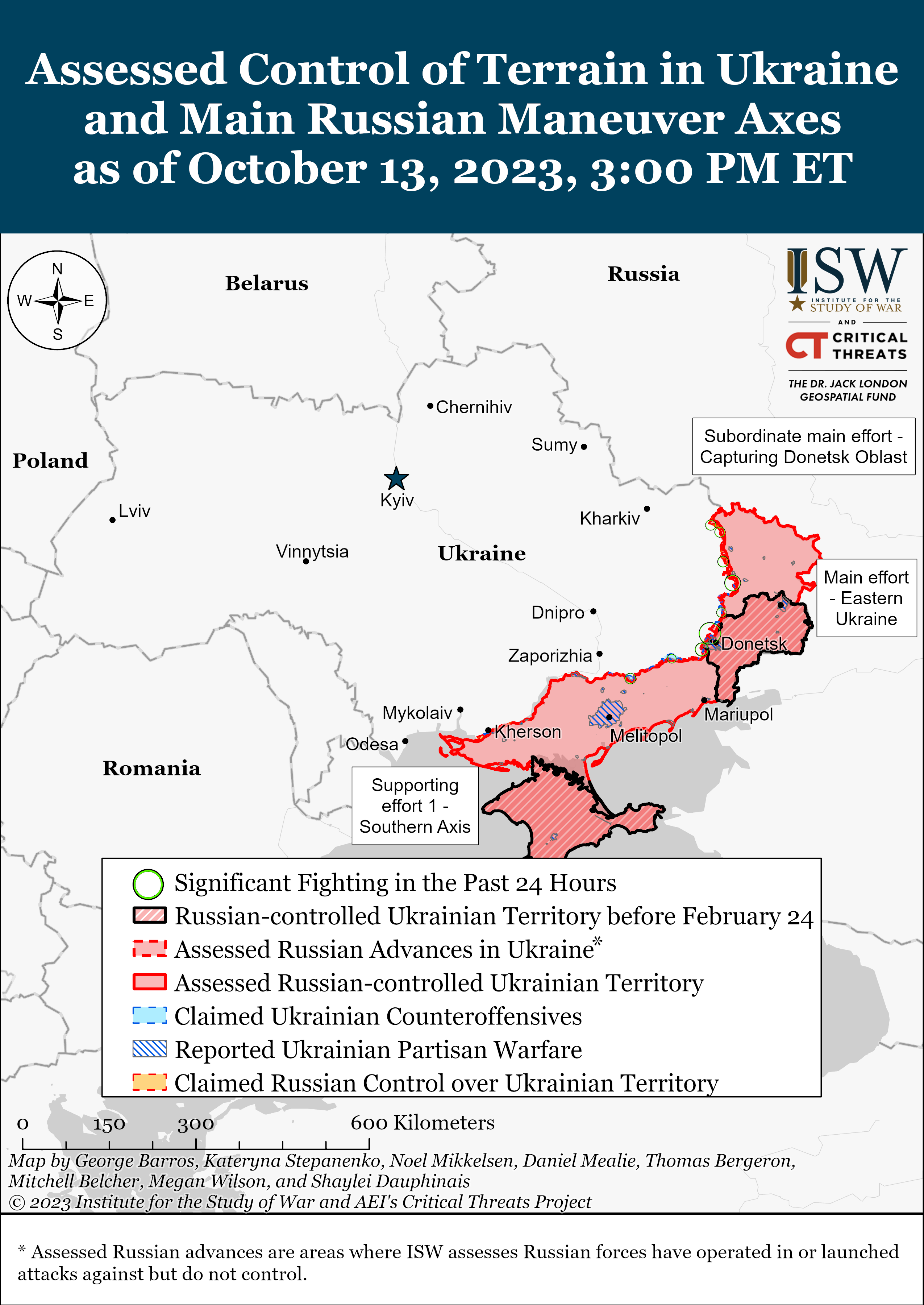
Previous versions of these static maps are available in our past publications.
Recent Updates
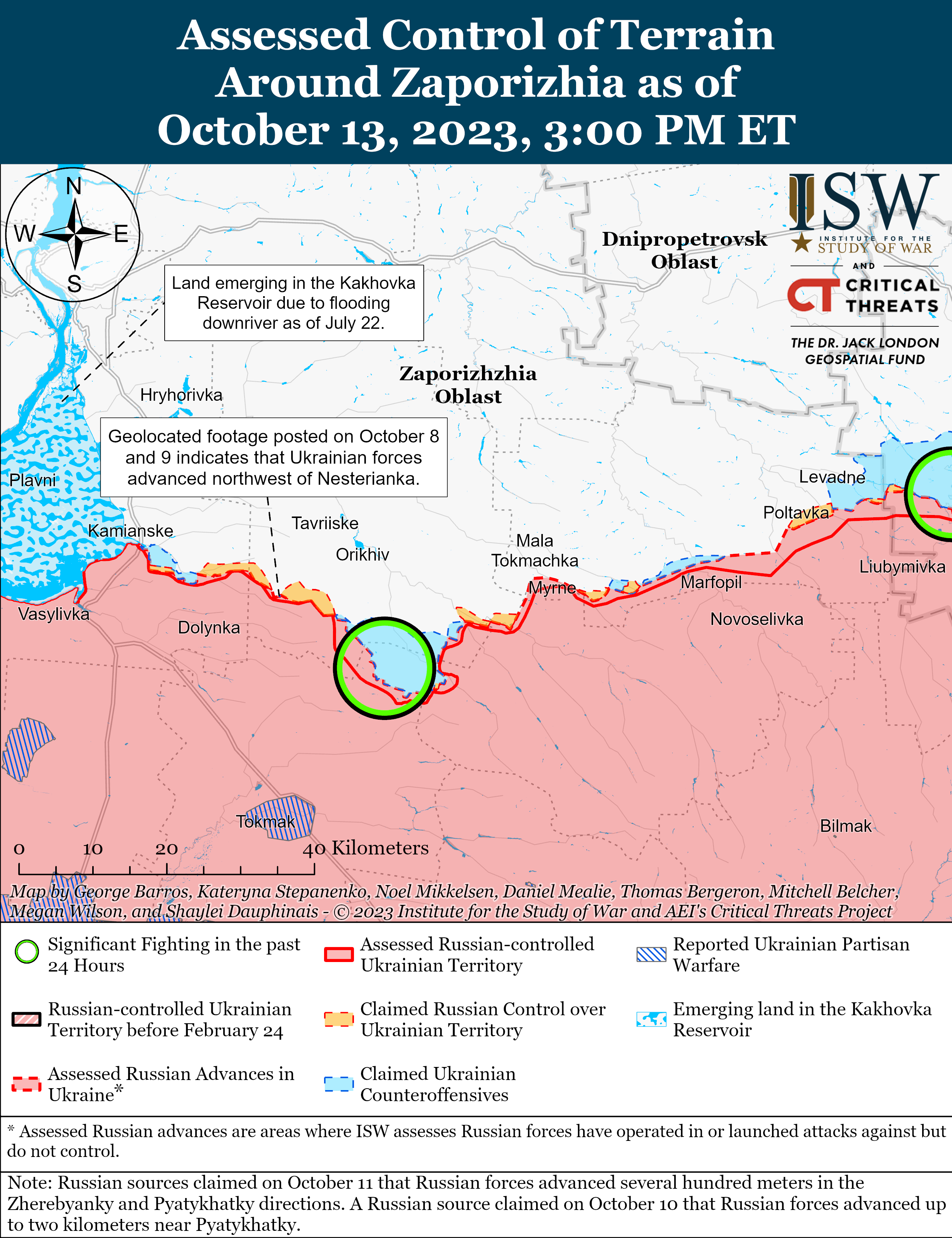
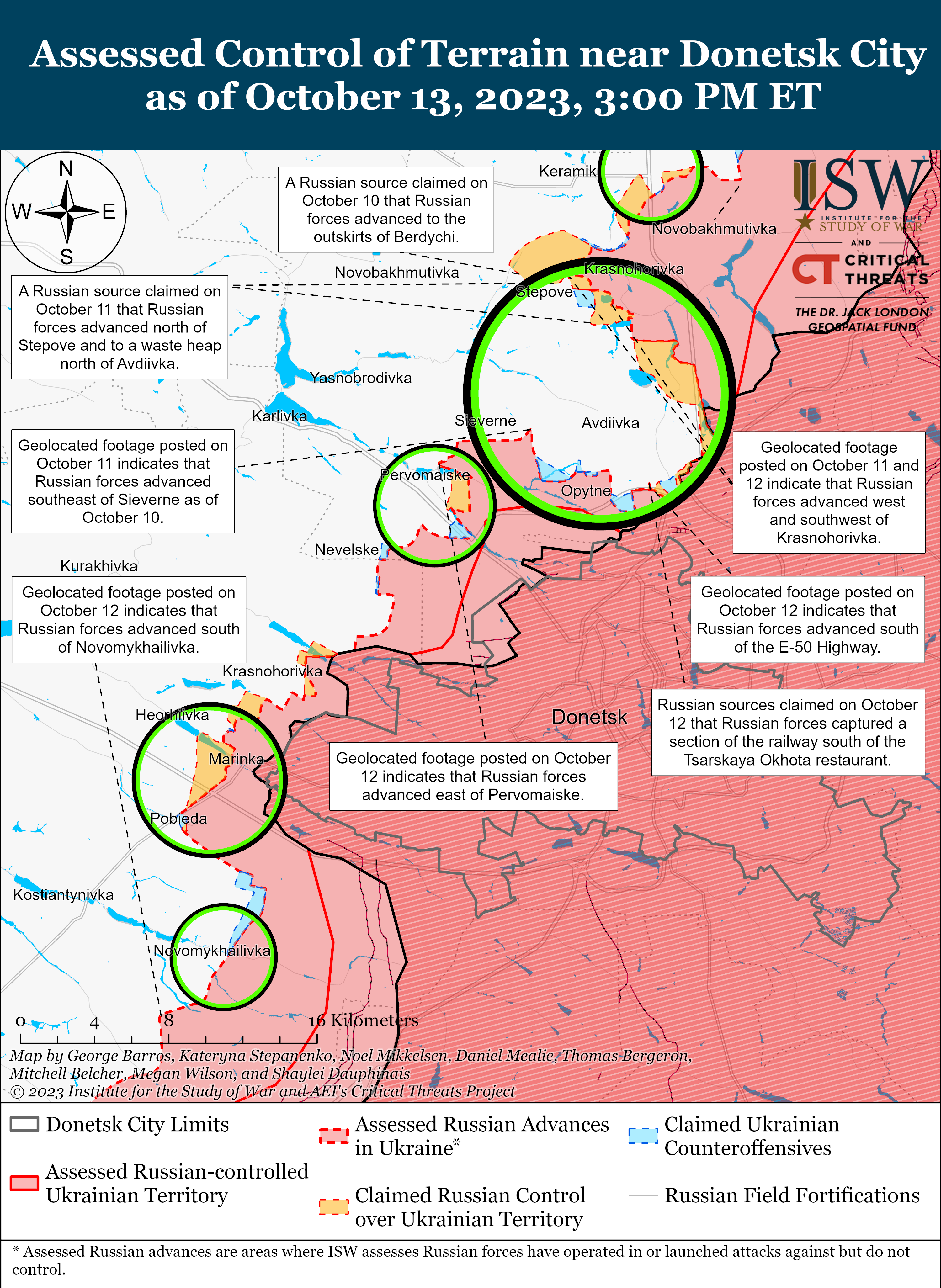
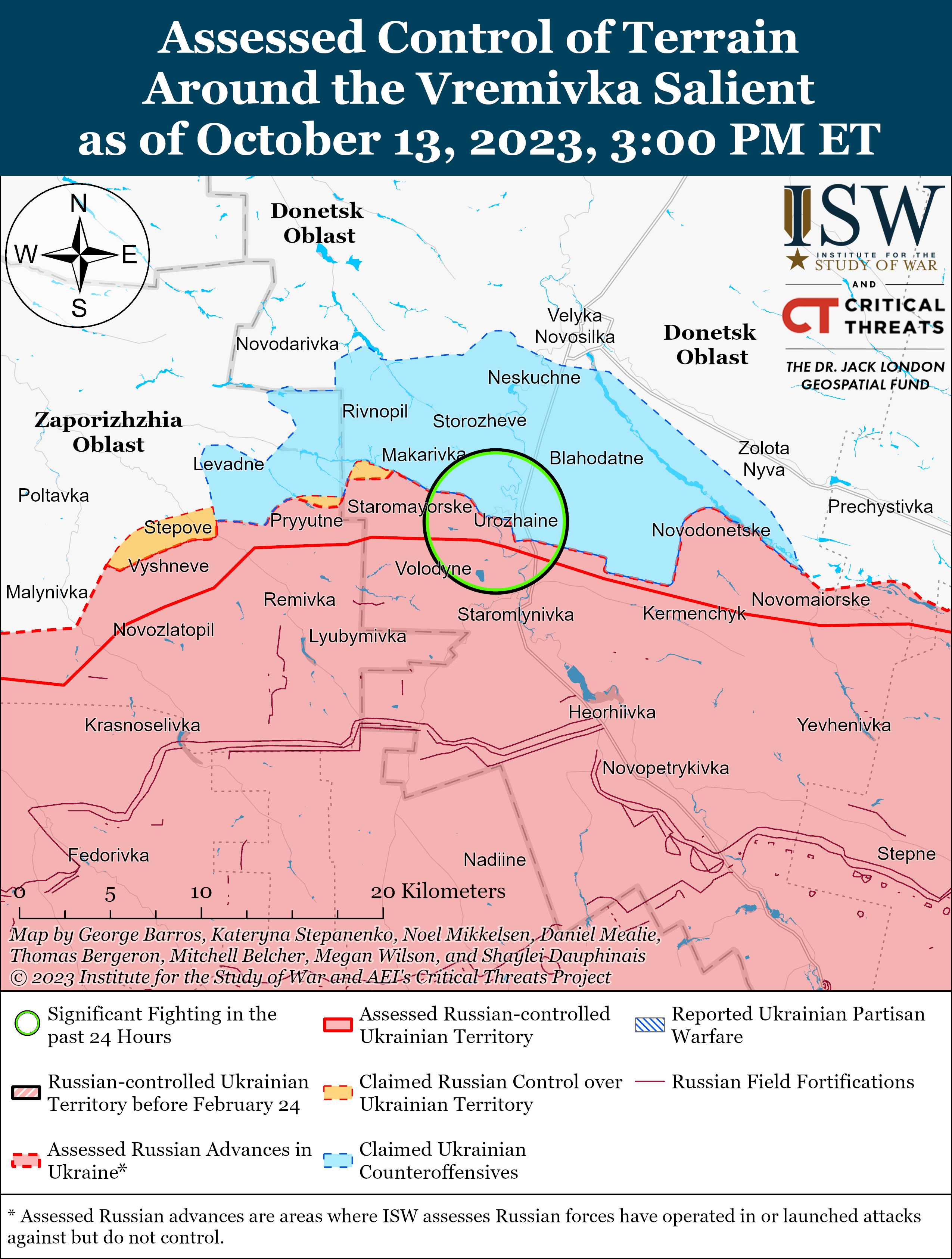
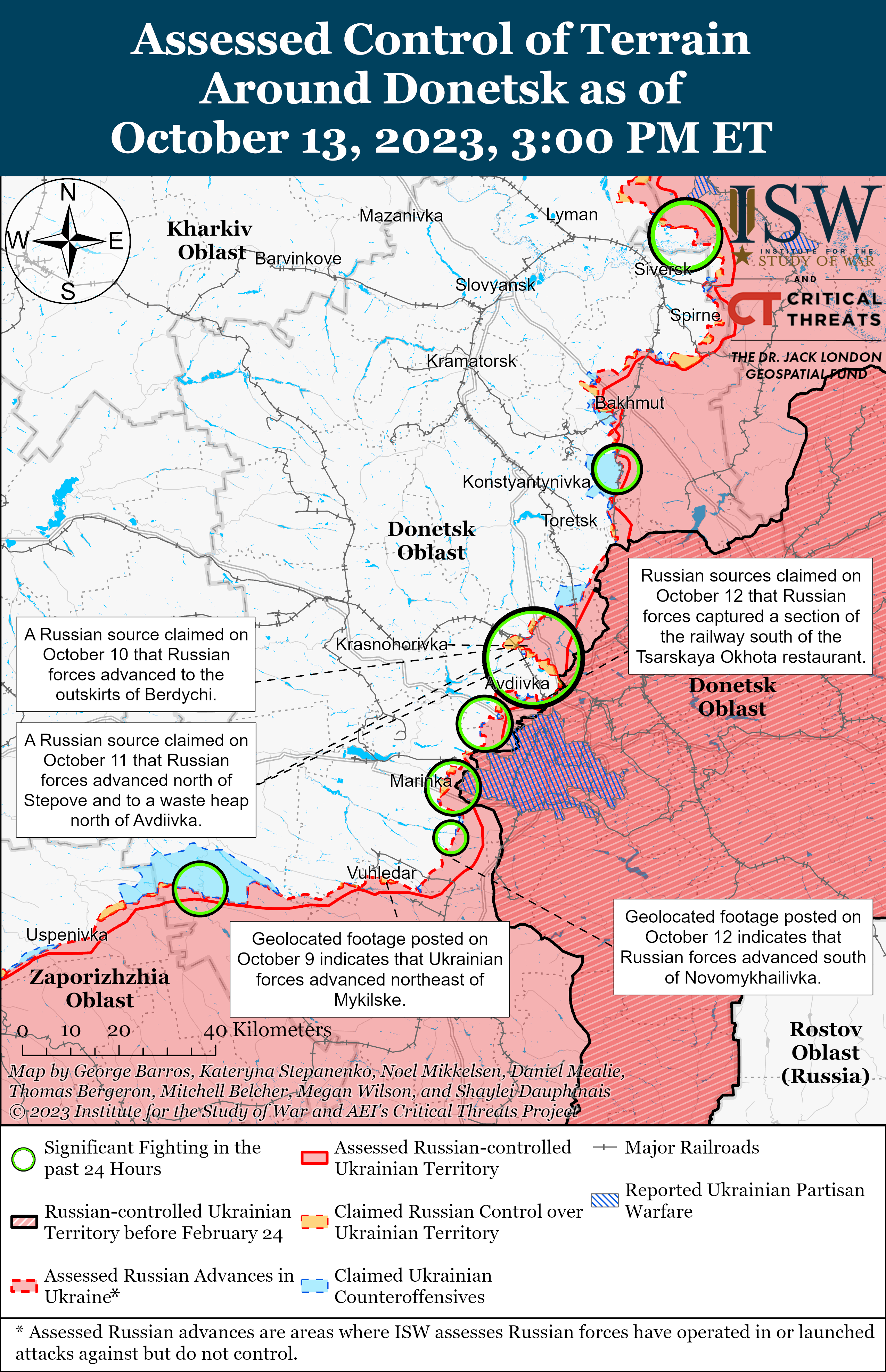
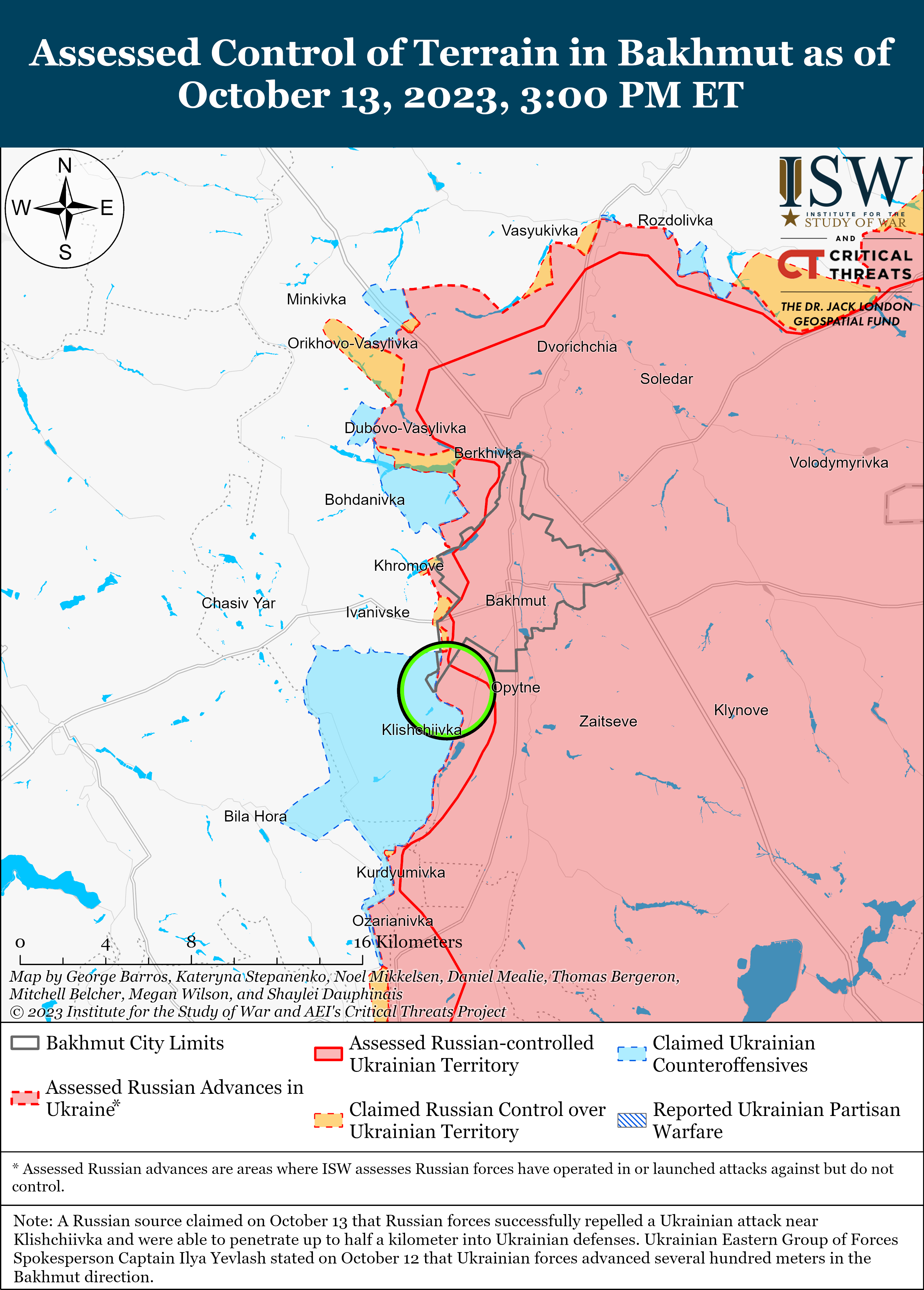
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, October 13, 2023
Ongoing Russian offensive operations throughout the Avdiivka, Donetsk Oblast area on October 13 reportedly faced setbacks around the city. Russian sources claimed that Russian forces continued to attack areas north and south of Avdiivka, and geolocated footage published on October 12 and 13 indicates that Russian forces advanced south of Krasnohorivka (5km north of Avdiivka) and southeast of Pervomaiske (11km southwest of Avdiivka).[i] Russian sources also published conflicting reports about previous claims by Russian sources of Russian control of the Avdiivka Coke Plant, and ISW has not observed any evidence to confirm that Russian forces control the plant as of publication.[ii] Ukrainian military officials reported that Ukrainian forces continue to repel Russian attacks around Avdiivka.[iii] A Russian milblogger noted that Ukrainian forces are using minefields to slow down Russian advances in the Avdiivka direction.[iv] A Russian volunteer in the 4th Luhansk People’s Republic (LNR) Brigade (2nd Army Corps, Southern Military District) claimed that worn out barrels are reducing the accuracy of Russian artillery near Avdiivka, a complaint about Russian artillery that ISW has previously observed from Russian sources.[v] The volunteer assessed that Russian forces can ”compress the [Ukrainian] perimeter” by capturing less fortified Ukrainian-held territory near Avdiivka, but expressed concern that Russian generals will misinterpret these limited advances and try to speed up offensive efforts towards Avdiivka. The volunteer noted that such a misinterpretation may lead Russian forces to “beat on concrete” fortifications until these forces run out.
The Russian military command appears to be restricting discussion of the Russian offensive operations around Avdiivka in the Russian information space, likely in an attempt to adapt to previous information shocks and control any narratives that emerge in the Russian information space around these operations. A prominent Russian milblogger claimed on October 12 that the Russian military command was “dispensing information [about Russian offensive operations] in doses,” but then claimed on October 13 that the Russian military command was ”minimizing the release of information into the public domain” as the Russian military does not want “media hype” surrounding operations near Avdiivka.[vi] Another Russian milblogger also claimed on October 13 that unspecified actors, likely Russian military leadership, instructed milbloggers to not discuss the details of the fighting near Avdiivka.[vii] A Russian source stated that he supported the Russian military’s decision and urged milbloggers to discuss only information that does not affect Russian military operational security, whereas other Russian milbloggers noted that this is the time to figure out which of the Russian milbloggers are lying about the situation on the frontlines.[viii] The Russian military command likely seeks to adjust for previous major offensives in which it lost control of perceptions of Russian actions in the Russian information space. Some milbloggers are following (and will likely continue to follow) the MoD-imposed narrative line, but this attempt at centralized control may provoke a backlash from select milbloggers.
Key Takeaways:
- Ongoing Russian offensive operations throughout the Avdiivka, Donetsk Oblast area on October 13 reportedly faced setbacks around the city.
- The Russian military command appears to be restricting discussion of the Russian offensive operations around Avdiivka in the Russian information space, likely in an attempt to adapt to previous information shocks and control any narratives that emerge in the Russian information space around these operations.
- The Kremlin is likely attempting to frame Russian offensive operations around Avdiivka and other localized efforts as Russian forces seizing the operational initiative in Ukraine.
- Ukrainian forces conducted counteroffensive operations near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on October 13.
- Russian forces continue to target Ukrainian critical infrastructure facilities with drone and missile strikes, as well as localized cross-border raids.
- Russian authorities arrested four lawyers who represent prominent opposition figures on extremism charges on October 13, likely to set conditions for the upcoming 2024 Russian presidential elections.
- Russian forces continued offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, Avdiivka, and Donetsk City, and in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area and western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in various sectors of the front.
- A Ukrainian military intelligence official reported that Russian forces are struggling to equip newly-formed military formations.
- Ukrainian partisans reportedly targeted Russian military assets in rear areas in southern Ukraine on October 12 and 13.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, October 1, 2023
Russian forces are conducting tactical counterattacks in the Robotyne area as part of their elastic defense against ongoing Ukrainian offensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast. The situation south of Robotyne is fluid as some tactically significant field fortifications have changed hands several times. Geolocated footage posted on September 30 shows Ukrainian forces striking Russian troops trying to enter a trench system about 1km southwest of Robotyne near the T0408 Robotyne—Tokmak road.[i] Footage posted on September 13 shows that Ukrainian forces had previously occupied segments of this trench and thus appear to have lost it to Russian counterattacks between September 13 and 30.[ii] ISW has recoded this area from Ukraine's counteroffensive to Russian advances.
A Ukrainian soldier analyzed the footage of the area and noted that the aforementioned Russian-controlled trench is a strongpoint in an interconnected system of trenches, firing systems, and dugouts that lie between Robotyne and Novoprokopivka.[iii] The Ukrainian soldier noted that the trenches are connected by underground tunnel-like structures and that Russian forces are prioritizing the defense of these positions, which have tactical significance in the area between Robotyne and Novoprokopivka.[iv] Geolocated footage posted on October 1 shows Russian forces striking a Ukrainian vehicle just south of the middle of the three trenches and about 1km west of the easternmost trench in the system, suggesting that Ukrainian forces control the easternmost trench and are attempting to push westward to recapture the remaining two trenches and connected dugouts and firing positions.[v] Commercially available satellite imagery indicates that Russian forces destroyed this vehicle between September 25 and 28, indicating that Russian forces repelled a Ukrainian attack and reconsolidated Russian positions near the trench systems in late September. The reported continued presence of Russian forces in the western and central trenches suggests that Russian forces have been conducting successful limited tactical counterattacks south of Robotyne and that the tactical situation in this area is complex and dynamic.
Key Takeaways:
- Russian forces are conducting tactical counterattacks in the Robotyne area as part of their elastic defense against ongoing Ukrainian offensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast. The situation south of Robotyne is fluid as some tactically significant field fortifications have changed hands several times.
- The Russian information space continues to falsely portray Western aid to Ukraine as escalatory in order to discourage continued Western support for Ukraine.
- The status of the Wagner Group remains unclear amid reported negotiations about the Wagner Group’s future cooperation with the Russian government.
- ISW will revise its assessment about the prospects for the Wagner Group to reemerge an as effective military organization if the Wagner Group successfully reconstitutes as a large, unitary organization under Rosgvardia, the Russian MoD, or a similar organization.
- Russian forces conducted another series of drone strikes against Ukraine on the night of September 30 to October 1.
- Russian forces continued offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Lyman line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and marginally advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) officially announced the beginning of its regular fall 2023 conscription cycle on October 1.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 30, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and near Bakhmut on September 30. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in the Melitopol direction (western Zaporizhia Oblast) and near Bakhmut.[1] Russian milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted unsuccessful ground attacks near Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut), Andriivka (10km southwest of Bakhmut), Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv), Novoprokopivka (13km south of Orikhiv), and Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv).[2] A fringe Russian milblogger reportedly affiliated with the Russian Airborne (VDV) forces implicitly recanted claims from September 24 that Ukrainian forces occupy half of Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv).[3] The fringe milblogger claimed on September 29 that elements of the 7th Guards VDV Division still hold Verbove despite suffering losses.[4]
The Kremlin has seemingly not yet clarified what Ukrainian territories it claims that Russia has annexed, leading to continued confusion among Russian government and occupation officials a year after the illegal annexation of occupied territories. Russian President Vladimir Putin gave a speech in honor of the so-called “Day of Reunification of the Donetsk People’s Republic, Luhansk People’s Republic, Zaporizhia, and Kherson Oblasts with Russia” on September 30 in which he reiterated boilerplate rhetoric about the international legitimacy of the illegal Russian annexation referenda, the West’s alleged role in starting the war in Ukraine, and the unity between Russia and occupied Ukraine.[5] Sevastopol occupation governor Mikhail Razvozhaev posted a map on his Telegram channel in honor of the holiday that showed the entirety of Crimea and Luhansk, Donetsk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson oblasts as Russian territory.[6] The Kherson Oblast occupation administration posted a different map that showed Russian territory roughly extending to the current frontlines in the four most recently annexed territories.[7] Russian Security Council Deputy Chairperson Dmitry Medvedev, a notable nationalistic and extreme voice in the Russian government, ambiguously claimed that the war in Ukraine will continue until “the original Russian territories are liberated.”[8] Medvedev’s unclear statement and occupation officials’ disparate maps indicate that the Kremlin has yet to clarify what territories it claims to have annexed or intends to annex.
Russian forces conducted a series of drone strikes primarily targeting Vinnytsia Oblast on the night of September 29 to 30. Ukrainian military sources reported on September 30 that Ukrainian forces downed 30 out of 40 Shahed-131/136 drones that Russian forces launched from occupied Crimea.[9] Ukrainian Southern Operational Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk stated that Russian forces struck an infrastructure facility in Vinnytsia Oblast.[10] Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian drones struck a Ukrainian military arsenal near Kalynivka (22km north of Vinnytsia) in Vinnytsia Oblast.[11] Russian sources also claimed that Russian drones struck Ukrainian port infrastructure in Odesa and Mykolaiv oblasts on the night of September 29 to 30.[12] The Romanian Ministry of Defense (MoD) stated that its radar systems indicated a possible unauthorized entry into Romanian airspace during the Russian strike series on the night of September 29 to 30.[13] The Romanian MoD stated that Romanian authorities have not yet identified any objects that may have fallen into Romanian territory.[14]
Russian milbloggers claimed on September 30 that the Russian military command removed the commander of the Russian 205th Motorized Rifle Brigade following recent outrage from milbloggers about the brigade’s command.[15] The same group of Russian milbloggers extensively amplified reports about elements of the 205th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (49th Combined Arms Army, Southern Military District) suffering significant losses due to inadequate artillery support and poor leadership in the Kherson direction in late August.[16] One of the Russian milbloggers stated on September 30 that the removal of this commander is a “rare case” in which truth and justice prevailed.[17] The removal of the commander suggests that Russian ultranationalist outrage may still be able to pressure the Russian military command despite the apparent decline in such reactions in the wider Russian information space since the Wagner Group‘s June 24 rebellion.
An organization with alleged ties to Russian First Deputy Presidential Chief of Staff Sergey Kiriyenko is reportedly categorizing Russian internet user data in an effort to disseminate tailored information to specific domestic populations as part of a wider attempt to control the Russian information space. Independent Belarusian outlet Vot Tak reported on September 29 that Russian non-profit organization Dialog is gathering Russian internet user data and information from Russian government agencies in order to categorize Russian media consumers and then feed tailored narratives to specific categories of users.[18] A former employee of Dialog told Vot Tak that Dialog’s database categorizes internet users by profession, interests, and political beliefs and specifically orients false news about the war in Ukraine and pro-war narratives toward Russian military personnel, relatives of military personnel, and civil servants.[19] The former Dialog employee also claimed that Dialog categorizes internet users as “loyal” and “disloyal” and shares its information with Russian security services.[20] The former Dialog employee claimed that Dialog has failed to make a significant ideological impact on the Russian information space because Dialog could not produce unified and clear narratives.[21] Dialog’s efforts to promote narratives to specific Russian populations are likely a more subtle part of the Kremlin’s effort to control the Russian information space and commensurate with the Kremlin’s more overt efforts to promote self-censorship.
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and near Bakhmut on September 30.
- The Kremlin has seemingly not yet clarified what Ukrainian territories it claims that Russia has annexed, leading to continued confusion among Russian government and occupation officials a year after the illegal annexation of occupied territories.
- Russian forces conducted a series of drone strikes primarily targeting Vinnytsia Oblast on the night of September 29 to 30.
- Russian milbloggers claimed on September 30 that the Russian military command removed the commander of the Russian 205th Motorized Rifle Brigade following recent outrage from milbloggers about the brigade’s command.
- An organization with alleged ties to Russian First Deputy Presidential Chief of Staff Sergey Kiriyenko is reportedly categorizing Russian internet user data in an effort to disseminate tailored information to specific domestic populations as part of a wider attempt to control the Russian information space.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations near Kupyansk, Kreminna, Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area and marginally advanced along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian authorities have started to conscript citizens in occupied Ukraine who have Russian passports.
- Russian authorities continue to forcibly deport children from occupied Ukraine to Russia in order to assimilate Ukrainian children into Russian culture.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 24, 2023
Elements of three Russian divisions are actively defending against Ukrainian assaults around the Ukrainian salient in the Orikhiv area in western Zaporizhia Oblast. Elements of the Russian 42nd Motorized Rifle Division (58th Combined Arms Army, Southern Military District) are deployed and are defending at the southernmost point of the Ukrainian penetration and are engaging Ukrainian forces in Novoprokopivka (13km south of Orikhiv).[i] Elements of the Russian 76th Air Assault Division deployed to the Ukrainian salient’s western flank near Kopani (11km southwest of Orikhiv) towards Robotyne (10m south of Orikhiv) and are counterattacking there.[ii] Elements of the 7th Air Assault Division are deployed on the Ukrainian salient‘s eastern flank near the Verbove-Novopokrovka line and are counterattacking there.[iii] Sources affiliated with the Russian Airborne (VDV) Forces report that the 56th Air Assault Regiment (7th Air Assault Division) is deployed about 5km north of Verbove near Novofedorivka.[iv]
A Russian source claimed that the 7th and 76th VDV Divisions were ordered to conduct an operational encirclement of the Ukrainian salient, but that they failed to do so and that the 7th VDV Division’s effectiveness significantly declined after a successful Ukrainian strike against the division headquarters on September 19.[v] ISW offers no assessment about these reported orders to encircle Ukrainian forces beyond noting that it would be a sound practice for Russian forces to conduct counterattacks against Ukrainian forces’ flanks within limits.
Ukrainian forces are attacking along three directions within the Orikhiv salient as of September 24. Ukrainian forces are conducting attacks from Robotyne against Novoprokopivka.[vi] Ukrainian forces are attacking directly into Verbove’s western side.[vii] Ukrainian forces are also attacking north of Verbove.[viii]
Russian sources report that Ukrainian forces broke into Verbove on September 22 and continued attacking the settlement with armored vehicles as of September 24. Geolocated combat footage posted on September 24 shows a Ukrainian BMP operating within Verbove’s westernmost village limits.[ix] A VDV-affiliated source reported that Ukrainian forces entered Verbove for the first time on September 22 and continued pushing east.[x] The VDV source later reported that Ukrainian forces occupy half of Verbove as of September 24.[xi] The VDV source accused the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) of trying to conceal Ukraine’s tactical progress in Verbove, rhetorically stating, “For how long can Shoigu’s MoD hide the breakthrough in Verbove?“[xii] Several Russian sources reported on September 24 that Ukrainian forces continue deploying vehicles against Verbove, including Bradley infantry fighting vehicles.[xiii] Some Russian sources are vehemently denying any Ukrainian breakthrough in Verbove as of September 24.[xiv] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces captured new unspecified locations near Verbove on September 24.[xv]
Key Takeaways:
- Elements of three Russian divisions are actively defending against Ukrainian assaults around the Ukrainian salient in the Orikhiv area in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Ukrainian forces are attacking along three directions within the Orikhiv salient as of September 24.
- Russian sources report that Ukrainian forces broke into Verbove on September 22 and continued attacking the settlement with armored vehicles as of September 24.
- Ukrainian forces are attacking north of Verbove and could isolate the 56th VDV Regiment deployed in Novofedorivka from its sister regiments in the Verbove area according to Russian sources.
- Russian forces continue to expend significant combat power on counterattacking to hold their current positions and appear to be resisting the operationally sound course of action of falling back to prepared defensive positions further south.
- The Russian military command may be ordering these counterattacks to buy time, but it is unclear how the Kremlin intends to use time bought at such a price.
- The Russian sacrifice of combat power to hold every meter may alternatively be intended to support the Kremlin’s informational and hybrid warfare objectives.
- The Russian resistance to ceding ground may also be tied to Russian military commanders’ and officials’ attempts to use the counteroffensive to achieve political goals, or it could result from Putin’s micromanagement.
- Ukrainian forces may be able to achieve an operationally significant breakthrough in the southern frontline if several key assumptions hold.
- Russian forces continued offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 24.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 23, 2023
ISW is now prepared to assess that Ukrainian forces have broken through Russian field fortifications west of Verbove in western Zaporizhia Oblast. These fortifications are not the final defensive line in Russia’s defense in depth in western Zaporizhia Oblast, but rather a specific series of the best-prepared field fortifications arrayed as part of a near-contiguous belt of an anti-vehicle ditch, dragon's teeth, and fighting positions about 1.7 - 3.5 km west of Verbove.[1]
Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Commander Brigadier General Oleksandr Tarnavskyi stated in an interview with CNN published on September 23 that Ukrainian forces achieved a “breakthrough” on the left flank near Verbove and that Ukrainian forces continue advancing.[2] Combat footage posted on September 22 shows a destroyed Ukrainian Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) and BMP-2 operating slightly beyond Russia’s fighting positions trench line near Verbove, indicating continued Ukrainian progress in deploying more heavy equipment beyond Russia’s triune belt of the anti-vehicle ditch, dragon’s teeth, and fighting positions.[3] Commercially available satellite imagery indicates that Ukrainian forces have brought heavy equipment closer to Verbove over the past 96 hours in a manner consistent with Tarnavskyi’s statement.[4] The Wall Street Journal reported on September 21 that Ukrainian forces achieved a “limited breakthrough” west of Verbove citing an unnamed Ukrainian Air Assault Forces officer.[5]
Ukrainian forces have not overcome all of the prepared Russian defensive positions near Verbove. Ukrainian forces’ rate of advance near their breakthrough remains unclear. Russian forces likely still control segments of the long trench line of Russian fighting positions between Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv) and Verbove, especially near the tactical high ground to the south. Russian forces have reportedly established prepared fighting positions in almost every tree line that Ukrainian infantry are slowly and systematically fighting through. Russian forces have more field fortifications beyond Verbove; there are more anti-vehicle trenches and fighting positions north of Ocheretuvate (26km southeast of Orikhiv), for example. It is unclear the extent to which those positions are manned, however. ISW continues to assess that the Russian military does not have sufficient forces deployed to this sector of the front to completely man its defenses in depth and that Ukrainian forces should be able to operate through Russian field fortifications more rapidly if they are not properly manned.[6]
Ukrainian forces are deepening their penetration in Zaporizhia Oblast and are assaulting Novoprokopivka – a frontline village 1.5 km immediately south of Robotyne. Geolocated combat footage posted on September 23 shows elements of the Russian 70th Regiment (42nd Motorized Rifle Division, 58th Combined Arms Army, Southern Military District) ambushing and killing two Ukrainian infantrymen in Novoprokopivka’s northeastern outskirts, indicating that Ukrainian forces have likely cleared Russian positions between Robotyne and Novoprokopivka.[7] Multiple Russian sources reported that Russian forces repelled a Ukrainian attack against northern Novoprokopivka on September 22.[8] This is the first confirmed Ukrainian ground attack in the immediate vicinity of Novoprokopivka.
Ukrainian military officials stated that the Ukrainian counteroffensive would continue in the winter. Tarnavskyi told CNN that he expected a major Ukrainian breakthrough after Ukrainian forces reach Tokmak (a major Russian stronghold in western Zaporizhia) and that it is important that Ukrainian forces not lose the initiative they currently hold.[9] Tarnavskyi also stated that Ukrainian operations will continue through the winter as Ukrainian forces are mostly advancing on foot without vehicles and that inclement weather will thus not have a major negative effect on the Ukrainian counteroffensive.[10] Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Head Lieutenant General Kyrylo Budanov echoed a similar assessment about continued Ukrainian winter operations in an interview with The War Zone published on September 22.[11] ISW has previously assessed that, while seasonal weather can slow ground movements and challenge logistics, it will not impose a definite end to Ukrainian counteroffensive operations.[12] The culmination of the Ukrainian counteroffensive will likely depend rather on the Russian and Ukrainian balance of forces as well as on Western aid to Ukraine.
The Ukrainian counteroffensive in western Zaporizhia Oblast has likely destroyed the Russian 810th Naval Infantry Brigade (Black Sea Fleet). Budanov stated in his interview with The War Zone published on September 22 that the 810th Brigade was “completely defeated” in southern Ukraine.[13] Budanov stated that the 810th Brigade has withdrawn and that Russian airborne (VDV) units replaced them on the front. Budanov‘s description of the status of the 810th Brigade corresponds most closely to the US military‘s doctrinal definition of the tactical mission task of “destroy”: “physically render[ing] an enemy force combat-ineffective until reconstituted.”[14] Elements of the 810th Brigade have reportedly been operating in the Zaporizhia direction since March 2023 and in western Zaporizhia Oblast since June 2023.[15] ISW previously observed the 810th Brigade in October 2022, when it was reportedly operating in Kherson Oblast, and the unit was likely reconstituting in the rear in the interim before assuming positions in Zaporizhia Oblast.[16] The 810th Brigade has repeatedly suffered significant losses, and Ukrainian forces have destroyed the unit in the past, following which the Russian military has reconstituted it. The Ukrainian General Staff reported on April 19, 2022, that the 158 soldiers of the 810th Brigade had been killed and about 500 wounded.[17] GUR Deputy Chief Major General Vadym Skibitskyi stated on July 31, 2022, that 200 servicemen of the 810th Brigade refused to return to the war in Ukraine, and the Ukrainian General Staff reported on September 12, 2022, that the 810th Brigade lost more than 85% of its personnel in the Kherson direction and that many again refused to return to combat.[18]
A senior Ukrainian official explicitly confirmed that Ukraine’s objective in Bakhmut is to fix Russian forces. Ukraine’s fixing of Russian forces in Bakhmut may be alleviating pressure on the Kupyansk frontline. Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Head Lieutenant General Kyrylo Budanov stated that Ukrainian forces achieved their objective of pinning Russian forces in Bakhmut and preventing their transfer to other areas of the theater – such as southern Ukraine – in a September 22 interview.[19] Budanov also stated that the Russian military deployed the recently created and not fully formed 25th Combined Arms Army (CAA) of the Eastern Military District “roughly north of Bakhmut.”[20] Budanov previously reported on August 31 that the Russian military deployed elements of the 25th CAA to replace elements of the 41st CAA (Central Military District) in the Kupyansk direction as elements of the 41st CAA began a ”slow” redeployment to southern Ukraine.[21] The Russian deployment of elements of the 25th CAA to Bakhmut instead of Kupyansk will likely disrupt Russian efforts to fix Ukrainian forces in the Kupyansk direction, as Russian forces need these troops to continue assaults in place of the 41st CAA. Ukrainian officials and Russian sources have indicated that the tempo and the intensity of Russian offensives on the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line has significantly decreased in recent weeks as Russian forces are continuing to regroup and rotate personnel in this direction, and the redirection of the deployment of 25th CAA may have alleviated some of the pressure from this frontline.[22] Budanov’s statement supports ISW’s recent assessment that Ukrainian counteroffensive operations on Bakhmut’s southern flank have fixed a large amount of Russian combat power in Bakhmut that would otherwise be available to reinforce Russian defenses in the south — or, in this case, to attempt to force Ukrainian forces to redeploy to defend against Russian assaults around Kupyansk.[23]
Ukraine’s simultaneous counteroffensives in Bakhmut and southern Ukraine are impeding Russia’s long-term force generation efforts as Russia redeploys its new reserves to defend against Ukrainian advances. Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) formed a “reserve army” at the end of June, likely referencing the 25th CAA among other formations, which began recruiting personnel from the Russian Far East in mid-May.[24] The formation of the 25th CAA was likely part of Shoigu’s announced intent to conduct large-scale force restructuring by 2026, and the use of these forces in combat and defensive operations will likely expend reserves intended for the long-term reconstitution and expansion of Russia’s military.[25] The Russian military command has also likely been unable to fully staff or properly train the 25th CAA at this time. Budanov specified that the unfinished 25th CAA has about 15,000 troops, whereas the Russian military had reportedly hoped to recruit 30,000 contract personnel for the 25th CAA.[26] Ukrainian military officials assessed that the 25th CAA would not be combat effective until at least 2024.[27] Russia had previously attempted to form the 3rd Army Corps over the summer of 2022 as a reserve force but had deployed and expended much of this ill-prepared formation defending against Ukrainian counteroffensives in the fall of 2022.[28]
A Ukrainian intelligence chief stated that the September 22 Ukrainian strike on the Russian Black Sea Fleet (BSF) Command headquarters in Sevastopol injured senior Russian commanders. Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Head Lieutenant General Kyrylo Budanov told Voice of America (VOA) in an interview published on September 23 that the Ukrainian strike on the BSF Command headquarters wounded the commander of the Russian grouping of forces in the Zaporizhia direction, Colonel General Alexander Romanchuk, who is in “very serious condition” and the commander of the 200th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (Northern Fleet), Lieutenant General Oleg Tsekov, who is “unconscious.”[29] Budanov also reported that the strike killed at least nine and injured 16 Russian personnel.[30] VOA reported that the GUR has no information about the alleged death of BSF commander Admiral Viktor Sokolov.[31] Ukrainian Special Operations Forces reported that Ukrainian forces “precisely” struck the BSF Command headquarters during a meeting of senior BSF leadership.[32] Satellite imagery published on September 22 showing the BSF Command headquarters before and after the strike indicates that Ukrainian forces conducted a precision strike.[33]
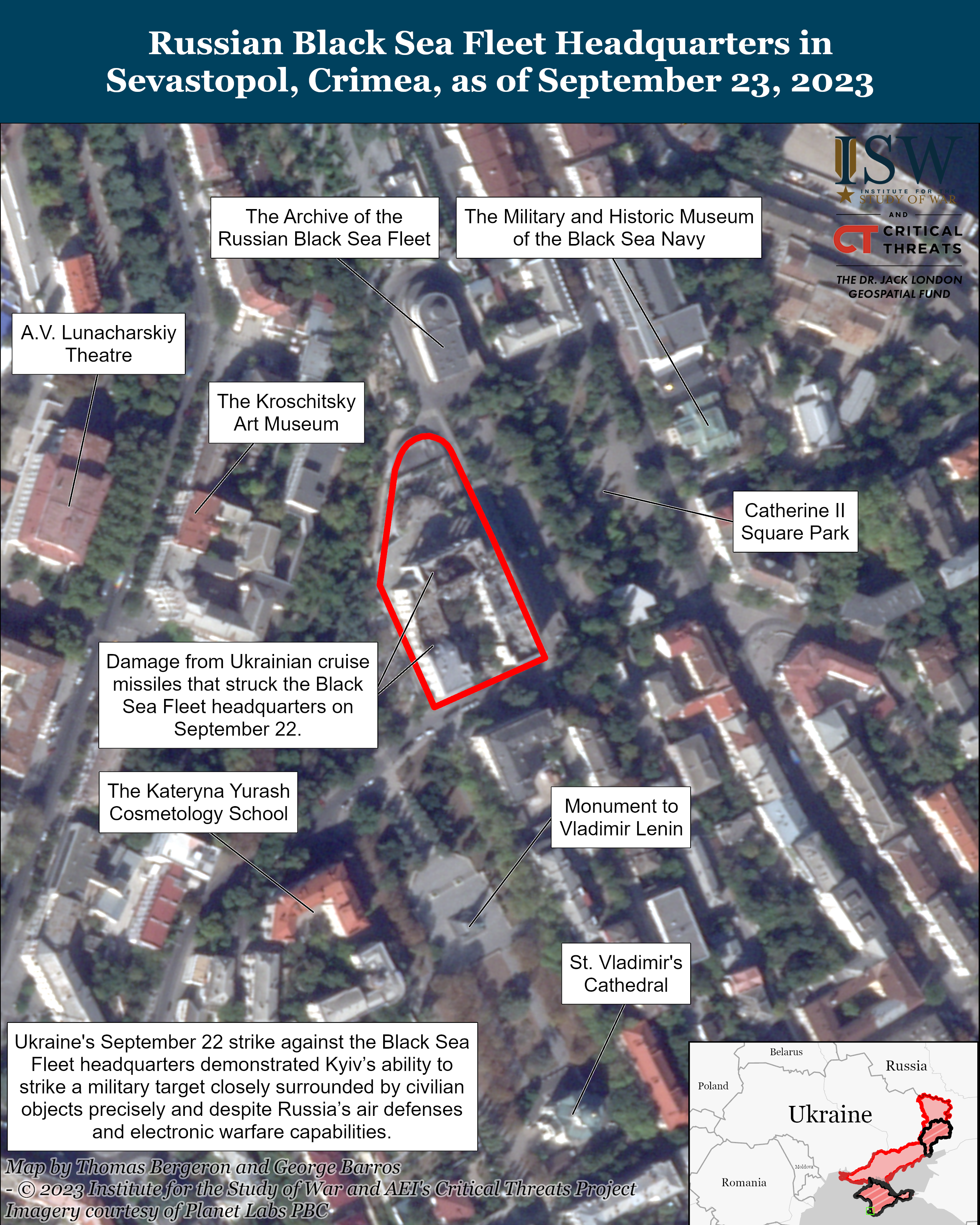
Imagery of the strike against the Black Sea Fleet Headquarters. September 23, 2023.
Imagery courtesy of Planet Labs PBC.
Russian forces conducted a series of missile and drone strikes against Ukraine on the night of September 22 to 23. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces destroyed 14 of 15 Shahed-131/136 drones and that Russian forces launched four missiles.[34] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces conducted a missile attack on Kremenchuk, Poltava Oblast.[35] Several Russian sources claimed that the Russian forces conducted a retaliatory strike on Kremenchuk airfield after the Ukrainian strike on the BSF Command headquarters.[36]
Zaporizhia Oblast occupation governor Yevgeny Balitsky appointed former Roscosmos (Russian space agency) head and ultranationalist figure Dmitry Rogozin as a Russian Federation Council senator representing occupied Zaporizhia Oblast.[37] Rogozin is affiliated with the “Tsarskiye Volky” (Tsar’s Wolves) volunteer battalion but has not held a position in the Russian government since his dismissal as head of Roskosmos in July 2022.[38] A Russian insider source claimed that Rogozin has ties to the “Convoy” private military company (PMC) and advocated for its use in Africa and Nagorno-Karabakh to Russian Presidental Administration Head Anton Vaino.[39] ISW previously reported that Crimean occupation head Sergey Aksyonov formed a “Convoy” with Wagner-affiliated Konstantin Pikalov.[40] The insider source claimed that unspecified Russian officials forced Rogozin to go on a “business trip (exile)” to defense industrial base enterprises in Belarus after multiple meetings with Vaino.[41] Rogozin’s appointment as occupied Zaporizhia Oblast Federation Council senator may be indicative of his ties to Russian occupation officials and his attempts to secure a new position in the Russian government.
A Russian insider source argued that the Russian military should reintroduce military officers for political affairs (zampolits) to address the Russian military’s problems with political and ideological commitment — a problem that Russian military thinkers identified in September 2018. The insider source claimed that GRU political officers are using an outdated “Soviet template” to conduct information operations against the enemy and are failing to provide political support to Russian military personnel.[42] The insider source noted that Russian political officers must resolve the contradictions between senior Russian political leaders‘ slogans and reality to ensure that military personnel can distinguish between possible and impossible objectives. The insider source claimed that Russian military-political work encourages blind repetition of phrases and orders, which prevents Russian military personnel from understanding and communicating Russian political decisions to their subordinates or explaining contradictions in political leadership messaging. Chairman of the Russian State Duma Defense Committee Colonel General Andrey Kartapolov identified similar issues in his September 2018 essay justifying the creation of the Russian Military-Political Directorate.[43] Kartapolov stated that Russian military-political leadership should adapt Soviet structures to new content. Kartapolov also argued that Russia must ensure the “information protection” of military personnel and create a stable conviction in both the military and broader society about why they must serve Russia. This insider’s argument suggests that the Russian military has not solved the problem that Kartapolov identified over the past five years.
Disjointed Wagner Group contingents reportedly returning to fight in Ukraine are likely to have a marginal impact on Russian combat capabilities without bringing the full suite of effectiveness Wagner had had as a unitary organization under financier Yevgeniy Prigozhin’s and founder Dmitry Utkin’s leadership. Former Luhansk Oblast Administration Head Serhiy Haidai stated on September 23 that Wagner personnel are operating in Luhansk Oblast and across different sectors of the frontline.[44] Haidai also stated that he did not know the number of Wagner personnel or the organization under which these Wagner personnel are operating in Ukraine.[45] A Wagner-affiliated source claimed that about 500 Wagner personnel including those who refused to participate in the Wagner rebellion on June 24 have joined a new unspecified organization organized by the former Wagner personnel department head and will likely return to Ukraine to fight on the southern flank of Bakhmut.[46] ISW previously observed reports that the Wagner personnel department head (previously referred to as Vadim V. “Khrustal”) is attempting to recruit Wagner fighters for a new PMC for operations in Africa.[47] These reports indicate that Wagner forces are fragmented and are unlikely to organize into a cohesive fighting force or have an impact on Russian combat capabilities if they return to fighting in Ukraine.
Key Takeaways:
- ISW is now prepared to assess that Ukrainian forces have broken through Russian field fortifications west of Verbove in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Ukrainian forces have not overcome all prepared Russian defensive positions near Verbove.
- Ukrainian forces are deepening their penetration in Zaporizhia Oblast and are assaulting Novoprokopivka – a frontline village 1.5 km immediately south of Robotyne.
- Ukrainian military officials stated that the Ukrainian counteroffensive would continue in the winter.
- The Ukrainian counteroffensive in western Zaporizhia Oblast has likely destroyed the Russian 810th Naval Infantry Brigade (Black Sea Fleet).
- A senior Ukrainian official explicitly confirmed that Ukraine’s objective in Bakhmut is to fix Russian forces. Ukraine’s fixing of Russian forces in Bakhmut may be alleviating pressure on the Kupyansk frontline.
- Ukraine’s simultaneous counteroffensives in Bakhmut and southern Ukraine are impeding Russia’s long-term force generation efforts as Russia redeploys its new reserves to defend against Ukrainian advances.
- A Ukrainian intelligence chief stated that the September 22 Ukrainian strike on the Russian Black Sea Fleet (BSF) Command headquarters in Sevastopol injured senior Russian commanders.
- Russian forces conducted a series of missile and drone strikes against Ukraine on the night of September 22 to 23.
- Zaporizhia Oblast occupation governor Yevgeny Balitsky appointed former Roscosmos (Russian space agency) head and ultranationalist figure Dmitry Rogozin as a Russian Federation Council senator representing occupied Zaporizhia Oblast
- A Russian insider source argued that the Russian military should reintroduce military officers for political affairs (zampolits) to address the Russian military’s problems with political and ideological commitment– a problem that Russian military thinkers identified in September 2018.
- Disjointed Wagner Group contingents reportedly returning to fight in Ukraine are likely to have a marginal impact on Russian combat capabilities without bringing the full suite of effectiveness Wagner had had as a unitary organization under financier Yevgeniy Prigozhin’s and founder Dmitry Utkin’s leadership.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in western Donetsk Oblast, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not make any confirmed advances on September 23.
- Russian authorities are reportedly embezzling funds from military facilities near the border of Ukraine.
- Russian government programs continue to forcibly deport children in occupied Ukraine to Russia.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 22, 2023
Ukrainian forces carried out drone and cruise missile strikes on occupied Crimea and significantly damaged the Russian Black Sea Fleet (BSF) Command headquarters in Sevastopol on September 22. The Ukrainian Armed Forces Center for Strategic Communications (StratCom) stated that Ukrainian forces launched a successful strike on the Russian BSF Command headquarters in Sevastopol, Crimea on September 22.[1] Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces used Storm Shadow cruise missiles to conduct the strike, and social media footage of the headquarters indicates significant damage to the building.[2] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian air defenses shot down five Ukrainian missiles and acknowledged that the Ukrainian strike damaged a building of BSF Command headquarters.[3] Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces launched a drone strike preceding the missile strike, and the Russian MoD claimed that Russian air defenses shot down two Ukrainian drones on the western coast of Crimea on the morning of September 22.[4]
Ukrainian Air Force Commander Lieutenant General Mykola Oleshchuk thanked Ukrainian pilots in general when amplifying footage of the strike.[5] Ukrainian Southern Operational Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk stated that Ukrainian forces will strike more Russian military targets in Crimea in the future.[6] Ukrainian National Security and Defense Council Secretary Oleksiy Danilov stated that Ukrainian forces will continue to strike Sevastopol and that the Russian BSF should destroy their own ships in order to avoid further Ukrainian strikes.[7]
The Russian information space heavily focused its attention on the Ukrainian strike on Sevastopol on September 22. One Russian milblogger complained about Russian authorities’ inability to control the spread of Ukrainian information about the consequences of the strike, and other milbloggers criticized Russian authorities and the Russian military for not retaliating sufficiently.[8] Another Russian milblogger claimed that such Ukrainian strikes on Crimea are expected as Ukraine and its Western partners consider Crimea to be Ukrainian territory.[9] Multiple Russian milbloggers claimed that Western partners helped Ukrainian forces target the BSF Command headquarters.[10]
Ukrainian forces advanced south of Bakhmut and reportedly advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 22. Geolocated footage published on September 22 indicates that Ukrainian forces advanced southeast of Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut).[11] A Kremlin-affiliated milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces slightly advanced north of Novoprokopivka and are currently about 800 meters away from the settlement’s outskirts, a claim that generally corresponds to ISW’s assessment of the closest approach of the Ukrainian counter-offensive to the settlement.[12] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces continued to conduct offensive operations in the Melitopol (western Zaporizhia Oblast) direction and offensive actions in the Bakhmut direction, exhausting and inflicting losses on Russian forces along the entire front.[13]
The US Department of Defense (DoD) announced a new security assistance package on September 21, providing Ukraine with $325 million worth of military equipment.[14] The DoD package includes AIM-9M missiles for air defense; additional ammunition for HIMARS systems; Avenger air defense systems; anti-drone machine guns; 155mm and 105mm artillery rounds, including dual-purpose improved conventional munitions (DPICM); Tube-Launched, Optically-Tracked, Wire-Guided (TOW) missiles; Javelin and AT-4 anti-armor systems; over three million rounds of small arms ammunition; light tactical vehicles; demolition munitions for obstacle clearing; and spare parts, maintenance equipment, and other field equipment.
The US will reportedly soon provide long-range army tactical missile systems (ATACMS) to Ukraine. Four unnamed US government officials told NBC News in an article published on September 22 that US President Joe Biden told Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky that the US would provide Ukraine with “a small number of long-range missiles.”[15] The officials did not state when the US would announce the provision of ATACMS or when the US would deliver them to Ukraine.[16] One US official told NBC News that US officials are still discussing the type of missile and the number of missiles the US would provide to Ukraine.[17] Several unnamed people familiar with ongoing deliberations on ATACMS also told the Washington Post that the Biden administration plans to provide Ukraine with a version of ATACMS armed with cluster bomblets rather than a single warhead.[18] The Washington Post reported that cluster-armed ATACMS have a range of up to 190 miles (depending on the version) and could allow Ukraine to strike Russian military positions far into the rear.
Russian efforts to intensify divisions between Ukraine and its Central European partners appear to have suffered a setback as Polish Prime Minister Andrzej Duda reiterated the strength of Polish-Ukrainian relations on September 22. Duda clarified Polish Prime Minister Mateusz Morwiecki’s September 21 statement that Poland would no longer transfer weapons to Ukraine and explained that Poland would continue to fulfill weapons supplies agreements with Ukraine but would not transfer new weapons that Poland purchases for its own military.[19] Duda also stated that the potential conflict between the two countries regarding the export of Ukrainian grain along European land routes does not “significantly affect” the two countries’ relationship.[20] ISW has previously assessed that Russian strikes on Ukrainian port and grain infrastructure are part of a Russian campaign to damage Ukrainian relations with its Western neighbors, and Poland’s swift reiteration of its commitment to Ukraine indicates that this campaign is not succeeding as much as Moscow likely intends.[21]
A Ukrainian military official swiftly denied Russian claims that Wagner Group forces are operating in occupied Kherson Oblast. Several Russian sources claimed on September 22 that Wagner personnel arrived in combat areas in occupied Kherson Oblast and that assault troops are distributed across sectors of the Kherson Oblast frontline.[22] Ukrainian Southern Operational Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk denied this claim on September 22 and stated that Russian sources likely disseminate such claims in order to improve Russian morale.[23] Humenyuk also stated that Chechen forces and Rosgvardia (Russian National Guard) forces arrived in occupied Kherson ”a few weeks ago” in order to prevent Russian military personnel from deserting.[24] Russian milbloggers may be claiming that Wagner forces have arrived in occupied Kherson Oblast amid rumors that Wagner forces will return to hostilities in Ukraine operating alongside Rosgvardia.[25]
The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) is reportedly investigating high-ranking Rosgvardia officials over their potential involvement in Wagner Group’s rebellion on June 24. A Russian insider source claimed on September 22 that the FSB is investigating Rosgvardia officials after Rosgvardia reportedly allowed Wagner to “hide” shells and equipment in Rosgvardia’s warehouses immediately after the Wagner rebellion and during the period of Wagner’s disarmament.[26] The source claimed that an unspecified Rosgvardia general with the first name “Roman” oversaw the storage of up to four large containers of Wagner military equipment near a Rosgvardia training ground in the area of “Kazachy Stan” (likely a settlement in an unspecified region of Russia).[27] ISW continues to assess that the Kremlin likely aimed to consolidate Russia‘s internal security apparatus around Rosgvardia following the Wagner rebellion.[28] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) announced on June 27 that it would prepare to transfer Wagner’s heavy military equipment to unspecified elements of the Russian military on the same day that Rosgvardia Head Viktor Zolotov announced that Rosgvardia would receive heavy weapons and tanks.[29] The Russian government also officially transferred the “Grom” special units of the Russian Federal Drug Control Service (of the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs) to the control of Rosgvardia in July.[30]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces carried out drone and cruise missile strikes on occupied Crimea and significantly damaged the Russian Black Sea Fleet (BSF) Command headquarters in Sevastopol on September 22.
- The Russian information space heavily focused its attention on the Ukrainian strike on Sevastopol on September 22.
- Ukrainian forces advanced south of Bakhmut and reportedly advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 22.
- The US Department of Defense (DoD) announced a new security assistance package on September 21, providing Ukraine with $325 million worth of military equipment.
- The US will reportedly soon provide long-range army tactical missile systems (ATACMS) to Ukraine.
- Russian efforts to intensify divisions between Ukraine and its Central European partners appear to have suffered a setback as Polish Prime Minister Andrzej Duda reiterated the strength of Polish-Ukrainian relations on September 22.
- A Ukrainian military official swiftly denied Russian claims that Wagner Group forces are operating in occupied Kherson Oblast.
- The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) is reportedly investigating high-ranking Rosgvardia officials over their potential involvement in Wagner Group’s rebellion on June 24.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations in the Kupyansk area, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Donetsk Oblast and reportedly advanced in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast administrative border area.
- The Russian government is reportedly planning to increase defense spending by 4.4 trillion rubles ($46 billion) in 2024.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 21, 2023
Ukrainian armored vehicles are operating beyond the final line of the Russian defensive layer that Ukrainian forces in western Zaporizhia Oblast are currently penetrating, although ISW is not yet prepared to assess that Ukrainian forces have broken fully through this Russian defensive layer. Geolocated footage posted on September 21 indicates that Ukrainian armored vehicles advanced south of the Russian anti-tank ditches and dragon’s teeth obstacles that are part of a tri-layered defense and engaged in limited combat immediately west of Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv).[1] It is unclear if Ukrainian forces retain these positions, however. This is the first observed instance of Ukrainian forces operating armored vehicles beyond the Russian tri-layer defense.[2] The presence of Ukrainian armored vehicles beyond the final line of the current Russian defensive layer indicates that the Ukrainians have secured their breach of the first two lines of this layer sufficiently to operate vehicles through the breach. Ukrainian forces have likely suppressed Russian artillery and other anti-tank systems in the area enough to bring their vehicles forward.[3] The Ukrainian ability to bring armored vehicles to and through the most formidable Russian defenses intended to stop them and to operate these vehicles near prepared Russian defensive positions are important signs of progress in the Ukrainian counteroffensive.[4] Additional geolocated footage published on September 20 and 21 indicates that Ukrainian forces also advanced west and southwest of Verbove.[5]
The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) reported on September 21 that Ukrainian forces have breached the main Russian defensive line in western Zaporizhia Oblast with armored vehicles, citing an unnamed Ukrainian officer serving in the area.[6] WSJ also reported that Ukrainian forces have advanced to the edge of Novoprokopivka (16km south of Orikhiv), although ISW has not observed visual confirmation of this report as of this publication.[7]
Russian forces currently defending in western Zaporizhia Oblast have been unable to prevent Ukrainian forces from making gradual but steady advances since mid-August. ISW has consistently observed Ukrainian forces making slow but regular advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast despite the Russian military’s lateral redeployment of elements of relatively elite units to reinforce Russian defensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast.[8] The Russian military laterally redeployed elements of the 7th Guards Mountain Airborne (VDV) Division and the 76th Guards VDV Division to the Robotyne area in mid-August to repel Ukrainian attacks and possibly to relieve elements of the 22nd and 45th Separate Spetsnaz Brigades that had been counterattacking against Ukrainian advances during the earlier phases of Ukrainian counteroffensive operations.[9] Geolocated footage published on September 20 and 21 shows elements of the 22nd Guards Spetsnaz Brigade operating west of Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv), suggesting that the Russian command has tactically transferred elements of the 22nd Guards Spetsnaz Brigade to support VDV elements already observed defending in the area.[10] A Ukrainian soldier defending in southern Ukraine told the WSJ in an article published on September 21 that Russian troops defending front-line trenches are “poor-quality,” but that counterattacking assault troops are “stronger.”[11] The Ukrainian soldier’s statements are consistent with ISW’s observations that relatively elite Russian Spetsnaz and VDV elements appear to be the primary counterattack elements in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
Ukrainian forces conducted a series of drone and missile strikes targeting the Russian airfield near occupied Saky, Crimea, and may have damaged Russian aircraft. The Department of Strategic Communications of the Ukrainian Armed Forces stated that Ukrainian forces launched a combined attack on the Russian airfield near Saky (60km north of Sevastopol).[12] Suspilne Crimea reported that sources in the Ukrainian Security Service (SBU) stated that the SBU and the Ukrainian Navy launched drones to overwhelm Russian air defense systems near the airfield and then conducted strikes with Neptune missiles.[13] Twelve Russian combat aircraft including Su-24 and Su-30 fighter-bombers, were reportedly present at the time of the strikes, and Suspilne’s SBU sources stated that strikes caused unspecified serious damage at the airfield.[14] ISW has yet to observe footage detailing the consequences of the Ukrainian strike, however. Russian sources, including the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD), claimed that Russian air defenses downed up to 19 Ukrainian drones over the Black Sea and Crimea on the night of September 20 to 21 but did not acknowledge any Ukrainian missile strikes.[15] Russia’s Black Sea Fleet manages the Saky airfield, which is the latest Black Sea Fleet target that Ukrainian forces have struck.
Satellite imagery confirms that Ukrainian forces also struck the 744th Communications Center of the Command of the Black Sea Fleet in occupied Crimea on September 20 as part of an apparent Ukrainian effort to target Black Sea Fleet facilities.[16] The imagery shows that the Ukrainian strikes destroyed a significant portion of the command post near Verkhnosadove (16km northeast of Sevastopol).[17] Ukrainian forces have increasingly targeted Black Sea Fleet naval assets in and around Crimea in recent weeks, including a strike that destroyed a Ropucha-class landing ship and a Kilo-class submarine and damaged the Sevmorzavod naval repair facility in Sevastopol.[18] Russia’s Black Sea Fleet is an element of the Russian navy subordinate to the Southern Military District (SMD), but commands air and ground units in occupied Crimea and elsewhere along the front in Ukraine in addition to its naval vessels. Elements of the Black Sea Fleet’s 810th Naval Infantry Brigade are engaged in critical defensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast, and the Black Sea Fleet’s 22nd Army Corps is defending positions on the east (left) bank of Kherson Oblast.[19] The Black Sea Fleet’s control of the Saky airfield gives it charge of ground-based aircraft in addition to its naval-based assets. The Black Sea Fleet appears to be heavily responsible for maintaining Russian logistics from Krasnodar Krai and occupied Crimea to the Russian grouping in southern Ukraine, especially since Ukrainian strikes have complicated Russian ground lines of communications (GLOCs) in the area.[20] Russian forces routinely launch drone and missile strikes from Black Sea Fleet assets and within the Black Sea Fleet’s area of responsibility in occupied Crimea and Krasnodar Krai.[21] The Black Sea Fleet is the only formal structure of the Russian military that has had a long-term presence in occupied Ukraine as it has been headquartered in Sevastopol since before Russia’s illegal annexation of Crimea in 2014. The Black Sea Fleet is more than its naval assets, and the Ukrainian attacks on the Black Sea Fleet will likely achieve effects beyond the degradation of Russian naval capabilities.
Russian forces conducted a notably large series of missile strikes against Ukraine on the night of September 20 to 21, likely to correspond with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s visit to the United States. Ukrainian sources reported on September 21 that Russian forces launched 44 Kh-101/Kh-555/Kh-55 cruise missiles targeting Ukrainian energy, industrial, and civilian infrastructure in Kyiv City, Cherkasy City, and Lviv City.[22] Ukrainian air defenses reportedly intercepted 38 Russian cruise missiles.[23] Ukrainian sources also reported that Russian forces launched six S-300 missiles at Kharkiv City.[24] Ukrainian Commander-in Chief General Valerii Zaluzhnyi stated that Russian forces launched the missiles in several waves from different directions and that the missiles changed course along their routes.[25] Russian milbloggers amplified photos and footage claiming to show the aftermath of Russian missile strikes throughout Ukraine.[26] Russian forces have not conducted a comparably large-scale missile strike since the night of August 29 to 30, when Russian forces launched 28 cruise missiles against Ukraine.[27]
The Kremlin continues to seek to intensify divisions between Ukraine and its Central European partners following Russia’s withdrawal from the Black Sea Grain Initiative. The export of Ukrainian grain along European land routes has emerged as an area of tension between Ukraine and its European partners since Russia’s withdrawal from the initiative in July and its attacks on Ukrainian port infrastructure since then, and ISW has previously assessed that Russian strikes on Ukrainian port and grain infrastructure are part of a Russian campaign to damage Ukrainian relations with its Western neighbors.[28] Polish Prime Minister Mateusz Morwiecki announced on September 20 that Poland would focus on building up its own weapons arsenals and would no longer transfer weapons to Ukraine.[29] The Polish and Ukrainian Ministers of Agrarian Policy agreed on September 21 to work together to find a solution regarding the export of Ukrainian agricultural products in the coming days, however.[30]
The Russian State Duma will reportedly propose a bill allowing the Russian National Guard (Rosgvardia) to include volunteer formations amid continued rumors about the Wagner Group operating alongside Rosgvardia. Russian Chairperson of the State Duma Committee on Information Policy Alexander Khinshtein announced that members of the State Duma and Federation Council plan to introduce a bill on September 22 that would allow for the inclusion of volunteer formations within Rosgvardia.[31] Khinshtein stated that the bill would extend all previously established powers and mechanisms of the Russian MoD to Rosgvardia as Rosgvardia performs tasks in the war in Ukraine similar to those of the Russian MoD.[32] Khinshtein claimed that the Russian president will make decisions regarding Rosgvardia volunteer formations.[33] ISW previously reported that Russian sources claimed that some Wagner Group personnel are working closely with Rosgvardia in order to rejoin the war in Ukraine.[34] A Russian milblogger claimed on September 18 that Rosgvardia Director Viktor Zolotov met with the son of deceased Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin, Pavel Prigozhin, and Wagner commander Anton Yelizarov (known under the callsign “Lotos”) and discussed the “preservation” of Wagner.[35] Russian opposition media, insider sources, and milbloggers have claimed that Yevgeny Prigozhin left his assets to Pavel Prigozhin and that Pavel Prigozhin will take over the management of Wagner.[36]
The Kremlin is reportedly pushing propaganda narratives that highlight Russian artillery and aviation while downplaying the efforts of Russian forces conducting ground operations, likely in order to avoid discussion of Russian personnel losses and poor counterbattery capabilities. Russian opposition news outlet Meduza reported on September 21 that the Russian Presidential Administration distributed a manual on September 19 instructing Kremlin-affiliated media to highlight Ukrainian equipment and personnel losses and emphasize that Russian artillery fire and air strikes are effectively suppressing Ukrainian offensive actions.[37] ISW has routinely observed Russian units actively engaged in ground assaults, and the Russian information space has repeatedly complained about Russian forces’ poor counterbattery capabilities.[38]
The Kremlin is likely aiming to blame Armenian leadership and the West for Azerbaijan’s recent military operation into Nagorno-Karabakh. The Russian Presidential Administration’s manual also reportedly advised Kremlin-affiliated media to blame the West and Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan for recognizing Azerbaijani sovereignty over Nagorno-Karabakh.[39] The manual also advised state media to emphasize Russian peacekeepers’ role in “evacuating civilians.”[40] The Russian government is likely attempting to portray Pashinyan’s leadership poorly after a series of statements criticizing Armenia’s ties to Russia.[41]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian armored vehicles are operating beyond the final line of the Russian defensive layer that Ukrainian forces in western Zaporizhia Oblast are currently penetrating, although ISW is not yet prepared to assess that Ukrainian forces have broken fully through this Russian defensive layer.
- Russian forces currently defending in western Zaporizhia Oblast have been unable to prevent Ukrainian forces from making gradual but steady advances since mid-August.
- Ukrainian forces conducted a series of drone and missile strikes targeting the Russian airfield near occupied Saky, Crimea, and may have damaged Russian aircraft.
- Satellite imagery confirms that Ukrainian forces also struck the 744th Communications Center of the Command of the Black Sea Fleet in occupied Crimea on September 20 as part of an apparent Ukrainian effort to target Black Sea Fleet facilities.
- Russian forces conducted a notably large series of missile strikes against Ukraine on the night of September 20 to 21, likely to correspond with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s visit to the United States.
- The Kremlin continues to seek to intensify divisions between Ukraine and its Central European partners following Russia’s withdrawal from the Black Sea Grain Initiative.
- The Russian State Duma will reportedly propose a bill allowing the Russian National Guard (Rosgvardia) to include volunteer formations amid continued rumors about the Wagner Group operating alongside Rosgvardia.
- The Kremlin is reportedly pushing propaganda narratives that highlight Russian artillery and aviation while downplaying the efforts of Russian forces conducting ground operations, likely in order to avoid discussion of Russian personnel losses and poor counterbattery capabilities.
- The Kremlin is likely aiming to blame Armenian leadership and the West for Azerbaijan’s recent military operation into Nagorno-Karabakh.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not advance.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 20, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued offensive actions near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 20. The Ukrainian General Staff stated that Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations and inflicted significant losses on Russian manpower and equipment in the Melitopol (western Zaporizhia Oblast) direction. The Ukrainian General Staff also reported that Ukrainian forces continued offensive actions in the Bakhmut direction and are consolidating in newly secured lines. The UK Ministry of Defense (MoD) assessed that Ukrainian forces secured positions in Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut) and Andriivka (10km southwest of Bakhmut) and that Russian redeployments of airborne (VDV) forces from Bakhmut to the Zaporizhia direction have weakened Russian defenses around Bakhmut. ISW had previously observed elements of the 83rd Separate Air Assault Brigade operating in Zaporizhia, although it is unclear how large a proportion of that unit was redeployed from Bakhmut. Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Captain Ilya Yevlash stated that Ukrainian forces are preparing defensive positions before Russian forces renew their assaults in the Kupyansk-Lyman direction.
Russian servicemen and milbloggers revealed that the Russian military command orders Russian troops to carry out “ill-conceived and unsupported” counterattacks on Bakhmut’s southern flank to urgently regain lost ground. Elements of Altai Krai’s 1st Battalion of the 1442nd Regiment (a mobilized unit) published a video appeal in which the soldiers claim that they abandoned their military equipment in the Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut) area after receiving an order from the Russian military command to form an assault group and attack in the Bakhmut direction. The servicemen noted that the Russian military command began deploying different types of personnel to the frontlines — including soldiers who are currently resting in the rear — without providing them with enough functional artillery shells. The servicemen noted that their shells do not explode when fired, which is likely a symptom of Russia's defense industrial base’s (DIB) efforts to speed up the production of shells and skipping quality assurance measures to do so. The servicemen added that the unit is suffering from low morale after hearing reports that Ukrainian forces destroyed most of an unspecified Russian regiment and almost an entire retreating assault group in the area. The servicemen also claimed that they do not have prepared defensive positions and have to rely on small arms whereas the Ukrainians have artillery. Relatives of the personnel in the 1442nd Regiment had previously appealed to Russian President Vladimir Putin after the Russian military command beat the troops for refusing to carry out an assault on September 14.
A Russian milblogger also accused the Russian military command of ordering Russian troops to recapture Andriivka (10km southwest of Bakhmut) and the surrounding area without setting proper conditions for such counterattacks. The milblogger claimed that the Russian military command was planning “weak” counterattacks and failed to provide accurate intelligence to Russian assault units. The milblogger observed that Russian forces also lack artillery support, while “hysterical” counterattacks are depleting Russian resources and reserves. The milblogger also claimed that Russian defenses on the adjacent heights in the Andriivka area had collapsed, and it is likely that the Russian military command’s efforts to regain lost positions are preventing Russian forces from preparing new defensive positions on Bakhmut’s southern flank.
Russian forces conducted another round of Shahed drones strikes against Ukraine overnight on September 19-20. Ukrainian military officials reported that Ukrainian forces shot down 17 of 24 launched Iranian-made Shahed 136/131 drones in Sumy, Poltava, Kirovohrad, and Dnipropetrovsk oblasts and that some of the drones struck an oil refinery in Poltava Oblast. Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Colonel Yuriy Ihnat reiterated that Russian forces have predictably increased the use of drones against Ukraine because Russia can obtain, manufacture, or assemble more drones domestically. Ihnat stated that Russian forces have not changed their drone tactics and continue attempts to bypass Ukrainian air defenses.
A Russian milblogger outlined Russian reconnaissance groups’ drone operator training and operation tactics in Ukraine. The milblogger claimed that most Russian reconnaissance groups have two types of drone operators — a Mavik drone operator who carries out reconnaissance operations and a first-person viewer (FPV) drone operator who conducts attacks. The milblogger noted that Mavik drone operators usually adjust fire and direct ground and drone attacks, while FPV drone operators strike targets that the Mavik drone operators identify. The milblogger claimed that competent Mavik operators will train for up to six months while FPV drone operators train for three months, but noted that the battlefield effectiveness of drones is contingent upon their operators’ skill. The milblogger noted that Russian reconnaissance group commanders do not need approval from senior commanders to strike targets. The milblogger also claimed that the Russian military is training fewer FPV drone operators due to the time and money needed for FPV drone repair, assembly, and operator training. ISW has not observed a decrease in reconnaissance and FPV drone usage, however. The milblogger may be claiming that the Russian military is decreasing drone usage due to high costs in order to generate monetary and drone donations.
Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) reported that unspecified saboteurs damaged Russian strategic aircraft at Chkalovsky airfield near Moscow on September 18. The GUR reported on September 20 that the saboteurs planted explosives on an An-148 and an Il-20 aircraft subordinate to the Russian 354th Special Purpose Aviation Regiment and an Mi-28N helicopter that Russian forces use to repel Ukrainian drones. The GUR stated that the explosions severely damaged the aircraft, including the Mi-28N's tail, and inflicted minor damage on a second An-148 nearby. Russian authorities have not yet reported an attack at the Chkalovsky airfield as of September 20.
Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov claimed on September 20 that he is in good health amidst continued speculations about his possible illness or death. Ramzan Kadyrov directly addressed speculations about his health in a social media post on September 20 claiming that he remains alive and in good health. Kadyrov claimed to not understand why speculations of his health necessitate “fuss” and stated that publications that speculate on his health are untrustworthy. Kadyrov included a video of himself visiting his uncle Magomed Kadyrov in the hospital.
Russian Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu met with Iranian Chief of the General Staff Mohammad Bagheri in Tehran, Iran to discuss Russian-Iranian military cooperation on September 19, a day after Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi denied Iran’s provision of drones to Russia. Raisi denied that Iran provides drones to Russia during his speech to the United Nations on September 18. Shoigu and Bagheri visited an Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps (IRGC) Aerospace Force facility where Shoigu saw Iranian-made drones, air defense systems, missiles; and tactical, medium, and long-range missile systems on September 20. Shoigu stated that Russia and Iran plan to implement a range of unspecified activities in spite of Western sanctions, likely in order to evade the sanctions.
Russian President Vladimir Putin emphasized Russian peacekeepers’ humanitarian actions in Nagorno-Karabakh as the Russian information space continues to observe that Russia is losing influence in Armenia. The Nagorno-Karabakh authorities accepted a Russian peacekeeper-mediated ceasefire agreement with Azerbaijan on September 20 and reported that Nagorno-Karabakh and Azerbaijani officials will meet in Yevlakh, Azerbaijan on September 21 to discuss “reintegration” and “ensuring the rights and security of Armenians in Nagorno-Karabakh.” Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan stated that Armenian authorities were not involved in the ceasefire agreement and that Armenian forces were not present in Nagorno-Karabakh. Putin emphasized on September 20 Russian peacekeepers’ roles in protecting civilians and claimed that Russia is in constant contact with Armenian, Azerbaijani and Nagorno-Karabakh authorities.
The Russian MoD reported that Azerbaijani small arms fire killed Russian peacekeeping personnel driving in Nagorno-Karabakh and that Russian and Azerbaijani investigative authorities are working to clarify the incident. Several milbloggers noted that the Russian military did not respond when Azerbaijani forces shot down a Russian Mi-24 helicopter during the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war and expressed irritation at the assumption that the Russian military would similarly ignore these deaths. Russian milbloggers continue to lament Russia’s waning influence in Armenia. Russia’s role as a security guarantor for Armenia may be declining as Russia continues to prioritize its military operations in Ukraine at the same time as the Armenian government increasingly expresses its dissatisfaction with its security ties to Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continued offensive actions near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 20.
- Russian servicemen and milbloggers revealed that the Russian military command orders Russian troops to carry out “ill-conceived and unsupported” counterattacks on Bakhmut’s southern flank to urgently regain lost ground.
- Russian forces conducted another round of Shahed drone strikes against Ukraine overnight on September 19-20.
- A Russian milblogger outlined Russian reconnaissance groups’ drone operator training and operation tactics in Ukraine.
- Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) reported that unspecified saboteurs damaged Russian strategic aircraft at Chkalovsky airfield near Moscow on September 18.
- Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov claimed on September 20 that he is in good health amidst continued speculations about his possible illness or death.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu met with Iranian Chief of the General Staff Mohammad Bagheri in Tehran, Iran to discuss Russian-Iranian military cooperation on September 19, a day after Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi denied Iran’s provision of drones to Russia.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin emphasized Russian peacekeepers’ humanitarian actions in Nagorno-Karabakh as the Russian information space continues to observe that Russia is losing influence in Armenia.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not make confirmed gains.
- The Russian Red Cross (RKK) indicated that the Russian full-scale invasion of Ukraine, particularly partial mobilization efforts in autumn 2022, caused a decline in mental health among many Russians.
- Russian and occupation authorities continue efforts to deport Ukrainian children to Russia and integrate Ukrainian children into Russian culture.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 19, 2023
The Russian government quickly signaled on September 19 that Russian peacekeeping forces would not intervene in Azerbaijan’s military operation into Nagorno-Karabakh, despite Russia’s previous security ties to Armenia. The Azerbaijani Ministry of Defense (MoD) announced that Azerbaijani forces began a military operation into Nagorno-Karabakh on September 19.[i] Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov claimed that the Russian military is in contact with Armenian and Azerbaijani officials “at the highest level.”[ii] Russian Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Maria Zakharova issued a general statement calling on “all sides” to stop the bloodshed, claimed that the Russian peacekeeping contingent in Nagorno-Karabakh continues to fulfil its assigned tasks, and cited the trilateral Russian-Armenian-Azerbaijani agreements signed in 2020 and 2022 as a path toward peace.[iii] Russian State Duma Defense Committee Chairman Andrei Kartapolov stated that the Russian peacekeeping contingent does not have the right to use weapons unless directly threatened.[iv] A Kremlin-affiliated milblogger claimed that the Russian peacekeeping contingent lacks any protocols on the use of force or rules of engagement in Nagorno-Karabakh, and instead operates on the basis of the November 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh peace agreement.[v] Russian Security Council Deputy Chairperson Dmitry Medvedev and RT Editor-in-chief and Russian propagandist Margarita Simonyan (both notably nationalistic and extreme voices in the Russian government) claimed that Armenia is experiencing the repercussions of its recent efforts to align with the West and distance itself from Russia, though mainline Russian government officials did not promote this framing and maintained equivocal language calling for an end to the fighting.[vi] Russian milbloggers expressed support for the safety of the Russian peacekeeping contingent in Nagorno-Karabakh while lamenting Russia’s waning influence with Armenia and Azerbaijan.[vii] The Russian military is unlikely to prioritize peacekeeping operations in Nagorno-Karabakh against the backdrop of the war in Ukraine, and minimal Russian peacekeeping operations in Nagorno-Karabakh are unlikely to affect Russian military operations in Ukraine.
Russian and Ukrainian sources credited superior Ukrainian combat coordination, more precise artillery fire, and stronger electronic warfare (EW) systems for recent Ukrainian advances south of Bakhmut amid continued discussions of significant Russian losses in the area. Ukrainian personnel that participated in the recent liberation of Klishchiivka (7km southeast of Bakhmut) stated on September 18 that high morale, sufficient training, sufficient resources for artillery fire and drone strikes, good coherence between Ukrainian units, and detailed reconnaissance enabled Ukrainian forces to advance.[viii] One Ukrainian commander stated that elements of various Russian units defending in the area suffered from a lack of coherence.[ix] Russian Airborne (VDV), Spetsnaz, and 3rd Army Corps elements defended near Klishchiivka; and persistent issues with horizontal integration among Russian forces in Ukraine likely prevented these disparate Russian elements from sharing information and coordinating combat operations.[x] A prominent Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian artillery units south of Bakhmut are increasingly accurate and precise, enabling Ukrainian forces to safely shell Russian advances closer to Ukrainian positions.[xi] The milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces have advantages in aerial reconnaissance as well as stronger EW systems.[xii]
A Russian milblogger with close ties to the VDV acknowledged that elements of the 83rd Guards VDV Brigade, which were defending near Klishchiivka, are now reconstituting in rear areas and that elements of the 31st Guards VDV Brigade continue to defend near the settlement.[xiii] Russian milbloggers claimed that elements of the Russian 72nd Motorized Rifle Brigade (3rd Army Corps) are still operating in the Bakhmut area, although Ukrainian forces have likely rendered these elements combat ineffective.[xiv] Ukrainian Ground Forces Commander Oleksandr Syrskyi stated on September 18 that Ukrainian forces completely destroyed the combat capabilities of elements of the 72nd Motorized Rifle Brigade, the 31st VDV Brigade, and the 83rd Brigade during the liberation of Andriivka and Klishchiivka.[xv] ISW previously assessed that Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast may correspond with the degradation of Russian forces defending in that sector of the front and that recent Ukrainian advances south of Bakhmut may correspond with a similar degradation of Russian forces.[xvi]
Russian losses have reportedly significantly increased in western Zaporizhia Oblast in recent days, and the Russian military likely struggles with a lack of available combat-effective units that the Russian command is willing to laterally redeploy to this sector of the front. Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Oleksandr Shtupun stated that Russian forces lost 313 personnel (likely a total of killed and wounded) in the Tavriisk direction on September 18, including western Zaporizhia Oblast. Shtupun stated that this is significantly higher than Russian losses during the previous two days when Russian forces lost roughly 200 personnel each day.[xvii] Shtupun stated that Russian Airborne (VDV) forces are conducting defensive operations in the Tavriisk direction (likely in western Zaporizhia Oblast) and that “Storm-Z” detachments with convict recruits have arrived to act as “cover” for VDV units, possibly referring to the need to cover the VDV units during a potential withdrawal.[xviii] ISW has previously observed elements of the 7th Guards Mountain VDV Division and 76th Guards VDV Division conducting counterattacks against Ukrainian forces in the Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv) area, and ISW has previously assessed that these operations have likely degraded these VDV forces heavily.[xix] “Storm-Z” detachments are often combat ineffective and will likely provide the Russian defense in western Zaporizhia Oblast with marginal combat power.
Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/-136 drone and ballistic missile strikes on Ukrainian rear areas on September 19. Ukrainian military officials stated that Russian forces launched 31 drones from Krasnodar Krai and 1 Iskander-M ballistic missile from occupied Crimea and that Ukrainian forces shot down 28 drones.[xx] The Ukrainian State Service for Emergency Situations reported that Russian drones hit industrial warehouses in Lviv, and the Ukrainian General Staff reported that the Russian Iskander missile hit Kryvyi Rih, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast.[xxi] US Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin stated on September 19 that Russian strikes on Ukrainian port and grain infrastructure have destroyed at least 280,000 tons of grain in recent months, which he stated would have been enough to feed up to 10.5 million people for a year.[xxii]
Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu met with Iranian Armed Forces General Staff Chief Major General Mohammad Bagheri in Tehran, Iran on September 19. Shoigu and Bagheri discussed Russian–Iranian bilateral military cooperation and the situation in Nagorno-Karabakh, Syria, and Afghanistan.[xxiii] Shoigu stated that Russian–Iranian military relations are developing “dynamically and positively.”[xxiv] A Kremlin-affiliated Russian milblogger claimed that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) planned Shoigu’s visit to Tehran in advance and that it was not coordinated with Azerbaijan’s escalation in Nagorno-Karabakh.[xxv] The milblogger also claimed that Shoigu aimed to expand military-technical cooperation with Iran and hypothesized that Russia may be interested in expanding Iranian Shahed drone production on Russian territory.[xxvi]
The Kremlin continues efforts to strengthen its control of the Russian information space ahead of the September 2024 Russian presidential elections. The Russian government announced a ban on services that provide virtual mobile numbers, which includes temporary numbers that individuals can use to sign up for anonymous social media accounts without using their personnel credentials, starting on September 1, 2024.[xxvii] This measure likely aims to crack down on anonymous Telegram accounts that criticize the Kremlin and allows the Kremlin to better control the Russian information space. Announcing this measure a year ahead of its implementation is likely a soft rollout designed to gauge a possible information space reaction to the announcement and allow time to soften or strengthen the measure as the implementation and presidential elections approach. The Russian government will reportedly provide a list of alternative services to allow individuals to anonymously sign up for social media accounts, but it is very unlikely that these alternatives will allow individuals to maintain a similar degree of anonymity from the Russian government as existing virtual mobile number services currently afford.[xxviii]
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky delivered a speech at the United Nations on September 19.[xxix] ISW will cover Zelensky’s trip to the United States after his upcoming visit to Washington, D.C.
Key Takeaways:
- The Russian government quickly signaled on September 19 that Russian peacekeeping forces would not intervene in Azerbaijan’s military operation into Nagorno-Karabakh, despite Russia’s previous security ties to Armenia.
- Russian and Ukrainian sources credited superior Ukrainian combat coordination, more precise artillery fire, and stronger electronic warfare (EW) systems for recent Ukrainian advances south of Bakhmut amid continued discussions of significant Russian losses in the area.
- Russian losses have reportedly significantly increased in western Zaporizhia Oblast in recent days, and the Russian military likely struggles with a lack of available combat effective units that the Russian command is willing to laterally redeploy to this sector of the front.
- Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/-136 drone and ballistic missile strikes on Ukrainian rear areas on September 19.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu met with Iranian Armed Forces General Staff Chief Major General Mohammad Bagheri in Tehran, Iran on September 19.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not advance on September 19.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in at least two sectors of the front on September 19 and advanced along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line and in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- A Latvian company has reportedly been exporting chips and microcircuits to Russian defense industrial base (DIB) companies despite international sanctions designed to prevent Russia from importing such components.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 18, 2023
Ukraine’s liberation of Klishchiivka and Andriivka south of Bakhmut may have degraded the Russian defense in the area south of Bakhmut and could have rendered combat ineffective in as many as three Russian brigades according to Ukrainian military officials. Ukrainian Ground Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi stated on September 18 that Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut) and Andriivka (10km southwest of Bakhmut) were important elements of the Russian Bakhmut-Horlivka defensive line that Ukrainian forces “breached.”[i] Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Captain Ilya Yevlash stated on September 17 that Ukraine’s liberation of Klishchiivka will allow Ukrainian forces to control Russian ground lines of communication (GLOCs) supplying the Russian force grouping in the Bakhmut area — likely referring to Ukrainian forces’ ability to establish fire control over the T0513 Bakhmut-Horlivka highway.[ii] ISW is currently unable independently to evaluate the strength and extent of the Russian defensive fortifications in the Bakhmut area, although Russian forces have likely fortified their defense lines near Bakhmut less heavily than they did in southern Ukraine. Russian forces south of Bakhmut are also likely battle-weary from the recent efforts to hold Klishchiivka and Andriivka, and the Ukrainian capture of two settlements defending a key Russian GLOC supporting Bakhmut indicates that these forces will likely struggle to replenish their combat strength and defend against any further Ukrainian offensive activity south of Bakhmut. There are no immediate indications that the liberation of Klishchiivka and Andriivka will portend a higher rate of Ukrainian advance south of Bakhmut, however, and the Russian defense of positions west of the T0513 will likely continue to present challenges for Ukrainian forces in the area.
The Ukrainian liberation of two villages that Russian forces were fighting hard to hold could correspond with the severe degradation of the Russian units defending them, as Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast appear to correspond with the significant degradation of defending Russian units and formations in that sector of the front. Russian forces defending in western Zaporizhia Oblast since the start of the counteroffensive have done so largely without operational-level unit rotations and have likely suffered compounding losses.[iii] Elements of the Russian 42nd Motorized Rifle Division’s 71st, 70th, and 291st Motorized Rifle Regiments (58th Combined Arms Army, Southern Military District) routinely repelled Ukrainian assaults and engaged in various “combat clashes,“ including limited engagements and some counterattacks, during the first phase of the counteroffensive from June to August 2023.[iv] In mid-to-late August, Ukrainian forces began breaking through the initial Russian defensive layer that these elements of the 42nd Motorized Rifle Division had spent considerable amounts of manpower, personnel, and effort to hold.[v] Russian reporting and footage suggest that many of these elements of the 42nd Motorized Rifle Division have since withdrawn to positions behind a subsequent Russian defensive layer between Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv) and Solodka Balka (20km south of Orikhiv) and now mainly shell advancing Ukrainian units.[vi] The absence of recent reports and footage of these elements participating in combat engagements in western Zaporizhia Oblast suggests that casualties sustained during the first phases of the Ukrainian counteroffensive rendered them combat ineffective. Elements of the 70th Motorized Rifle Regiment reportedly temporarily withdrew to a rear area during the Ukrainian breakthrough and returned to frontline positions in early September, suggesting that Ukrainian advances had degraded this unit enough to compel the Russian command to give it time to refit in the rear — which would be one of the very few unit rotations ISW has observed on this sector of the front.[vii] Elements of the 810th Naval Infantry Brigade (Black Sea Fleet), which also held forward positions at the initial Russian defensive layer during the earlier phases of the counteroffensive, similarly appear to be deployed further behind the Russian defensive layer ahead of the current Ukraine advance.[viii] Elements of the 810th Naval Infantry Brigade reportedly engaged in close combat during the Ukrainian push through Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv), and Russian milbloggers maintain that some elements of the unit hold positions near the southern outskirts of Robotyne.[ix]
Ukrainian counteroffensive operations may have resulted in the particularly severe degradation of critical elements of the Russian elastic defense in western Zaporizhia Oblast. Elements of the Russian 22nd and 45th Separate Spetsnaz Brigades appeared to be responsible for counterattacking against significant Ukrainian advances in the Robotyne area during the earlier phases of the counteroffensive and likely suffered heavy losses in these operations.[x] Russian reporting and footage of the Robotyne area in recent weeks has largely omitted mention of these Spetsnaz brigades, suggesting that this degradation may have severely impacted their ability to continue counterattacking. A prominent milblogger claimed that elements of the 45th Spetsnaz Brigade were still operating near the frontline as of September 12, however.[xi] Elements of the Russian 7th Guards Mountain Airborne (VDV) Division that laterally deployed to the Robotyne area in mid-August during the Ukrainian breakthrough now appear to be responsible for conducting counterattacks against the most forward advances of the Ukrainian breach.[xii] Russian sources routinely claim that VDV elements, which may include elements of the 76th Guards VDV Division that also laterally redeployed to the area, repel Ukrainian assaults and conduct counterattacks near Robotyne[xiii] The degradation of the elements of the 22nd and 45th Separate Spetsnaz Brigades initially responsible for counterattacking in the Robotyne area likely prompted the Russian command to laterally redeploy these elements of the 7th and 76th VDV Divisions to assume responsibility for counterattacking. The Russian elastic defense requires one echelon of Russian forces to slow a Ukrainian tactical advance while a second echelon of forces rolls back that advance through counterattacking. Counterattacking requires significant morale and relatively high combat capabilities, and the Russian military appears to rely on relatively elite VDV units and formations for this undertaking, possibly at the expense of heavily degrading these forces.[xiv]
ISW has not directly observed the level of degradation among the Russian units referenced above and it is possible that some have suffered heavier losses than others. It is also possible that the Russians have used the arrival of elements of the 76th and 7th VDV Divisions to conduct belated unit rotations of their tired frontline units. The current battlefield geometry between the Ukrainian advance and current Russian defensive positions may also be contributing to the apparent absence of these likely degraded units from combat engagements, as the gap between Ukrainian advances and Russian defensive positions may result in less direct combat engagements. Ukrainian forces may engage these units in more direct combat as they further advance into and past the current Russian defensive layer. It is thus too soon to assess with high confidence that the initial defenders in this sector have been rendered combat ineffective, but the evidence currently available points in that direction.
Recent Ukrainian advances south of Bakhmut may correspond with the similar degradation of defending Russian units in the area. Syrskyi stated that Ukrainian forces completely destroyed the combat capabilities of elements of the 72nd Motorized Rifle Brigade (3rd Army Corps), the 31st Guards VDV Brigade, and the 83rd Guards VDV Brigade during the liberation of Andriivka and Klishchiivka.[xv] Russian “Vostok” Battalion commander Alexander Khodakovsky’s claim that the 31st VDV Brigade commander has been killed supports this statement.[xvi] The 72nd Motorized Brigade has likely been rendered combat ineffective, although the exact level of losses among the two VDV brigades remains unclear.[xvii] These VDV elements were involved in counterattacking and attempting to roll back Ukrainian advances around Bakhmut — similar to the way that VDV elements operate in western Zaporizhia Oblast — and likely suffered heavy losses.[xviii] If recent Ukrainian advances south of Bakhmut resulted in the destruction of the 31st and 83rd VDV brigades’ combat capabilities, then the Russian command will likely laterally redeploy elements of another relatively elite formation to maintain critical elements of the Russian defense south of Bakhmut. Ukrainian counteroffensive operations have pinned elements of two VDV divisions and another VDV brigade in addition to the 83rd and 31st in the Bakhmut direction, and the Russian command may decide to conduct tactical redeployments to make up for the reported losses among the 83rd and 31st VDV brigades.[xix] Lateral redeployments from elsewhere in Ukraine or substantial tactical redeployments of other VDV elements in the Bakhmut area would therefore indicate that recent Ukrainian advances have resulted in significant Russian losses.
Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/136 drone and cruise missile strikes on coastal and rear areas of Ukraine on the night of September 17-18. Ukrainian officials reported that Russian forces launched 24 Shahed drones from Krasnodar Krai and occupied Crimea and 17 Kh-101/555/55 air-launched cruise missiles from Tu-95MS strategic bombers that took off from Volgograd Oblast.[xx] Ukrainian officials reported that Ukrainian forces shot down 18 drones and all 17 missiles.[xxi] The Ukrainian Air Force noted that the Russian drone strike targeted Mykolaiv and Odesa oblasts.[xxii] Russian sources claimed that Russian drones hit ports in Odesa Oblast and that the Russian missiles targeted the Starokostyantyniv airfield in Khmelnytskyi Oblast.[xxiii]
An organization with alleged ties to Russian First Deputy Presidential Chief of Staff Sergey Kiriyenko is reportedly responsible for disseminating pro-war propaganda and false information about Ukraine to prominent figures in the Russian information space. Russian opposition news outlets Meduza, Vazhnye Istorii, and the Bell reported on September 13 that the non-profit organization “Dialog” created multiple popular Telegram channels to increase pro-Russian reporting on the war in Ukraine at the start of Russia’s full-scale invasion and has subsequently been distributing false information about the war in Ukraine to prominent figures in the Russian information space, including Kremlin propagandist Vladimir Solovyov, prominent milbloggers, and popular news aggregators.[xxiv] Dialog is also reportedly affiliated with pro-Russian Telegram channels that mimic Ukrainian channels.[xxv] Dialog reportedly advised unspecified individuals in the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) to issue a “tough” and “prompt” response following increasing reports of a lack of ammunition and provisions among Russian mobilized personnel in Ukraine.[xxvi] Dialog-affiliated sources also reportedly disseminated negative reports about deceased Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin while Wagner forces were fighting in Ukraine.[xxvii] The Russian Ministry of Digital Development reportedly transferred 6.5 billion rubles (about $67.7 million) to Dialog in 2022, and its deputy general director, Vladimir Tabak, reportedly has ties to Kiriyenko.[xxviii] ISW has consistently observed some Russian sources making similar claims with similar language on the same days, which may suggest that some Russian sources receive information from the same source. Kiriyenko’s reported affiliation with Dialog is consistent with ISW’s assessment that some Russian siloviki and senior military commanders control various Telegram channels intended to further their individual objectives in the Russian information space.[xxix]
Russian Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergey Lavrov met with Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi in Moscow on September 18. Lavrov stated in his opening remarks that the world is undergoing “tectonic shifts” and reiterated boilerplate rhetoric on the importance and previous successes of Russian-Chinese cooperation.[xxx]
Imprisoned ardent nationalist and former Russian officer Igor Girkin issued a direct criticism of Russian President Vladimir Putin to rally supporters to his cause. Girkin, via his lawyer Alexander Molokhov, posted a statement on September 18 dated September 15 that justifies Girkin’s opposition to Putin.[xxxi] Girkin humorously answered the question “why Strelkov [Girkin] has gone crazy” for asserting that he is “better than Putin.” Girkin claimed that the “Troubles” (likely referencing the Time of Troubles in 17th century Russia that preceded the rise of the Romanov dynasty) have begun in Russia and that the Kremlin’s attempts to address the direst issues have failed, so the current “bureaucratic-oligarchic system” will eventually “collapse.” Girkin claimed that it is his “duty” to try to unite other patriots to be a suitable alternative but acknowledged that he may lack the resources to succeed or may have begun his initiative too early. Girkin expressed hope that his efforts will inspire others to “act as leaders of the national-patriotic movement” because “it is too late to be afraid and wait” as it is the “eve of the collapse of Russian statehood.”
Key Takeaways:
- Ukraine’s liberation of Klishchiivka and Andriivka south of Bakhmut may have degraded the Russian defense in the area south of Bakhmut and could have rendered combat ineffective as many as three Russian brigades according to Ukrainian military officials.
- Ukrainian counteroffensive operations may have resulted in the particularly severe degradation of critical elements of the Russian elastic defense in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Ukrainian counteroffensive operations may have resulted in the particularly severe degradation of critical elements of the Russian elastic defense in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Recent Ukrainian advances south of Bakhmut may correspond with the similar degradation of defending Russian units in the area.
- Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/136 drone and cruise missile strikes on coastal and rear areas of Ukraine on the night of September 17-18.
- An organization with alleged ties to Russian First Deputy Presidential Chief of Staff Sergey Kiriyenko is reportedly responsible for disseminating pro-war propaganda and false information about Ukraine to prominent figures in the Russian information space.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia and advanced in some areas on September 18.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in at least two sectors of the front and advanced in western Zaporizhia on September 18.
- Some Russian sources claimed that former Wagner Group personnel are working closely with Rosgvardia (Russian National Guard) in order to return fighting in Ukraine.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 17, 2023
Ukrainian forces liberated Klishchiivka, south of Bakhmut, on September 17 and continued successful offensive operations elsewhere in the Bakhmut direction. Geolocated footage posted on September 17 shows Ukrainian forces holding up flags in Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut).[i] Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Captain Ilya Yevlash later confirmed that Ukraine has liberated Klishchiivka, and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky congratulated the Ukrainian 80th Air Assault Brigade, 5th Assault Brigade, 95th Air Assault Brigade, and National Police “Lyut” Assault Brigade for their role in liberating the settlement.[ii] Further geolocated footage posted on September 16 shows that Ukrainian forces have captured positions east of Orikhovo-Vasylivka (10km northwest of Bakhmut).[iii] The liberation of Klishchiivka, as well as continued Ukrainian tactical gains northwest of Bakhmut, are tactical gains of strategic significance because they are allowing Ukrainian forces to fix a considerable portion of Russian airborne (VDV) elements in the Bakhmut area, as ISW’s Daniel Mealie discusses in the September 17, 2023 special edition.
Russian forces launched another series of Shahed-131/136 drone and cruise missile strikes at southern Ukraine on the night of September 16-17. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces launched six Shahed drones from the southeastern and southern directions and 10 Kh-101/555/55 air-launched cruise missiles from nine Tu-95MS strategic bombers that took off from Engels Airbase, Saratov Oblast.[iv] Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Colonel Yuriy Ihnat noted that Russian forces mainly targeted grain infrastructure in southern Odesa Oblast, and Ukrainian military sources stated that Ukrainian forces shot down six Shaheds and six cruise missiles.[v] Ukraine’s Southern Operational Command posted images of the aftermath of one Russian strike in an unspecified part of Odesa Oblast.[vi] Russian forces additionally struck civilian enterprises in Kharkiv City with four S-300 missiles.[vii]
North Korean dictator Kim Jong Un concluded his trip to Russia on September 17 and received several pieces of military technical equipment from the governor of Primorsky Krai. Kremlin newswire TASS reported that Kim visited the Far Eastern Federal University on September 17, where he met with Russian military engineers.[viii] TASS and other Russian sources additionally noted that Primorsky Krai Governor Oleg Kozhemyako gifted Kim a military vest, an unspecified loitering munition, and an unspecified long-range reconnaissance drone.[ix] ISW previously reported that Russia may be open to forms of technological and defensive cooperation with North Korea but is unlikely to provide physical systems due to Russian fears that providing the North Korean regime with such systems may trigger further sanctions against Russia.[x] It is therefore notable that a Russian official gifted Kim with pieces of military technology that will presumably return to North Korea with Kim. United Nations sanctions specify that ”All Member States are required to prevent the direct or indirect supply, sale, or transfer to the DPRK, through their territories or by their nationals, or using their flag vessels or aircraft, and whether or not originating in their territories, of all arms and related materiel, including small arms and light weapons...”[xi]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces liberated Klishchiivka, south of Bakhmut, on September 17 and continued successful offensive operations elsewhere in the Bakhmut direction.
- Russian forces launched another series of Shahed-131/136 drone and cruise missile strikes at southern Ukraine on the night of September 16-17.
- North Korean dictator Kim Jong Un concluded his trip to Russia on September 17 and received several pieces of military technical equipment from the governor of Primorsky Krai.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense’s (MoD) effort to subsume the Wagner Group is prompting Russian officials to more openly back military juntas in West Africa.
- Prolonged concern about Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov’s health in the Russian information space highlights Russian President Vladimir Putin’s dependence on Kadyrov for continued stability in Chechnya.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast area on September 17 and advanced in some areas.
- Ukrainian forces also continued counteroffensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Recent Russian claims that small contingents of former Wagner Group personnel are returning to fight in Ukraine do not indicate that a fully reconstituted Wagner fighting force will return to Ukraine anytime soon if ever.
- Russian occupation administrations continue to forcibly deport Ukrainian children to Russia and erase Ukrainian cultural identity.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 16, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in the Bakhmut direction on September 16 and continued to make gains in the area. Geolocated footage posted on September 15 confirms that Ukrainian forces have advanced south of Rozdolivka (about 13km northeast of Bakhmut) and in northern Klishchiivka (about 6km southwest of Bakhmut).[1] Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar noted that fighting is ongoing near Klishchiivka and Kurdyumivka (12km southwest of Bakhmut) and stated that Ukrainian forces continue to be successful in the Klishchiivka area.[2] Ukrainian Ground Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrsky posted footage of Ukrainian personnel in Andriivka (8km southwest of Bakhmut) following the Ukrainian liberation of the settlement on September 14.[3]
Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast have likely forced the Russian command to prioritize the Russian defense there and laterally redeploy elements of a relatively elite formation away from the Russian defense south of Bakhmut. North Ossetian volunteer battalions “Storm Ossetia” and “Alania,” which are operating in western Zaporizhia Oblast, posted an image on September 16 purporting to show a small detachment of the Russian 83rd Separate Guards Air Assault (VDV) Brigade in Nesteryanka (on the western shoulder of the current Ukrainian breach in western Zaporizhia Oblast).[4] Elements of the 83rd Brigade deployed to defend against Ukrainian counteroffensive operations around Klishchiivka in late June and were observed in combat in the area in late August.[5] Elements of the 83rd Brigade were reportedly still operating in the Bakhmut area as of September 11, although elements of the brigade may have been split across two different sectors of the front.[6] Klishchiivka has been a focal point of fighting in the Bakhmut area in recent weeks, and the redeployment of any elements of the 83rd VDV Brigade amid Ukrainian advances near Klishchiivka suggests a deep concern about Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast and the Russian prioritization of the defense there.
ISW has previously assessed that Ukrainian counteroffensive operations along several lines of effort would force the Russian command to prioritize certain sectors of the front and conduct lateral redeployments that offer Ukraine opportunities for exploitation.[7] Ukrainian counteroffensive operations have fixed relatively elite units and formations to the area, including elements of the 98th VDV Division, the 83rd VDV Brigade, the 11th VDV Brigade, the 31st VDV Brigade, the 106th VDV Division, and the 364th Spetsnaz Brigade (Russian General Staff Main Directorate).[8] Russian forces have thus far been unwilling to send these relatively elite formations to aid in the critical defensive effort in western Zaporizhia Oblast, and Ukrainian operations around Bakhmut appear to continue preventing the Russian command from doing so at scale. ISW will publish a review of the strategic significance of how Ukrainian operations have fixed Russian forces to the Bakhmut area in an upcoming special edition.
Ukrainian forces also advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 16 and continued to penetrate the Russian defensive layer that lies ahead of the current extent of Ukrainian advances. Geolocated footage published on September 16 indicates that Ukrainian forces advanced along Russian defensive positions to the west of Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv).[9] Additional geolocated footage published on September 15 indicates that Ukrainian infantry advanced further along a series of Russian defensive positions immediately west of Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv) but likely did not maintain control of these positions.[10] The Ukrainian presence at these Russian defensive positions indicates that Russian forces do not control these positions either and that Ukrainian forces are continuing to operate past the Russian defensive layer that that runs northwest of Verbove to north of Solodka Balka (20km south of Orikhiv).
Ukrainian forces have likely made a significant tactical breach along a section of the current Russian defense layer in the Robotyne area over the past several weeks that they continue to widen. Ukrainian forces have continued offensive operations past a section of the Russian defensive layer west of Verbove since penetrating it on September 4 and have widened their breach along a 2.6km section of those Russian defensive positions.[11] The continued absence of observed Ukrainian heavy equipment and vehicles past this defensive layer continues to indicate that Ukrainian forces have yet to complete a breakthrough of this defensive layer, however.[12] Ukrainian officials have indicated that the series of Russian defensive positions currently ahead of the Ukrainian advance may be less challenging than the initial Russian defensive layer that Ukrainian forces broke through to the north.[13] Russian forces had concentrated the majority of their combat power at those forward-most Russian defensive positions to defend against Ukrainian counteroffensive operations, and these Russian forces have likely suffered heavy losses and conducted fighting withdrawals to prepared positions behind the current defensive layer.[14] ISW has long assessed that Russian forces lack the manpower to man the entire multi-echeloned Russian defensive fortification systems in southern Ukraine, and the Russian forces defending the current layer of defense are likely elements of formations that have been fighting in the area without operational-level unit rotation since the start of the counteroffensive or elements of formations that laterally transferred from elsewhere along the front.[15]
Russian ultranationalists continued to complain about endemic lying within the Russian military after Russian State Duma Deputy and former Deputy Commander of the Southern Military District (SMD) Lieutenant General Andrei Gurulev voiced similar complaints on September 15. A Russian milblogger posted a statement reportedly from a subscriber on September 16 that concurred with Gurulev’s assertion that the culture of lying in the Russian military is the main issue preventing a Russian victory in Ukraine.[16] Another Russian milblogger stated that the issue is a “disaster” and that lies occur at all levels of the Russian military as subordinate commanders are afraid to report the truth about the condition and needs of units and formations.[17] The milblogger stated the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and Russian President Vladimir Putin are likely receiving false reports. The milblogger added that tyranny (bad command culture), fraud, and a lack of military resourcefulness are some of the issues affecting the Russian military in Ukraine and that the main goal of the Russian military should be to minimize personnel losses. A Russian insider source compared Gurulev to deceased Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin in his role as the “front line truth teller.”[18]
A Ukrainian naval drone strike likely damaged a Russian ship in the Black Sea on September 14. Ukrainian newspaper Ukrainska Pravda published a photo reportedly from a source within the Ukrainian Security Service (SBU) that indicates that Ukrainian naval drones struck and damaged a Russian Bora-class corvette near the entrance to Sevastopol Bay in occupied Crimea on September 14.[19] Ukrainian Digital Transformation Minister Mykhailo Fedorov stated on September 16 that Ukraine will conduct more drone attacks on Russian ships in the future.[20] Ukrainian Southern Operational Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk stated that Russian ships do not stay at their bases but are constantly moving between naval bases in Russia and occupied Crimea to avoid strikes against them.[21] Russian forces have previously used large ships in the Black Sea to mitigate the damage that Ukrainian strikes have inflicted on other Russian ground lines of communication (GLOCs) in southern Ukraine, and Ukrainian forces are likely targeting Russian ships in the Black Sea to further damage Russia’s ability to mitigate ongoing logistics complications among other things.[22]
A Ukrainian official confirmed on September 16 that a civilian vessel used the Ukrainian corridor in the Black Sea to reach a Ukrainian port for the first time. Ukrainian Minister for Communities, Territories, and Infrastructure Oleksandr Kubrakov announced that civilian bulk carriers flying the Palau flag used the existing Ukrainian corridor to sail towards Chornomorsk, where the vessels will load over 20,000 tons of grain for export to countries in Africa and Asia.[23] The Kremlin previously escalated its posturing in the Black Sea to curtail maritime traffic to Ukraine and increase its leverage to extract maximalist concessions to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative.[24] United Kingdom military aircraft are reportedly conducting patrols over the Black Sea to deter Russian forces from acting aggressively towards civilian vessels.[25] Kubrakov stated that five civilian vessels have traveled from Ukraine along the Ukrainian Black Sea corridor since August 15: Joseph Schulte, Primus, Anna-Theresa, Ocean Courtesy, and Puma.[26]
Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu and North Korean leader Kim Jong Un met in Vladivostok, where Kim viewed pieces of Russian weapons technology on September 16. Kim viewed Tu-22MS, Tu-95MS, and Tu-160 strategic bombers; Su25SM3, Su-30SM, and Su-34 fighter-bombers; a MiG-31I missile carrier with Kinzhal missiles; the frigate Marshal Shaposhnikov; a Uranus anti-ship missile system; and Kalibr cruise missiles.[27] Russian Aerospace Forces (VKS) Commander Lieutenant General Sergey Kobylash told Kim that the Tu-160 strategic bombers received new Kh-BD cruise missiles with a claimed range of over 6,500 kilometers and can carry 12 such missiles.[28] Russia is highly unlikely to provide physical systems or weapons to North Korea due to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s likely concern that this provision may trigger secondary sanctions against Russia, but Putin may be open to other forms of technological and defensive cooperation with North Korea in return for North Korean artillery ammunition.[29]
The Russian military leadership may be removing ineffective air defense officials on the pretext of corruption charges to avoid admitting the failures of Russian air defenses against increasing drone strikes on Russian cities including Moscow. Russian outlet Kommersant reported on September 16 that the Tula Oblast Venesky District Court sentenced Vladislav Gukov, former head of the MoD Department of State Defense Procurement, to a nine-year prison term for corruption.[30] Kommersant noted that the investigation found that Gukov accepted over 15 million rubles ($154,950) in bribes from various enterprises that were meant to supply the MoD with “urgently needed” X-ray diagnostic systems for KamAZ vehicles.[31] A Russian insider source alleged that Gukov was a close personal friend of Major General Vyacheslav Lobuzko, former commander of a division of the 3rd Separate Air Defense Army and one of the designers of the “Voronezh” cruise and ballistic missile detection system, whom Russian authorities also imprisoned for corruption in May.[32] The insider source additionally claimed that Gukov was personally responsible for signing off on the procurement of air defense systems and complexes.[33]
Gukov’s corruption charge and his role as a prominent Russian air defense official closely mirror the case of the commander of the Moscow-based 1st Special Purpose Air and Missile Defense, Army Major General Konstantin Ogienko, whom Moscow Oblast authorities arrested on similar corruption and bribery charges relating to giving state defense property to an unnamed civilian organization.[34] ISW has no reason to doubt that these air defense officials are complicit in corruption and bribery schemes, but the recent trend of arrests of prominent air defense officials on corruption charges may suggest that higher echelons of the Russian military wish to remove these air defense officials from their positions without having to admit that the Russian domestic air defense system is failing.[35]
Russian military officials continue efforts to solidify Russia’s relationship with African states amidst changing dynamics on the continent resulting from the Russian MoD’s efforts to subsume the Wagner Group. Russian milbloggers and Malian national broadcaster ORTM reported that Russian Deputy Defense Minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov arrived in Bamako, Mali on September 16 and met with the Malian and Nigerien defense ministers and Malian junta head Assimi Goita.[36] Russian milbloggers speculated that Yevkurov and the Malian and Nigerien ministers discussed military-technical cooperation, the implications of the coup in Niger, and increased Russian MoD support for the Malian junta against Tuareg rebels in northern Mali.[37] One Russian source suggested that the MoD seeks to take over Wagner Group remnants in northern Mali, which is consistent with ISW’s previous observation that the Russian MoD has recently made efforts to assume control of Wagner’s operations on the African continent.[38] Yevkurov notably visited multiple African countries including Burkina Faso, Libya, and Syria in early September to replace “private military companies” with MoD elements.[39] The Ukrainian Resistance Center relatedly reported on September 16 that the Russian MoD is increasingly sending representatives to Algeria, Mali, and Sudan to convince remaining Wagner fighters to sign contracts with a structure affiliated with and supervised by the MoD.[40]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in the Bakhmut direction on September 16 and continued to make gains in the area.
- Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast have likely forced the Russian command to prioritize the Russian defense there and laterally redeploy elements of a relatively elite formation away from the Russian defense south of Bakhmut.
- Ukrainian forces also advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 16 and continued to penetrate the Russian defensive layer that lies ahead of the current extent of Ukrainian advances.
- Ukrainian forces have likely made a significant tactical breach along a section of the current Russian defense layer in the Robotyne area over the past several weeks that they continue to widen.
- Russian ultranationalists continued to complain about endemic lying within the Russian military after Russian State Duma Deputy and former Deputy Commander of the Southern Military District (SMD) Lieutenant General Andrei Gurulev voiced similar complaints on September 15.
- A Ukrainian naval drone strike likely damaged a Russian ship in the Black Sea on September 14.
- A Ukrainian official confirmed on September 16 that a civilian vessel used the Ukrainian corridor in the Black Sea to reach a Ukrainian port for the first time.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu and North Korean leader Kim Jong Un met in Vladivostok, where Kim viewed pieces of Russian weapons technology on September 16.
- The Russian military leadership may be removing ineffective air defense officials on the pretext of corruption charges to avoid admitting the failures of Russian air defenses against increasing drone strikes on Russian cities including Moscow.
- Russian military officials continue efforts to solidify Russia’s relationship with African states amidst changing dynamics on the continent resulting from the Russian Ministry of Defense’s (MoD) efforts to subsume the Wagner Group.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia on September 16 and advanced in some areas.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in at least two sectors of the front on September 16 and advanced near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Russian milbloggers continue complaining about the role of the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) in perpetuating issues affecting Russian military personnel.
- Russian occupation officials continue efforts to resettle residential areas of occupied Ukraine with Russians.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 15, 2023
Ukrainian forces liberated Andriivka in the Bakhmut area on September 14 and continued offensive operations near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 15. The Ukrainian General Staff and other Ukrainian officials reported that Ukrainian forces liberated Andriivka on September 14 and achieved unspecified partial success near Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut) on September 15.[i] The Ukrainian 3rd Separate Assault Brigade reported that its personnel liberated Andriivka and “completely destroyed“ the Russian 72nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (3rd Army Corps) after encircling the settlement.[ii] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and are inflicting significant losses on Russian manpower and equipment near Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv).[iii]
Russian State Duma Deputy and former Deputy Commander of the Southern Military District (SMD) Lieutenant General Andrei Gurulev complained about lying within the Russian military and highlighted the effectiveness of Ukrainian air defenses against Russian helicopters. Gurulev published a Telegram message on September 15 largely reiterating known Russian challenges, though with several notable points. Gurulev complained that the culture of lying in the Russian military is the main issue preventing a Russian victory in Ukraine and claimed that false reports are leading to poor decision-making at many levels within the Russian military.[iv] Gurulev also stated that Ukrainian air defenses at the front are effective against Russian helicopters and are preventing Russian helicopters from using previously highly effective anti-tank missiles, and he reiterated common complaints about Ukraine’s ability to conduct drone strikes on Russian rear areas and insufficient Russian counterbattery capabilities.[v] Gurulev is notable for having previously leaked the audio message of former Commander of the 58th Combined Arms Army (SMD) Major General Ivan Popov’s grievances over the lack of support for Russian forces on July 12, and Gurulev‘s likely senior ties with the SMD lend weight to his complaints.[vi]
Ukrainian forces conducted naval drone strikes on Russian ships in the Black Sea on September 14.[vii] Ukrainian Stategic Command reported that Ukrainian forces caused unspecified damaged to two Russian “Vasily Bykov” Project 22160-class patrol ships in the southwestern Black Sea on September 14.[viii] The Russian MoD claimed that Russian Black Sea Fleet forces destroyed two Ukrainian naval drones in this area.[ix] Ukrainian newspaper Ukrainskaya Pravda reported that sources in the Ukrainian Security Service (SBU) stated that a Ukrainian naval drone significantly damaged a Russian Bora-class corvette near the entrance to Sevastopol Bay on September 14 but the Russian MoD claimed that Russian Black Sea Fleet forces destroyed a Ukrainian naval drone and repelled the attack.[x] A Russian source claimed that the corvette was not visibly damaged.[xi]
Russian forces conducted another series of Shahed-131/-136 drone strikes targeting Ukrainian rear areas on September 15. Ukrainian officials reported that Russian forces launched 17 drones from Krasnodar Krai in the direction of Khmelnytskyi Oblast and that Ukrainian air defenses shot down all 17 drones.[xii] Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Yuriy Ihnat stated that the Russian strike targeted Ukrainian aircraft.[xiii]
Russian State Duma Defense Committee Chairman Andrei Kartapolov explicitly stated that mobilized personnel will only demobilize at the end of Russia’s “special military operation.”[xiv] Kartapolov added that Russian mobilized personnel will not receive rotations, but that they are entitled to leave every six months.[xv] Kartapolov’s explicit commentary is likely meant to dissuade Russian legislators from considering a proposed amendment that would establish terms for demobilizing personnel mobilized in autumn 2022.[xvi] The Kremlin continues to resist formally rescinding the partial mobilization decree in order to legally justify the continued service of mobilized personnel for an indefinite period of time.[xvii]
Russian President Vladimir Putin and Belarusian President Aleksander Lukashenko reiterated standing claims about negotiations and perceived grievances against the West during a meeting in Sochi on September 15. Putin and Lukashenko reportedly also discussed economic issues, Kim Jong Un’s visit to Russia, and Russian force generation efforts.[xviii] Putin and Lukashenko reiterated boilerplate rhetoric accusing the West of manipulating Ukraine. Putin claimed that 300,000 people have signed military service contracts with the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) - presumably within the past six to seven months, updating a figure given by Putin on September 12.[xix]
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) continues efforts to assume control over the Wagner Group’s operations in North Africa and may have assigned former commander of the Aerospace Forces (VKS) Sergei Surovikin to this task. Russian sources posted pictures of Army General Sergei Surovikin, the previously dismissed Wagner-affiliated former VKS commander, in Algeria on September 15.[xx] Russian state news outlet Kommersant reported that a source close to Surovikin stated that the trip may be connected to Surovikin’s possible appointment to oversee unspecified operations in Africa.[xxi] Russian milbloggers claimed that Surovikin’s new formal position as Head of the Coordination Committee on Air Defense Issues under the Council of Defense Ministers of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is purely nominal and speculated that Surovikin may take over Wagner assets and operations in the region.[xxii] Surovikin may be involved in Russian efforts to subsume Wagner operations due to his affiliation with Wagner and his command experience, although it is unclear if the Russian MoD intends for Surovikin to assume direct command of these efforts. Russian Deputy Defense Minister Colonel-General Yunus-Bek Yevkurov and elements of the Main Directorate (GRU) of the General Staff have also been reportedly heavily involved in efforts to subsume Wagner’s operations in the Middle East and Africa.[xxiii] The Wall Street Journal reported that Russian officials, including Yevkurov, met with Khalifa Haftar, commander of the Tobruk-based Libyan National Army, in recent weeks to request access to ports in Benghazi or Tobruk for Russian warships.[xxiv] Yevkurov reportedly visited Libya several times in the past months to replace “private military companies” (PMCs) with Russian MoD-controlled formations.[xxv] The Kremlin may be attempting to revive a longstanding campaign to secure access to a Mediterranean port in Libya in parallel with the effort to subsume Wagner’s operations in Libya.
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces liberated Andriivka in the Bakhmut area on September 14 and continued offensive operations near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 15.
- Russian State Duma Deputy and former Deputy Commander of the Southern Military District (SMD) Lieutenant General Andrei Gurulev complained about lying within the Russian military and highlighted the effectiveness of Ukrainian air defenses against Russian helicopters.
- Ukrainian forces conducted naval drone strikes on Russian ships in the Black Sea on September 14.
- Russian forces conducted another series of Shahed-131/-136 drone strikes targeting Ukrainian rear areas on September 15.
- Russian State Duma Defense Committee Chairman Andrei Kartapolov explicitly stated that mobilized personnel will only demobilize at the end of Russia’s “special military operation.”
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) continues efforts to assume control over the Wagner Group’s operations in North Africa and may have assigned former commander of the Aerospace Forces (VKS) Sergei Surovikin to this task.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 15.
- Russian occupation authorities continue efforts to strengthen ground lines of communication (GLOCs) connecting occupied southern Ukraine to Russia and occupied Crimea.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 14, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and around Bakhmut and reportedly advanced south of Bakhmut on September 14. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces achieved unspecified partial successes near Bakhmut, Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut), Andriivka (10km southwest of Bakhmut), and Kurdyumivka (13km southwest of Bakhmut). Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar prematurely announced the Ukrainian liberation of Andriivka but later clarified that heavy fighting for the settlement is still ongoing. Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Ilya Yevlash stated on September 13 that Ukrainian forces pushed Russian forces out of positions near Minkivka (15km northwest of Bakhmut) and Dubovo-Vasylivka (6km northwest of Bakhmut). The Ukrainian General Staff and Malyar stated that Ukrainian forces continue to gradually advance in the Melitopol direction (western Zaporizhia Oblast).
Ukrainian forces struck a Russian air defense system near occupied Yevpatoria, Crimea, on September 14, suggesting that there may be systemic tactical failures with Russian air defense systems in occupied Crimea. The Department of Strategic Communications of the Ukrainian Armed Forces stated that Ukrainian forces struck the location of a Russian surface-to-air missile system near Yevpatoria (68km northwest of Sevastopol). Ukrainian news outlet Ukrainska Pravda reported that a source affiliated with the Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) stated that the SBU and the Ukrainian Navy conducted a “unique special operation” that destroyed a Russian S-400 “Triumf” system near Yevpatoria. Ukrainian forces reportedly struck the S-400 system’s radar and antennas with drones and struck the launch complexes with two Neptune cruise missiles. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) reported that Russian air defenses intercepted 11 Ukrainian drones over Crimea but did not mention any Ukrainian missile strikes. Geolocated footage published on September 14 shows an explosion near Yevpatoria and subsequent smoke plumes in the area. Additional geolocated footage shows that Russian forces had recently deployed an S-400 battery outside of Yevpatoria and that the explosion occurred in the same location where a Russian S-400 system had been deployed in August 2022. The strike suggests that Russian forces were unprepared to intercept missiles with the system or were unable to do so. Ukrainian forces struck a Russian S-400 air defense system near Olenivka, Crimea (117km northwest of Sevastopol) on August 23, and the second Ukrainian strike on a significant Russian air defense system in recent weeks indicates that such tactical failures may reflect a wider systemic issue with Russian air defenses in occupied Crimea.
Russian forces conducted another series of Shahed-131/136 drone strikes targeting Ukrainian port infrastructure on September 14. The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Russian forces launched 22 drones in the direction of Mykolaiv, Zaporizhia, Dnipropetrovsk, and Sumy oblasts and that Ukrainian air defenses shot down 17 of the drones. Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Colonel Yuriy Ihnat stated that Russian forces primarily targeted port infrastructure in Odesa Oblast. Ukrainian Minister for Communities, Territories, and Infrastructure Development Oleksandr Kubrakov stated that Russian strikes from July 18 to September 12 have damaged or partially destroyed 105 Ukrainian port facilities and that the monthly export of Ukrainian grain has decreased by almost three million tons as a result. The Russian strike campaign against Ukrainian grain and port infrastructure is likely meant to support the Kremlin’s effort to leverage international desire for Russia’s return to the Black Sea Grain Initiative to exact extensive concessions. The Kremlin may have no intention of returning to the deal, however, and may instead aim to increase the market share and attractiveness of Russian grain by degrading Ukraine’s grain export potential. The Kremlin also likely intends for continued strain on Ukrainian grain export routes to intensify divisions between Ukraine and its Central European partners as Ukraine and the West continue to work on re-routing Ukrainian grain exports along land corridors.
The commander of the Russian 247th Guards Air Assault (VDV) Regiment (7th VDV Division) Vasily Popov was reportedly killed in combat in Ukraine. Vasily Popov likely recently replaced Pyotr Popov as commander of the 247th VDV Regiment in August or September 2023, and Vasily Popov is the second commander of the 247th Regiment to be killed in action in Ukraine after Colonel Konstantin Zizevsky died in February 2022. Elements of the 247th Regiment are reportedly operating in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area. ISW has previously assessed that relatively elite VDV forces are conducting limited counterattacks in critical sectors of the front, and Vasily Popov’s death supports ISW’s assessment that these counterattacks will likely attrit these units further.
The European Parliament adopted a resolution on September 13 recognizing Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko as complicit in Russian crimes committed in Ukraine and called on the International Criminal Court (ICC) to issue an arrest warrant for him. The European Parliament’s resolution stated that Belarus is complicit in the war in Ukraine and is involved in the deportation of Ukrainian children to Belarus, Russia, and occupied areas of Ukraine. ISW continues to assess that Belarus is a co-belligerent in the war and is involved in the deportation of Ukrainian children. ISW has also assessed that Belarus may be facilitating sanctions evasion schemes for Russia. Russian President Vladimir Putin and Lukashenko will meet in Sochi, Russia on September 15.
Russian State Duma and Federation Council members proposed blocking WhatsApp likely as part of the Kremlin’s broader initiative to establish central control over the Russian information space. Facebook’s parent company Meta announced on September 13 that WhatsApp launched a channel feature to over 150 countries, likely including Russia, that will function similarly to Telegram channels. Russia designated Meta as an extremist organization in March 2022 and banned its Facebook and Instagram services in Russia. Federation Council Committee on Defense and Security Head Viktor Bondarev, State Duma Committee on Information Policy Head Alexander Khinshtein, and State Duma Deputy Anton Gorelkin said that Russia should consider blocking WhatsApp in Russia if WhatsApp launches Russian language channels. Russian state media censor Roskomnadzor reported that Russia could block WhatsApp if it disseminates prohibited information. Russian authorities are likely attempting to funnel the Russian information space onto a limited number of closely monitored or controlled social media platforms.
Some Russian sources suggested that ongoing tensions between the Russian MoD and the Wagner Group are diminishing Wagner’s ability to operate across the African theater. A Russian insider source claimed on September 12 that “difficult logistics” are forcing Wagner forces in Africa to “make do with local reserves” to continue operations after the rebel coalition Coordination of the Movement of Azawad (CMA) claimed to have captured Bourem, Gao Region, Mali. Russian sources, including a prominent Kremlin-affiliated milblogger, claimed that the Russian MoD and Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) deliberately disrupted Wagner's logistics by preventing Wagner from using Russian airbases in Syria to reinforce the Wagner contingent in the Central African Republic (CAR) — reports consistent with ISW’s recent observations. The milblogger claimed that the CMA took advantage of destabilization fueled in part by tensions resulting from the MoD’s ongoing effort to subsume Wagner. The milblogger warned that other armed groups may also take advantage of the destabilization and that the MoD will have to invest resources in the region to avoid reputational fallout. Wagner forces in Africa notably conduct counterterrorism operations, but these operations are often ineffective, and the current Wagner group contingent in MENA is likely insufficient to conduct counterterrorism operations at a scale that could meaningfully contain new or escalating conflicts.
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) declared two US diplomats persona non grata and expelled them from Russia on September 14. The Russian MFA accused the US Embassy’s first and second secretaries of illegally maintaining contact with an arrested former US Consulate employee and ordered the diplomats to leave Russia within the next seven days.
Western defense sources reportedly stated that a Russian fighter jet intentionally fired at a British surveillance plane in September 2022 due to ambiguous commands rather than because of a missile malfunction as the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed at the time. The BBC reported that three senior Western defense sources stated that a Russian Su-27 fighter jet pilot intentionally fired a missile at a British Royal Air Force (RAF) plane but missed on September 29, 2022. The Western defense sources reportedly stated that the Russian pilot believed he had permission to fire after receiving an ambiguous command from a Russian ground station and fired a second missile, which reportedly either malfunctioned or was aborted. A second Russian pilot flying another Su-27 reportedly interpreted the order differently and did not fire at the British aircraft. The Russian MoD claimed in October 2022 that the Su-27 jet fired the missile due to a “technical malfunction.”
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and around Bakhmut and reportedly advanced south of Bakhmut on September 14.
- Ukrainian forces struck a Russian air defense system near occupied Yevpatoria, Crimea, on September 14, suggesting that there may be systemic tactical failures with Russian air defense systems in occupied Crimea.
- Russian forces conducted another series of Shahed-131/136 drone strikes targeting Ukrainian port infrastructure on September 14.
- The commander of the Russian 247th Guards Air Assault (VDV) Regiment (7th VDV Division) Vasily Popov was reportedly killed in combat in Ukraine.
- Some Russian sources suggested that ongoing tensions between the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and the Wagner Group are diminishing Wagner’s ability to operate across the African theater.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 14.
- Ukrainian forces also advanced along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- The Kremlin is reportedly trying to censor Russian media coverage of a possible second wave of reserve mobilization in order to prevent protests and voter discontent ahead of the 2024 Russian presidential elections.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 13, 2023
Ukrainian forces conducted missile strikes on occupied Sevastopol, Crimea, on September 13, damaging a Russian landing ship, a Kilo class submarine, and port infrastructure. The Department of Strategic Communications of the Ukrainian Armed Forces stated that Ukrainian forces successfully conducted missile strikes on Russian naval means and port infrastructure in occupied Sevastopol.[1] Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Spokesperson Andriy Yusov stated that the missiles struck the Russian state-owned ship repair facility Sevmorzavod, damaging repair facilities as well as a landing ship and a submarine, both of which he described as unrecoverable.[2] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian air defenses intercepted seven out of 10 Ukrainian cruise missiles targeting the Sevmorzavod ship repair facility but acknowledged that Ukrainian missiles struck two ships under repair.[3] Geolocated footage published on September 13 shows explosions at the dry dock in the Sevastopol port.[4] Satellite imagery published on September 12 shows one Ropucha class landing ship and one Kilo class submarine at the dry dock, and satellite imagery published on September 13 shows that the Ukrainian missile strike likely destroyed the two vessels.[5] Ukrainian Southern Operational Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk stated that there were no Russian missile carriers present during the strike but noted that Ukrainian intelligence is still unaware of which submarine was at the dry dock.[6] The apparent destruction of the two vessels will likely render the dry dock inoperable until Russian forces can clear the debris, which may take a significant amount of time. The extent of the damage to Sevmorzavod’s repair facilities beyond the dry dock is unclear, and any damage to one of the Russian Black Sea Fleet’s main repair facilities in occupied Crimea will likely have reverberating impacts in the event of further Ukrainian strikes on Russian naval assets.
Russian officials largely did not address the strike, while select Russian ultranationalists responded with predictable outrage. Crimean occupation officials claimed that the strikes damaged residential buildings and injured several dozen people, although they did not say whether the injured were Russian military personnel.[7] Prominent Kremlin propagandist Vladimir Solovyov expressed deep anger at the strike and called for retaliatory strikes on Western facilities that produced the alleged missiles that Ukraine used in the strike.[8] Solovyov’s call for escalation with the West is boilerplate rhetoric for his domestic audience but is not reflective of any actual Kremlin position on the matter. Russian milbloggers expressed concerns that the Ukrainian strike portends an intensification of Ukraine’s interdiction campaign targeting occupied Crimea.[9] One milblogger argued that Russian forces are unable to strike Ukrainian airfields at scale and that Russian military inaction allowed Ukrainian forces to sufficiently strengthen airfields against Russian strikes.[10]
Ukrainian forces advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly advanced near Bakhmut amid continued counteroffensive operations on both sectors of the front on September 13. Geolocated footage published on September 12 indicates that Ukrainian forces made limited gains south of Robotyne (12km south of Orikhiv) in western Zaporizhia Oblast.[11] The Ukrainian General Staff reported on September 13 that Ukrainian forces achieved unspecified partial successes near Robotyne as well as near Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut), Andriivka (10km southwest of Bakhmut), and Kurdyumivka (13km southwest of Bakhmut) in the Bakhmut direction.[12]
Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/136 drone strikes targeting Sumy and Odesa oblasts on the night of September 12 to 13. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian air defenses destroyed 34 of 45 Shaheds, which mainly targeted port infrastructure in Izmail and Reni, Odesa Oblast.[13] Odesa Oblast Administration Head Oleh Kiper reported that the drone strikes damaged the port and civilian infrastructure in Izmail Raion.[14] The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Russian forces launched the drones from occupied Cape Chauda in Crimea, Primorsko-Akhtarsk in Krasnodar Krai, and Kursk Oblast.[15]
Russian President Vladimir Putin is likely concerned that Russia’s growing relationship with North Korea may endanger Russia’s existing sanctions evasion schemes. Putin met with North Korean dictator Kim Jong Un at the Vostochny Cosmodrome in Amur Oblast on September 14.[16] Putin called the meeting “productive” and reported that he and Kim had a “frank exchange of views on the situation in the region and on bilateral relations.”[17] Putin also stated that Russia continues to comply with restrictions on military-technical cooperation with North Korea but noted that within the “framework of the current rules, there are opportunities.”[18] Putin is likely neutrally portraying his meeting with Kim in order to balance Russia’s interest in acquiring North Korean artillery munitions with concerns about the risk of triggering secondary international sanctions on Russia due to potential trade with North Korea amidst increased international scrutiny of Russian sanctions evasion.
The Russian MoD reportedly temporarily disrupted a Wagner Group force rotation to Syria amid reports of the Russian MoD’s ongoing efforts to subsume Wagner operations in Syria. A prominent Kremlin-affiliated milblogger amplified a claim on September 13 that the Russian MoD blocked Wagner forces from rotating personnel from Africa through the Hmeimim airbase in Latakia, Syria, prompting the Wagner forces to negotiate with the Syrian MoD to rotate through the Tiyas airbase in Homs Governorate instead.[19] The milblogger claimed that the Russian MoD used vehicles on the runway to prevent a Wagner plane from landing at the Tiyas airbase on September 12, and then deployed helicopters threatening to shoot down a Wagner plane. The milblogger claimed that the Wagner leadership in Syria contacted Russian Deputy Defense Minister Colonel General Yunus-Bek Yevkurov who allowed the plane to land.[20] Yevkurov’s reported involvement in this engagement as well as his recent trips to Africa continues to suggest that Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu has likely appointed Yevkurov to oversee the MoD‘s effort to subsume the remnants of the Wagner Group.[21]
This reported Russian MoD-Wagner conflict in Syria suggests that elements of the Wagner Group may still have a cohesive leadership and that the MoD has deep concerns about the semi-independence of Wagner’s Syria contingent. Wagner’s ability to negotiate with senior Russian and Syrian MoD officials indicates that Wagner likely retains a cohesive-enough leadership to operate semi-independently of the Russian MoD. The Russian MoD’s decision to deny Wagner’s use of the Hmeimim airbase and disrupt the force rotation indicates that the MoD is likely concerned about Wagner’s insubordination toward the Russian military in Syria, though the precise concerns are unclear. The Wagner contingent in Syria may have better combat capabilities than Wagner contingents in other African states due to some combination of training, provisions, and organization. The MoD may also be concerned that the Syria Wagner contingent is more loyal to Prigozhin than the other Wagner arms. Syria is the only country in which the Wagner Group has a major contingent co-located with a major Russian MoD presence, and the Russian MoD detained Wagner commanders only in Syria and not elsewhere abroad following the June 24 rebellion.[22]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces conducted missile strikes on occupied Sevastopol, Crimea, on September 13, damaging a Russian landing ship, a Kilo class submarine, and port infrastructure.
- Ukrainian forces advanced in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly advanced near Bakhmut amid continued counteroffensive operations on both sectors of the front on September 13.
- Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/136 drone strikes targeting Sumy and Odesa oblasts on the night of September 12 to 13.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin is likely concerned that Russia’s growing relationship with North Korea may endanger Russia’s existing sanctions evasion schemes.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) reportedly temporarily disrupted a Wagner Group force rotation to Syria amid reports of the Russian MoD’s ongoing efforts to subsume Wagner operations in Syria.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not make any confirmed advances.
- Reports from Western and Russian independent sources indicate that Russia has circumvented some Western sanctions to increase weapons production but still struggles to produce weapons at the pace required by the war in Ukraine.
- The Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) published footage showing GUR and Ukrainian partisans conducting a drone strike on a Russian occupation passportization office in occupied Enerhodar, Zaporizhia Oblast on September 12.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 12, 2023
Russian insider sources claimed that the Kremlin’s inner circle is again actively disagreeing about the necessity of and preparations for a second wave of reserve mobilization ahead of the semi-annual fall conscription cycle, which starts on October 1. A Russian Telegram channel with alleged connections to Russian security sources claimed that select Russian officials are “seriously” preparing for a second wave of reserve mobilization and are hoping to conduct another reserve mobilization wave in the fall.[1] It is important to distinguish between Russia’s normal semi-annual conscription callup, a large-scale reserve mobilization like the one that brought more than 300,000 reservists into the Russian armed forces in Fall 2022, crypto-mobilizations that bring reservists into the force at lower numbers over a long period of time, and various efforts to encourage or coerce Russians to sign ostensibly voluntary contracts with the Russian military. The channel claimed that Russian officials want to mobilize between 170,000 to 175,000 reservists and move the fall conscription date from October 1 to November 1 to accommodate a reserve mobilization processes, while simultaneously conducting “contract mobilization” to recruit an additional 130,000 personnel for contract service using coercive measures.[2] The channel claimed that a powerful group of “siloviki hawks” is also proposing stricter reserve mobilization measures such as restricting certain individuals from obtaining mobilization deferrals, which has sparked major disagreements with officials in the Russian Presidential Administration. The channel claimed that the Presidential Administration fears a response to such measures from other Russian officials and broader Russian society.
These plans, proposals, and disagreements are not new and do not indicate that Russian President Vladimir Putin has ultimately decided to conduct a second reserve mobilization wave in the near term. ISW previously observed an increase in discussions about reserve mobilization preparations and speculations in the lead-up to the spring conscription cycle earlier in 2023.[3] Select Russian officials have also proposed more dramatic mobilization measures that have not materialized.[4] Putin also emphasized Russian contract service recruitment rates when responding to the question about the potential second reserve mobilization wave at the Eastern Economic Forum on September 12.[5] Putin’s response does not necessarily set information conditions to prepare Russian society for involuntary mobilization and instead may suggest his commitment to ongoing crypto mobilization practices. Any new reserve mobilization wave depends on Putin.[6]
Putin also reamplified several boilerplate information operations falsely framing the Ukrainian counteroffensive as a failed endeavor and accused Ukraine of being unwilling to negotiate during his address at the Eastern Economic Forum. Putin claimed that the Ukrainian counteroffensive has failed to produce concrete results and presented likely very inflated numbers of claimed Ukrainian personnel and equipment losses.[7] Putin also accused Ukraine of being unwilling to negotiate and claimed that Russia cannot pursue an end to hostilities as long as Ukraine is pursuing a counteroffensive, thereby furthering a longstanding Russian information operation that seeks to accuse Ukraine as being the party disinterested in negotiations in order to undermine Ukrainian battlefield successes and reduce international support for Ukraine, as ISW has previously reported.[8]
Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in Donetsk and Zaporizhia oblasts on September 12 and have reportedly advanced south of Bakhmut and Robotyne. Ukrainian military sources stated that Ukrainian forces are conducting active offensive operations near Klishchiivka (6km southwest of Bakhmut).[9] The Ukrainian General Staff also stated that Ukrainian forces were additionally successful south and southeast of Robotyne (about 13km south of Orikhiv).[10] Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Oleksandr Shtupun clarified that Ukrainian forces have advanced between 300-500 meters south and southeast of Robotyne.[11] The Ukrainian Military Media Center noted that Russian forces are increasingly pulling reserves from deep within Russian territory to the frontline in Ukraine out of fear of a Ukrainian breakthrough.[12]
North Korean leader Kim Jong Un arrived in Primorsky Krai on September 12 and will meet with Putin in the coming days, likely to discuss the provision of North Korean artillery munitions to Russia. Kim met with Russian Minister of Natural Resources and Ecology Alexander Kozlov and Primorsky Krai Governor Oleg Kozhemyako upon arriving in Russia.[13] Kim’s trip to Russia is his first known trip outside of North Korea since the COVID-19 pandemic.[14] ISW will continue to follow developments in the lead-up to the meeting and will report on the content of the meeting once it becomes available.
Russian authorities have reportedly adjusted air defense systems around Moscow in light of recent increased drone strikes on the city, likely in part to assuage complaints in the Russian information space about the ineffectiveness of air defenses around the capital. The United Kingdom Ministry of Defense (UK MoD) stated that Russian authorities have moved short and medium-range air defense systems, including Pantsir-S1 systems, to elevated positions around Moscow City to target drones.[15] The UK MoD noted that these adjustments are also likely meant to visibly demonstrate to the population that Russian authorities are taking steps to combat increasingly frequent drone strikes in the Russian rear, particularly in Moscow Oblast.[16] ISW has previously reported that Russian sources have complained about Moscow air defenses’ inability to stop such drone strikes, with some blaming Moscow Mayor Sergei Sobyanin and his administration directly.[17]
A car killed a Russian milblogger in occupied Donetsk City on September 11. Russian milblogger Gennady Dubovoy died after a car struck him as he crossed the road, and some other Russian milbloggers mourned Dubovoy’s death.[18] Dubovoy’s death comes amid an ongoing Kremlin and Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) campaign to censor Russian ultranationalist milbloggers whose narratives and complaints deviate too far from accepted official narratives.[19] Dubovoy has recently levied criticisms against the Russian government for its treatment of Russian combat veterans and former Wagner Group fighters, and recently stated that he took a step back from the ultranationalist information space due to demands to report on the “confirmation of your [referring to Russian officials] delusions.”[20] Dubovoy recently indicated that he is not a supporter of imprisoned ultranationalist and former Russian officer Igor Girkin, whose supporters have recently been the targets of official and public censorship.[21]
Key Takeaways:
- Russian insider sources claimed that the Kremlin’s inner circle is again actively disagreeing about the necessity of and preparations for a second wave of reserve mobilization ahead of the semi-annual fall conscription cycle, which starts on October 1.
- These plans, proposals, and disagreements are not new and do not indicate that Russian President Vladimir Putin has ultimately decided to conduct a second reserve mobilization wave in the near term.
- Putin also reamplified several boilerplate information operations falsely framing the Ukrainian counteroffensive as a failed endeavor and accused Ukraine of being unwilling to negotiate during his address at the Eastern Economic Forum.
- North Korean leader Kim Jong Un arrived in Primorsky Krai on September 12 and will meet with Putin in the coming days, likely to discuss the provision of North Korean artillery munitions to Russia.
- Russian authorities have reportedly adjusted air defense systems around Moscow in light of recent increased drone strikes on the city, likely in part to assuage complaints in the Russian information space about the ineffectiveness of air defenses around the capital.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia and advanced in some areas on September 12.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in at least two sectors of the front on September 12 and advanced near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Russian officials introduced a bill to the Russian State Duma that would punish Russian servicemen fighting within volunteer armed formations for losing or deliberately destroying military equipment or supplies.
- Russian occupation officials continue to deport children from occupied areas of Ukraine to Russia under the guise of recreational programs.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 11, 2023
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 10, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued to advance south of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly advanced near Bakhmut on September 10. Geolocated footage posted on September 10 shows that Ukrainian forces have advanced east of Novoprokopivka (18km southeast of Orikhiv).[i] Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Spokesperson Oleksandr Shtupun noted that Ukrainian forces continue to advance near Robotyne (12km south of Orikhiv) and have liberated 1.5 square kilometers of territory in this direction.[ii] The Ukrainian General Staff and Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Ilya Yevlash reported that Ukrainian forces achieved unspecified success near Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut) in Donetsk Oblast.[iii]
.[iv] Cold and wet weather will affect but not halt active combat, as it has done in the first 18 months of the war. Chairman of the US Joint Chiefs of Staff General Mark Milley stated on September 10 that Ukrainian forces probably have 30 to 45 days of “fighting weather” left.[v] Seasonal heavy rains and heavy mud in late autumn will slow ground movements for both sides, and low temperatures impose a variety of logistics challenges. The start of such seasonal weather is variable, however.[vi] While weather considerations will affect Ukrainian counteroffensive operations, they will not impose a definite end to them. A hard freeze occurs throughout Ukraine in the winter that makes the ground more conducive to mechanized maneuver warfare, and Ukrainian officials expressed routine interest in exploiting these weather conditions in winter 2022–2023.[vii]
- Ukrainian forces continued to advance south of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly advanced near Bakhmut on September 10.
- Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Head Kyrylo Budanov stated on September 10 that Ukrainian forces will continue counteroffensive operations into late 2023. Cold and wet weather will affect but not halt active combat, as it has done in the first 18 months of the war.
- Russian military personnel continue to detail persistent problems hindering Russian operations along the frontline in Ukraine.
- Russian forces conducted a series of Shahed-131/-136 drone strikes targeting Kyiv Oblast on the night of September 9 to 10.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly regained some lost positions in some areas.
- Ukrainian Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Spokesperson Major General Vadym Skibitskyi stated on September 10 that the Russian military has concentrated over 420,000 military personnel in occupied Ukraine, not including Rosgvardia (Russian national guard) and other military units and structures.
- Russian occupation officials held the final day of voting for Russian regional elections in occupied territories on September 10, continuing efforts to coerce residents to vote and portray the elections as legitimate.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 9, 2023
Ukrainian forces made confirmed advances in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and made claimed advances south of Bakhmut on September 9. Geolocated footage published on September 9 shows that Ukrainian forces advanced northwest of Novomayorske (18km southeast of Velyka Novosilka) along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border, where Russian sources claim fighting has intensified in recent days.[i] Additional geolocated footage published on September 9 shows that Ukrainian forces also advanced northeast and east of Novoprokopivka (13km south of Orikhiv) and west of Verbove (20km southeast of Orikhiv) in western Zaporizhia Oblast.[ii] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces achieved unspecified successes south of Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv).[iii] A Kremlin-affiliated Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces forced Russian forces to withdraw from Andriivka (9km southwest of Bakhmut), and another prominent milblogger claimed that Andriivka is now a contested “gray zone.”[iv] Ukrainian officials reported that Ukrainian forces also achieved unspecified success south of Klishchiivka.[v]
Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Spokesperson Vadym Skibitskyi reemphasized Ukraine’s right to target critical Russian strategic and military objects in rear areas. Skibitskyi stated on September 8 that Ukraine identifies and strikes the most critical Russian objects in Russian rear areas using drones, missiles, and agents on Russian territory.[vi] Skibitskyi emphasized that Ukrainian forces target military facilities and objects of the military-industrial complex that help with missile production and logistics support. Skibitskyi stated that Ukraine purposefully targets these objects to degrade Russian offensive potential and achieve a “domino effect” where destroying one object forces other dependent enterprises to stop production.
Russia’s war in Ukraine is increasingly constraining Russian local and regional politics, with even the minimal pre-war competition suppressed and regional governments increasingly focused on their ability to generate resources for the war. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL)’s Tatar-Bashkir service Idel Realii posted an interview on September 8 with Russian political scientist Dmitry Loboyko regarding “the peculiarities of election campaigns during the war.”[vii] Loboyko stated that this election season is one of the most “uncompetitive” in Russian history and that it particularly lacks opposition alternatives, especially as people are increasingly voting with the mindset that the war in Ukraine may last a year, five years, or even ten years.[viii] Loboyko also noted that Russian federal subjects (regions) are competing for resources on the basis of how many military personnel each region was able to mobilize for the war, with the insinuation that the federal government allocates more resources to regions that mobilized more personnel, thereby increasing inter-regional competition.[ix] Loboyko’s insights suggest that the war in Ukraine, and its continued drain on Russian regions, has contributed to a more muted political atmosphere within Russia. ISW has previously observed that Russian officials, particularly those affiliated with the leading United Russia party, appear concerned with the impacts the war will have on the electorate during local and regional elections, and the muted political atmosphere outlined by Loboyko aligns with these observations.[x] Various Russian insider sources additionally reported on September 9 that Russian President Vladimir Putin has publicly backed Nizhny Novgorod Governor Gleb Nitkin, Moscow Mayor Sergei Sobyanin, and Smolensk Governor Vasily Anokhin in the regional elections.[xi] The insider sources suggested that the Kremlin is invested in publicly backing the infrastructure and connectivity projects that these regional leaders espouse.[xii] As the war continues, Russian officials will likely continue to have to balance the suppression of domestic political opposition with the need to posture the government as being actively involved in ameliorating domestic matters.
The Kremlin continues to refuse to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative in an attempt to extract maximum concessions from the West and may believe that apparent support or acceptance for its demands from some international actors offers it more leverage in renegotiating the deal. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov reiterated on September 9 that Russia will not resume its participation in the grain deal until all its demands are met.[xiii] Peskov specifically highlighted the Kremlin’s demand for the reconnection of the Russian Agricultural Bank to the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT) banking system and suggested that the reconnection of one of the bank’s subsidiaries is insufficient.[xiv] UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres recently sent a letter to Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov offering extensive concessions for Russia’s return to the deal, which included SWIFT reconnection for a Russian Agricultural Bank subsidiary in Luxembourg.[xv] Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan similarly supported offering Russia extensive concessions during the G20 summit in New Delhi, where he reportedly called on G20 leaders to resume insurance for Russian grain and fertilizer cargos and to reconnect Russian banks to SWIFT.[xvi] The Kremlin may believe that Erdogan’s and Guterres’ support for offering concessions places further pressure on the West to acquiesce to Russian demands for rejoining the grain deal, and Russian officials will likely continue to reject offers that meet many of these demands in the hope of extracting a maximalist set of concessions.[xvii] The Kremlin may alternatively have no intention of returning to the grain deal, however, and may instead aim to increase the market share and attractiveness of Russian grain by degrading Ukrainian grain export potential through continued strikes on grain and port infrastructure.[xviii]
The Telegraph reported on September 8 that the United Kingdom’s military aircraft are conducting patrols over the Black Sea to deter Russian forces from conducting attacks against civilian vessels carrying grain exports.[xix] NATO previously announced on July 26 that it would increase surveillance and reconnaissance in the Black Sea region, including with maritime patrol aircraft and drones, given Russian threats against civilian ships and attacks on Ukrainian ports.[xx]
The Group of 20 (G20) adopted a standard and boilerplate consensus declaration during the G20 summit on September 9 that called for a “durable peace” in Ukraine without explicitly condemning Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.[xxi] The G20 advocated for all states party to the G20 mandate to uphold the rules and principles of international law and called for initiatives that would lead to a “comprehensive, just, and durable peace in Ukraine.”[xxii]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces made confirmed advances in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and made claimed advances south of Bakhmut on September 9.
- Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Spokesperson Vadym Skibitskyi reemphasized Ukraine’s right to target critical Russian strategic and military objects in rear areas.
- Russia’s war in Ukraine is increasingly constraining Russian local and regional politics, with even the minimal pre-war competition suppressed and regional governments increasingly focused on their ability to generate resources for the war.
- The Kremlin continues to refuse to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative in an attempt to extract maximum concessions from the West and may believe that apparent support or acceptance for its demands from some international actors offers it more leverage in renegotiating the deal.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia and advanced in some areas on September 9.
- Russian occupation authorities continue efforts to manufacture a guise of legitimacy and legality around ongoing local elections in occupied regions of Ukraine.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 8, 2023
Russian forces have reportedly made notable changes to their command and control (C2) in Ukraine to protect command infrastructure and improve information sharing, although Russian force deployments are likely still exacerbating issues with horizontal integration. Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET) Deputy Director of Analysis Magarita Konaev and CSET Fellow Owen Daniels stated on September 6 that Russian forces moved headquarters out of range of most Ukrainian strike systems and have placed forward command posts further underground and behind heavily defended positions.[1] It is unclear if Russian forces have employed this more protected command infrastructure throughout Ukraine and to what degree these defensive efforts have impeded Ukraine’s ongoing interdiction campaign.[2] Konaev and Daniels stated that Russian forces have improved communications between command posts and units at the front by laying field cables and using safer radio communications.[3] The Royal United Services Insitute (RUSI) stated on September 4 that Russian forces are also trying to improve signals through the wider use of application-based C2 services that require less training.[4] Konaev and Daniels noted that signals at the battalion level downward are still often unencrypted and that Russian personnel still frequently communicate sensitive information through unsecure channels.[5]
Konaev and Daniels concluded that Russian forces still face challenges creating a horizontally integrated command structure to share information across different units in real time, a challenge the Russian military previously identified which has been exacerbated by Russia’s current force structure in Ukraine.[6] The Russian force grouping in Ukraine is comprised of both regular and irregular units, often deployed together and separate from their respective parent formations, further complicating efforts to horizontally integrate units. Russian forces in western Zaporizhia Oblast, for example, are notably comprised of elements of the 58th Combined Arms Army (Southern Military District), Russian Airborne Forces (VDV), Spetsnaz, naval infantry, irregular volunteer battalions, and brigades entirely made up of mobilized personnel.[7] Russian command is likely struggling to share information and create a common command space across these widely disparate forces defending against Ukrainian counteroffensive operations.
Artillery constraints in Ukraine are reportedly prompting the Russian military to accelerate longstanding efforts to implement a fires doctrine prioritizing accuracy over volume. Konaev and Daniels stated that Russian forces have tightened the link between reconnaissance systems and artillery units to improve fire accuracy, as Russian forces face growing constraints on their ability to leverage mass indirect fire.[8] RUSI noted on September 4 that Russian commanders are doubling down on the need to prioritize the development of a reconnaissance fires complex (RFC) due to assessing that existing Russian fires doctrine, which heavily relies on a high volume of fires and pre-established calculations of the density of fires needed to achieve certain effects, without a reliable system of rapid battle damage assessment is non-viable.[9] Russian forces have long sought to implement the concept of RFC prior to the 2022 invasion of Ukraine, which dictates that Russian forces employ high-precision, long-range weapons linked to real-time intelligence data and precise targeting provided by an intelligence and fire-direction center.[10] RUSI added that Russian forces are prioritizing strike accuracy over volume because they lack the ammunition to sustain mass indirect fires, have difficulties transporting a large volume of ammunition to the frontline, and see diminishing effectiveness with mass strikes.[11] Russia is also reportedly increasing the production of Krasnopol laser-guided shells and Lancet drones (loitering munitions) to increase fires accuracy.[12] Russian units at the front are rapidly learning and innovating, but their ability to fully implement the desired RFC will likely be constrained by their ability to issue improved communications systems — and provide necessary training — to forces in combat.
Russian forces are additionally reportedly adapting their deployment of electronic warfare (EW) complexes. Konaev and Daniels stated that Russian forces have dispersed their deployment of EW complexes since spring 2022 from a concentration of roughly 10 EW complexes for every 20 kilometers of the frontline to 1 major EW system every 10 kilometers, with additional supporting EW assets deployed as needed.[13] The dispersal of these EW assets suggests that Russian forces have improved the coverage that a single EW complex provides, although Konaev and Daniels noted that the systems still have issues with limited coverage and EW fratricide.[14] RUSI stated that Russian forces are dispersing Pole-21 systems and treating them as disposable EW systems in order to provide wide-area protection from Ukrainian drone strikes.[15] Russian sources particularly credited superior Russian EW capabilities for aiding Russian forces’ successful defense against the start of the Ukrainian counteroffensive in southern Ukraine in June.[16] Konaev and Daniels added that these EW systems continue to present challenges for Ukrainian drones transmitting targeting information and securing Ukrainian signals.[17]
Ukrainian forces reportedly continued to advance south of Bakhmut and south of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not make any confirmed gains on September 8. Ukrainian military officials reported that Ukrainian forces are continuing to advance south of Bakhmut and achieved unspecified successes south of Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv).[18] One Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces advanced north of Andriivka (9km southwest of Bakhmut) and in Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut), although another milblogger noted that the situation in Klishchiivka is unclear at this time.[19] Russian sources also claimed that Ukrainian forces seized positions on the northwestern outskirts of Novomayorske (18km southwest of Velyka Novosilka) on the Donetsk–Zaporizhia Oblast border.[20]
Russian forces conducted another series of Shahed-131/136 drone strikes targeting Odesa Oblast on the night of September 7–8. The Ukrainian General Staff reported on September 8 that Ukrainian forces downed 16 of 20 Shahed drones that Russian forces launched at grain and port infrastructure in Odesa Oblast.[21] Ukrainian Southern Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk stated that Russian forces are launching drone strikes from Crimea in order to bypass Ukrainian air defenses.[22] Humenyuk also noted that the number of drones that Russian forces have launched and markings on the drones indicate that Russia has established domestic drone production.[23] ISW reported on September 6 that Russian authorities intend to expand domestic drone production beyond the Alabuga Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in the Tatarstan Republic into the Bashkortostan Republic.[24] Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Colonel Yuriy Ihnat noted that Russian forces may increase the frequency of drone strikes on Ukraine.[25] Romanian news agency Digi24 reported on September 8 that the Romanian National Committee for Emergency Situations authorized the General Inspectorate for Emergency Situations to issue warning and alarm messages where there are Russian drone attacks in the area.[26]
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov publicly rejected an offer from the UN Secretariat that met many of Russia’s stated demands to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative on September 6, indicating that the Kremlin is either delaying its return to the grain deal in an attempt to extract maximum concessions from the West or has no intention whatsoever of returning to the grain deal. Lavrov stated on September 6 that the Russian government received a letter from UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres offering several concessions in exchange for the resumption of the grain deal.[27] Lavrov stated and Reuters reported that the concessions in the letter included: reconnection to SWIFT for a Russian Agricultural Bank subsidiary in Luxembourg within 30 days, the creation of an insurance platform for Russian cargo and ships against Ukrainian strikes in the Azov and Black seas; the unblocking of Russian fertilizer assets in the EU, and approval for Russian ships carrying food and fertilizers to dock in European ports.[28] Lavrov publicly dismissed the UN Secretariat’s offer as a “workaround” that does not create a real solution to the problem.[29] Guterres stated on September 7 that the UN is “actively engaged” in attempting to improve Russia’s grain and fertilizer exports in order to convince Moscow to allow the safe export of Ukrainian grain through the Black Sea.[30] Reuters confirmed the existence of the letter and its contents on September 8.[31] The UN‘s letter notably offers concessions to most of the previously expressed Russian demands, with the exception of the renewal of operations for the Togliatti–Odesa ammonia pipeline as Lavrov noted on September 6.[32] ISW previously assessed that the Kremlin likely views the Black Sea Grain Initiative as one of its few remaining avenues of leverage against the West and has withdrawn from the deal and engaged in escalatory rhetoric to extract extensive concessions.[33]
Russian President Vladimir Putin reiterated boilerplate rhetoric justifying the current war in Ukraine while commemorating a Soviet military victory during the Second World War on September 8. Putin claimed that soldiers of the Donetsk and Luhansk People’s Republics’ (DNR and LNR) militias inherited their courage and resilience from ancestors who fought to recapture Donbas in the Second World War and reamplified the narrative falsely portraying the current Ukrainian government as “Nazis.”[34] Putin’s September 8 speech is a continuation of the rhetoric from his September 5 speech invoking the memory of significant Soviet military victories to set ideological conditions for a prolonged war effort.[35]
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) directly responded to recent indications that the Armenian government may be questioning its decades-long security relationship with Russia. The Russian MFA claimed on September 8 that it observed doubts within Armenian official circles and political elite about Armenian bilateral ties with Russia, trilateral Russian-Armenian-Azerbaijani ties, and ties to the Russian-dominated Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO). The MFA claimed that Armenian leadership has conducted “unfriendly actions,” including indicators that ISW recently identified: the provision of humanitarian aid to Ukraine, the visit of Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan’s wife Anna Hakobyan to deliver the humanitarian aid to Ukraine, and Armenia’s decision to host joint military exercises with the United States.[36] The MFA also criticized Armenian leadership for moving to ratify the International Criminal Court (ICC) Rome Statute and stated that it issued a formal protest to the Armenian Ambassador to Russia, Vagharshak Harutyunyan, in response to these “unfriendly actions.”[37] The MFA’s direct response to these events indicates that Russian anger over indications of Armenian dissatisfaction with Russian security guarantees are not confined to the Russian ultranationalist information space but includes the Russian government.[38]
The US Department of Defense (DoD) announced a new security assistance package on September 7, providing Ukraine with $600 million worth of military equipment.[39] The DoD reported that the package includes: equipment to sustain Ukraine’s air defense systems, additional ammunition for HIMARS systems, 105mm artillery rounds, electronic warfare and counter–electronic warfare equipment, demolition munitions for obstacle clearing, mine-clearing equipment, and support and equipment for training, maintenance, and sustainment activities.
Unknown Russian actors may be helping Russian officials to censor Russian milbloggers who have previously criticized the Kremlin’s war effort in Ukraine. Supporters of imprisoned former Russian officer and ultranationalist Igor Girkin amplified an appeal from a Russian milblogger and serviceman Mikhail Polynkov who claimed that unknown individuals hacked into and stole access to his Telegram channel.[40] Polynkov claimed that these hackers began to impersonate him and are writing social media posts that contradict his opinions. Polynkov added that the hackers also published a post attacking another prominent milblogger (who advocates for veteran rights), unlisted many of his popular posts, and are trying to find information to blackmail him and his affiliates. Polynkov claimed that these hackers are not ordinary thieves who are attempting to scam his audience for money but instead are individuals who disagreed with his criticism of the Kremlin. ISW has recently observed several crackdowns against Russian ultranationalist veterans who consistently criticized the Kremlin likely as part of a centralized effort to silence some critical milblogger voices.[41]
Key Takeaways:
- Russian forces have reportedly made notable changes to their command and control (C2) in Ukraine to protect command infrastructure and improve information sharing, although Russian force deployments are likely still exacerbating issues with horizontal integration.
- Artillery constraints in Ukraine are reportedly prompting the Russian military to accelerate longstanding efforts to implement a fires doctrine prioritizing accuracy over volume.
- Russian forces are additionally reportedly adapting their deployment of electronic warfare (EW) complexes.
- Ukrainian forces reportedly continued to advance south of Bakhmut and south of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not make any confirmed gains on September 8.
- Russian forces conducted another series of Shahed-131/136 drone strikes targeting Odesa Oblast on the night of September 7–8.
- Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov publicly rejected an incredibly favorable offer from the UN Secretariat that met many of Russia’s stated demands to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative on September 6, indicating that the Kremlin is either delaying its return to the grain deal in an attempt to extract maximum concessions from the West or has no intention whatsoever of returning to the grain deal.
- The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) directly responded to recent indications that the Armenian government may be questioning its decades-long security relationship with Russia.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove line, near Bakhmut, and along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line but did not make any confirmed advances on September 8.
- The New York Times (NYT) — citing Western, African, and Russian sources — reported that Russian intelligence structures are competing for control of the Wagner Group’s assets and operations in Africa.
- Russian occupation officials continue to hold illegal regional elections in occupied Ukraine. Russian occupation officials in Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson oblasts announced the start of in-person voting in occupied territories on September 8.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 6, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations in the Bakhmut and western Zaporizhia Oblast directions and have made gains in western Zaporizhia Oblast as of September 6. Geolocated footage shows that Ukrainian forces have advanced along the trench line west of Verbove (about 20km southeast of Orikhiv), and the Ukrainian General Staff stated that Ukrainian forces achieved unspecified successes in the Robotyne—Novoprokopivka direction south of Orikhiv. The Ukrainian General Staff additionally reported that Ukrainian forces are continuing successful offensive operations south of Bakhmut.
Ukrainian and Russian sources report the Russian defense industrial base (DIB) faces growing challenges in replacing basic supplies in addition to known challenges in rebuilding its stocks of precision weapons. Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence (GUR) Representative Andriy Yusov reported on September 6 that Russia can only produce “dozens” of Kalibr cruise missiles and smaller numbers of Iskander missiles per month, which will not enable Russia to the replenish its pre-2022 stocks. Yusov reported that Russia struggles to obtain modern optical equipment, electronics, chips, and circuits and that “gray imports” and smuggling cannot completely cover the Russian DIB’s needs. Russian sources additionally noted that the Russian DIB cannot produce enough rubber to replace worn tires for military equipment vital to frontline operations, and noted that increasing wear on tires will make it difficult for wheeled vehicles to move in muddy, rainy, and icy conditions. The Russian sources claimed that Russian authorities claimed at an unspecified time that they would find solutions to worn tires by mid-August, but the situation has not changed as of September 5. Poor quality and insufficient tires will impose increasing constraints on Russian mobility in the muddy season and winter.
Russian forces conducted a large missile and drone strike against Ukraine overnight on September 5-6. Ukrainian officials reported that Russian forces launched seven Kh-101, Kh-555, and Kh-55 air-launched cruise missiles from aircraft operating out of Engels airbase in Saratov Oblast; one Iskander-M ballistic missile; and 25 Shahed 136/131 drones from the Primorsko-Akhtarsk direction. Ukrainian air defenses shot down all eight missiles and 15 drones. Ukrainian officials reported that the Russian strike damaged the port and agricultural infrastructure in Odesa Oblast. Romanian Defense Minister Angel Tilvar stated on September 6 that several pieces of a Russian drone fell on Romanian territory near its border with Ukraine. The Romanian Ministry of Defense previously denied the Ukrainian Foreign Ministry’s September 4 statement that a Russian drone fell on Romanian territory.
Russian sources continue to speculate on the current role and future of dismissed Wagner-affiliated Army General Sergei Surovikin, the former commander of Russia’s Aerospace Forces (VKS). Several Russian insider sources and milbloggers remarked that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) removed Surovikin’s profile from the official MoD website other than his video appeal released during the Wagner rebellion asking the group to stand down. The removal of Surovikin’s profile is not remarkable in itself — Russian military leadership removed Surovikin as commander of the Aerospace Forces (VKS) in August, and the absence of his profile from the MoD website could be a simple reflection of this fact. Some Russian insider sources additionally claimed that State Duma Deputy and retired Colonel General Viktor Zavarzin stated that Surovikin has taken a new position in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). ISW has previously observed a pattern of Russian generals who underperform in command roles in Ukraine (such as former Eastern Military District (EMD) Commander Alexander Chaiko and former Airborne Forces (VDV) Commander Andrey Serdyukov) being reassigned to external theaters and peripheral locations such as Syria as a form of punishment, while not being entirely removed from the Russian military. Appointing Surovikin to a role in the CIS, which does not appear to be a military or command role, suggests that Russian military leadership is likely continuing the practice of shifting disgraced or ineffective commanders to positions not involved in the war in Ukraine.
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken announced an additional $175 million military assistance package for Ukraine during an unannounced visit to Kyiv on September 6. The package includes air defense equipment, artillery rounds, and anti-tank weapons. Blinken stated that the United States aims to ensure that Ukraine “has what it needs” to both succeed in the current counteroffensive and to develop long term defensive capabilities. Blinken called Ukrainian progress in the counteroffensive “very, very encouraging.”
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations in the Bakhmut and western Zaporizhia Oblast directions and have made gains in western Zaporizhia Oblast as of September 6.
- Ukrainian and Russian sources report the Russian defense industrial base (DIB) faces growing challenges replacing basic supplies in addition to known challenges rebuilding its stocks of precision weapons.
- Russian forces conducted a large missile and drone strike against Ukraine overnight on September 5-6.
- Russian sources continue to speculate on the current role and future of dismissed Wagner-affiliated Army General Sergei Surovikin, the former commander of Russia’s Aerospace Forces (VKS).
- US Secretary of State Antony Blinken announced an additional $175 million military assistance package for Ukraine during an unannounced visit to Kyiv on September 6.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donestk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 6.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in at least two sectors of the front and advanced near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 6.
- Russian authorities continue crypto-mobilization efforts amid continued rumors of a new wave of general mobilization.
- Ukrainian reports indicate that Russian and occupation authorities continue attempts to increase social control in occupied Ukraine by cracking down against pro-Ukrainian materials in occupied schools.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 5, 2023
Ukrainian forces continue to advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast. Geolocated footage posted on September 5 shows Russian forces striking Ukrainian positions northwest and west of Robotyne, indicating that Ukrainian forces have advanced into an area near the settlement that Russian forces previously claimed to control.[1] Additional geolocated footage posted on September 5 shows that Ukrainian forces have also advanced south of Robotyne and northwest of Verbove (about 10km east of Robotyne).[2] Geolocated evidence of Ukrainian forces northwest of Verbove suggests that Ukrainian forces are advancing along the line of Russian fortifications that runs into the settlement. Ukrainian military sources also confirmed that Ukrainian forces have been successful in the Robotyne—Novoprokopivka directions south of Orikhiv, and further reported that Ukrainian forces are pursuing successful offensive operations south of Bakhmut.[3]
Russian sources continue to complain that Russian forces lack sufficient counterbattery capabilities and artillery munitions in the face of ongoing Ukrainian counteroffensive activities, which the Kremlin and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) are reportedly attempting to combat. Russian milbloggers claimed on September 4 and 5 that Russian counterbattery systems are performing poorly along the front in Ukraine.[4] The milbloggers claimed that Russian forces are relying heavily on Lancet drones and 220mm and 300mm rounds for Multiple Launch Rocket Systems (MLRS), of which there are limited stockpiles.[5] One Russian milblogger noted that the Russian MoD‘s plans to form five new artillery brigades in each of Russia’s five military districts are in part meant to improve general counterbattery capabilities.[6] It is unclear if the milblogger is claiming that the MoD plans to form five or 25 brigades total. The milblogger claimed that the Russian MoD would equip the new brigades with 203-mm 2S7 Pion and 2S7M Malka artillery systems from Russian stores.[7] The New York Times reported on September 4 that North Korean leader Kim Jong Un and Russian President Vladimir Putin will meet at the Eastern Economic Forum in Vladivostok from September 10-13 and will reportedly discuss North Korea’s supply of artillery shells to Russia.[8] Russian sources have continually complained that Russian forces face problems with counterbattery operations.[9]
Ukrainian counteroffensive operations in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area are likely succeeding in pinning elements of the 7th Guards Mountain Airborne (VDV) Division and preventing them from laterally redeploying to critical areas of the front in western Zaporizhia Oblast. A Russian milblogger posted an audio recording on September 5 purportedly from a soldier in the Russian 247th VDV Regiment in which the soldier claims that he has to retrieve bodies of Russian personnel near Staromayorske because the Russian command is not overseeing the retrieval of bodies and claimed that his unit lost 49 killed in action in one day of fighting.[10] The Russian soldier’s claims suggest that elements of the 247th Regiment remain defending in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast area, despite claims from a prominent Russian source in late August that some elements are fighting in the Robotyne area.[11] ISW previously observed that elements of 108th VDV Regiment and 56th VDV Regiment — the two other constituent regiments of the 7th VDV Division — have redeployed to the Robotyne area.[12]
Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu reiterated boilerplate rhetoric intended to dismiss recent Ukrainian advances and highlight the beginning of a new academic year for Russian military institutions during a meeting with Russian military leadership on September 5. Shoigu claimed that the Ukrainian forces had not achieved any of their goals for the counteroffensive.[13] Shoigu noted that the Zaporizhia direction, most likely referring to the Robotyne area, has become the tensest area of the front lines and that Ukrainian forces have committed several brigades from their “strategic reserve” to this area.[14] Shoigu claimed that Russian forces have destroyed a heavily exaggerated amount of Ukrainian personnel and military equipment since the Ukrainian counteroffensive began in June 2023.[15] Shoigu noted that Russian military schools and training programs began a new academic year on September 1.[16] Shoigu also noted that the curriculum of Russian military training programs has been adjusted to prepare students for the conditions they would face fighting in Ukraine.[17]
Russian President Vladimir Putin drew historical parallels between Soviet participation in the Second World War and the current war in Ukraine to set ideological expectations for a prolonged war effort. Putin gave a speech on September 5 that invoked the memory of significant Soviet military victories during the Second World War, including turning points in the battles of Stalingrad and Kursk and recapturing the Caucasus and Donbas.[18] Putin had notably attended a concert in honor of the Battle of Kursk’s 80th anniversary as Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin’s plane crashed on August 23.[19] Putin criticized the international community’s “attitude” to the buildup to the Second World War — very likely criticizing European countries for failing to intervene against Nazi Germany prior to the outbreak of war (and ignoring the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact that briefly allied the Soviet Union with Nazi Germany, permitted the Soviet invasion of the Baltic States, and partitioned Poland) — as also creating conditions for the current conflict in Ukraine and drew parallels between reconstruction efforts and veterans assistance measures during and after the Second World War and the current war in Ukraine.[20] Putin also reamplified the Kremlin information operation falsely portraying the Ukrainian government as a “Nazi regime.” These direct parallels between the “special military operation” and the Second World War are likely the closest that Putin or any other senior Russian official has come to acknowledging the war in Ukraine as an actual war. These parallels also message to a domestic Russian audience that the ongoing Russian war effort is really a war effort despite the insistence on the euphemistic “special military operation.”
The Armenian government appears to be seriously questioning its decades-long security relationship with Russia, amid reports of Armenian humanitarian aid to Ukraine and increasing public dissatisfaction with Russia’s security guarantees. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty’s Armenia service Radio Azatutyun reported on September 5th that the Armenian government has reportedly sent unspecified humanitarian aid to Ukraine for the first time since the war in Ukraine began.[21] Radio Azatutyan’s sources claimed that Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan’s wife Anna Hakobyan will personally deliver the aid to Kyiv and attend the “Third Summit of First Ladies and Gentlemen” that begins on September 6.[22] The Armenian government has not officially confirmed this information. Pashinyan notably stated that Russia cannot meet Armenia’s security needs in an interview with Italian newspaper La Repubblica published on September 4 and called Armenia’s dependence on Russia for security a “strategic mistake.”[23] Pashinyan also reported that Russia could not meet Armenia’s security needs even if it so desired, given the Russian military’s current need for weapons and ammunition likely referring to use in Ukraine.[24] Kremlin newswire TASS notably reported on August 28 that Azerbaijani law enforcement officers detained three Nagorno-Karabakh residents, reportedly escorted by Russian peacekeepers, at a checkpoint in the Lachin corridor, prompting protests outside the Russian embassy in Yerevan.[25] A Kremlin-affiliated Russian milblogger confirmed on September 5 that Major General Kirill Kulakov replaced Colonel General Alexander Lentsov as the commander of the Russian peacekeeping contingent in Nagorno-Karabakh.[26]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continue to advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Russian sources continue to complain that Russian forces lack sufficient counterbattery capabilities and artillery munitions in the face of ongoing Ukrainian counteroffensive activities, which the Kremlin and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) are reportedly attempting to combat.
- Ukrainian counteroffensive operations in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area are likely succeeding in pinning elements of the 7th Guards Mountain Airborne (VDV) Division and preventing them from laterally redeploying to critical areas of the front in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu reiterated boilerplate rhetoric intended to dismiss recent Ukrainian advances and highlight the beginning of a new academic year for Russian military institutions during a meeting with Russian military leadership on September 5.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin drew historical parallels between Soviet participation in the Second World War and the current war in Ukraine to set ideological expectations for a prolonged war effort.
- The Armenian government appears to be seriously questioning its decades-long security relationship with Russia, amid reports of Armenian humanitarian aid to Ukraine and increasing public dissatisfaction with Russia’s security guarantees.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 5.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in at least two sectors of the front and advanced near Bakhmut, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 5.
- Russian sources continue to report on Russian efforts to recruit volunteers amid continued rumors of general mobilization.
- The Ukrainian Security Service (SBU) reportedly attempted to assassinate a Russian occupation official in occupied Luhansk Oblast on September 5.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 4, 2023
Ukrainian light infantry has advanced to positions beyond anti-tank ditches and dragon’s teeth anti-tank obstacles that comprise the current Russian defensive layer ahead of the Ukrainian advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast, and Ukrainian forces likely intend to hold those positions. ISW is not prepared to assess that Ukrainian forces have breached this Russian defensive layer in the absence of observed Ukrainian heavy equipment in these areas. Geolocated footage published on September 4 indicates that Ukrainian forces advanced to tree-line positions that are east of the Russian anti-tank ditches and dragon’s teeth obstacles that are a part of a tri-layered defense immediately west of Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv).[i] Geolocated footage published on September 4 indicates that Ukrainian light infantry has also advanced further into a series of prepared Russian defensive positions along the road that runs northwest into Verbove.[ii] Other geolocated footage published on September 4 indicates that Ukrainian forces have advanced up to Russian defensive positions between Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv) and Novoprokopivka (13km south of Orikhiv).[iii] Ukrainian forces are widening the breach they have already made in one Russian defensive layer and are reportedly maneuvering more equipment and personnel into tactical rear areas of this layer.[iv] Ukrainian forces appear to be making gains in the immediate vicinity of the not-yet-breached Russian defensive layer that runs northwest of Verbove to north of Solodka Balka (20km south of Orikhiv) with infantry assaults and heavy artillery fire on Russian positions further into and south of this layer.[v] The deployment of Ukrainian heavy equipment and more substantial forces to these areas than ISW has so far observed would indicate both a breach of this Russian defensive layer and an effort to widen that breach.
Russian forces reportedly attempted to expand minefields in southern Ukraine following the start of the Ukrainian counteroffensive in June. The Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) reported that the Russian command determined at the start of the Ukrainian counteroffensive that Ukrainian forces might be able to easily breach the Russian doctrinal minefield depth of 120 meters leading Russian forces to aim to increase the depth of their minefields up to 500 meters.[vi] RUSI stated that Russian forces lacked enough mines to mine these larger areas as densely as Russian doctrine dictates, causing Russian forces to deviate from doctrine, including by using improvised explosive devices and a wider and differential distance between mines.[vii] RUSI stated that Russian forces tried to compensate for decreased minefield density by increasing the effectiveness of anti-tank mines by placing two on top of each other.[viii] Ukrainian operations across several sectors of the front have likely further compounded these constraints on the Russian effort to expand minefields by forcing Russian forces to disperse their mining efforts along wide sectors of the frontline. Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Spokesperson Oleksandr Shtupun stated on September 3 that minefields near the next series of Russian defensive positions in western Zaporizhia are less dense than the initial defensive layer that Ukrainian forces advanced through.[ix] ISW has previously assessed that Ukrainian forces may encounter denser minefields at certain sections of subsequent series of Russian defensive positions, however.[x]
Limitations on Russian artillery capabilities and Ukrainian advantages in counter-battery fire are forcing the Russians to deviate from their own doctrine, RUSI reported. RUSI stated that Russian forces have been attempting to adapt their fire doctrine since before Ukrainian counteroffensive operations began.[xi] RUSI noted that Russian forces are attempting to prioritize strike accuracy over volume because they lack enough ammunition to sustain doctrinally designated artillery fire, have difficulties transporting a large volume of ammunition to frontline areas, and are seeing diminishing effectiveness of mass strikes as they lose counterbattery radars and their guns suffer from barrel wear.[xii] RUSI stated that Russian forces are attempting to increase the production of Krasnopol laser-guided shells and the use of Lancet drones (loitering munitions) in order to increase accuracy and reduce the number of munitions used in attacks.[xiii] RUSI also observed that Russian forces have often prepared their fighting positions for remote demolition with improvised explosives instead of striking their own positions with artillery after Russian forces have withdrawn, as Russian doctrine dictates.[xiv] These adaptations suggest that reduced Russian artillery capabilities may be further weakening the Russian defense in certain sectors as artillery fire is a critical component of the Russian elastic defense. A shift towards more precise fire doctrine may allow Russian forces to strengthen these capabilities, but constraints on Russian training capacity will likely prevent Russian forces from implementing this shift at scale in the near term. Russian sources have continually claimed since the start of the counteroffensive that the Russians lack sufficient counterbattery capabilities on various sectors of the front.[xv] Estonian Defense Forces Intelligence Center Commander Colonel Margo Grosberg reported on September 1 that Ukrainian artillery capabilities are “equal or even better” than those of Russian forces and have been able to push Russian artillery units back from the frontline, preventing them from supporting Russian forces.[xvi]
Russian forces conducted a drone strike on Dnipropetrovsk and Odesa oblasts on the night of September 3-4. The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Russian forces launched 32 Shahed 136/131 drones from Cape Chauda, Crimea, and Primorske-Akhtarsk, Krasnodar Krai on the night of September 4 and that Ukrainian air defenses shot down 23 of the drones.[xvii] Ukrainian Southern Command Spokesperson Captain First Rank Nataliya Humenyuk stated that Russian drones struck civilian infrastructure in Odesa Oblast, and Russian sources claimed that drones struck port infrastructure in Reni and Izmail, Odesa Oblast.[xviii] Head of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Council Mykola Lukashuk reported that a drone strike destroyed 1,500 tons of grain in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast.[xix] Ukrainian Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Oleg Nikolenko stated that a Russian drone fell on Romanian territory, which the Romanian Ministry of Defense subsequently denied.[xx]
Russian President Vladimir Putin reiterated Russia’s unwillingness to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative until all of Russia’s extensive terms are met at a meeting with Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan. Putin reiterated claims that the West ignored its obligations to allow Russia to export grain and fertilizer at a meeting with Erdogan in Sochi, Russia on September 4.[xxi] Putin claimed that Russia will supply 25,000 to 50,000 tons of grain for free to unspecified African countries in “the coming days.”[xxii] Putin and Erdogan claimed that Turkey is willing to help process and transport one million tons of grain intended for these countries.[xxiii] Putin and Erdogan also announced Qatar’s interest in providing financial support so that these countries can receive free grain.[xxiv]
Head of the UN Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine Erik Mose stated on September 4 that the commission has not yet concluded that Russia is committing genocide in Ukraine. Mose stated that the commission must determine the intent of the perpetrators and identify the “need” to physically or biologically exterminate a certain group to meet the legal qualifications under the Genocide Convention.[xxv] Mose stated that the commission has found evidence for a large number of war crimes, specifically evidence of torture and strikes on Ukrainian energy infrastructure that the commission could consider as crimes against humanity.[xxvi] Mose also stated that the commission previously determined that certain statements in Russian mass media could be considered as incitement to commit genocide.[xxvii] Mose noted that the commission’s investigation into genocide in Ukraine will continue.[xxviii] Article II of the 1948 Convention of the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (the Genocide Convention) states that “genocide means any of the following acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial, or religious group, as such: killing members of the group; causing serious bodily or mental harm to members of the group; deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part; imposing measure intended to prevent births within the group; forcibly transferring children of the group to another group.”[xxix] Article III states that “the following acts shall be punishable: genocide; conspiracy to commit genocide; direct and public incitement to commit genocide; attempt to commit genocide; complicity in genocide.”[xxx]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian light infantry has advanced to positions beyond anti-tank ditches and dragon’s teeth anti-tank obstacles that comprise the current Russian defensive layer ahead of the Ukrainian advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast, and Ukrainian forces likely intend to hold those positions. ISW is not prepared to assess that Ukrainian forces have breached this Russian defensive layer in the absence of observed Ukrainian heavy equipment in these areas.
- Russian forces reportedly attempted to expand minefields in southern Ukraine following the start of the Ukrainian counteroffensive in June.
- Limitations on Russian artillery capabilities and Ukrainian advantages in counter-battery fire are forcing the Russians to deviate from their own doctrine, RUSI reported.
- Russian forces conducted a drone strike on Dnipropetrovsk and Odesa oblasts on the night of September 3-4.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin reiterated Russia’s unwillingness to rejoin the Black Sea Grain Initiative until all of Russia’s extensive terms are met at a meeting with Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan.
- Head of the UN Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine Erik Mose stated on September 4 that the commission has not yet concluded that Russia is committing genocide in Ukraine.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the western Donetsk-eastern Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 4.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations and advanced near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 4.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced on September 4 that the Russian military will not be holding “Zapad-2023” joint strategic exercises scheduled for September.
- Russian occupation officials continued the fifth day of early voting for Russian regional elections in occupied territories on September 4.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 3, 2023
Ukrainian military officers offered notably frank and direct commentary about the prospects of further Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast and indicated that the series of prepared Russian defensive positions immediately ahead and further south of the Ukrainian advance may be less challenging to Ukrainian forces. Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Commander Brigadier General Oleksandr Tarnavskyi, who commands the Ukrainian grouping in southern Ukraine, discussed Ukraine’s counteroffensive in an interview with The Guardian on September 2.[i] Tarnavskyi stated that Ukrainian forces have decisively breached Russian forces’ “first line of defense” and that he expects faster Ukrainian gains as Ukrainian forces press on a weaker “second line” of defense.[ii] Ukrainian forces have advanced up to the next series of prepared Russian defensive positions in certain areas in the Robotyne area in western Zaporizhia Oblast, although many Russian sources assert that these positions are the first, not the second, defensive layer in a multi-echeloned Russian defense in southern Ukraine.[iii] Ukrainian officials and Russian milbloggers are using different terminology to describe the same positions. Russian sources characterize the first series of positions that Ukrainian forces have previously breached as a forward line without giving it an ordinal number, and the series Ukrainian forces are currently approaching as the first main line of defenses — while Ukrainian forces characterize these positions as Russia’s second line of defenses.
Tarnavskyi stated that Russian forces devoted 60 percent of their time and resources into building the series of defensive positions that Ukrainian forces have now breached and only 20 percent each to the two subsequent defensive layers further south.[iv] This breached series of Russian defensive positions consists of a system of interconnected Russian trenches and dugouts guarded by anti-tank ditches and dense minefields, and Tarnavskyi’s reporting supports ISW’s previous observation that Russian forces may have not extended similarly challenging preparations throughout subsequent series of defensive layers, particularly regarding the density of minefields.[v] Russian defensive positions are not uniform in strength across the frontline in western Zaporizhia Oblast, and Tarnavskyi’s description of weaker Russian defensive positions may refer only to the immediate Robotyne area. Tarnavskyi also commented on the weight of Ukrainian efforts elsewhere in southern Ukraine and suggested that the Ukrainian advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast is an operational priority.[vi]
Ukrainian military officials particularly noted that advancing Ukrainian forces can operate more freely in areas with sparser Russian minefields. Ukrainian Tavriisk Group of Forces Spokesperson Oleksandr Shtupun stated on September 3 that minefields near the next series of Russian defensive positions are less dense than the initial defensive layer that Ukrainian forces advanced through.[vii] Shtupun and Tarnavskyi both stated that Ukrainian forces are deploying more vehicles in these areas and maneuvering more equipment and troops towards the next Russian defensive layer, but they acknowledged that minefields will still present a significant threat.[viii] Tarnavskyi stated that Ukrainian forces spent more time on mine clearing than they expected to at the beginning of the counteroffensive and that consistent Russian artillery and aviation fire forced Ukrainian infantry to conduct mine clearing only at night.[ix] Shtupun added that heavy minefields forced Ukrainian breaching operations onto narrow paths — the exact intent of minefields under Russian defensive doctrine.[x] Ukrainian forces may now be better positioned to maneuver more freely in the tactical rear of the breached Russian defensive layer. Tarnavskyi’s description of the Russian minefields may pertain only to the immediate Robotyne area, and Ukrainian forces may encounter heavily dense minefields at certain sections of subsequent series of Russian defensive positions. Although Ukrainian forces certainly face further hard fighting regardless, Tarnavskyi characterized Ukrainian forces as having successfully broken through the most difficult Russian defenses.
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian military officers offered notably frank and direct commentary about the prospects of further Ukrainian advances in western Zaporizhia Oblast and indicated that the series of prepared Russian defensive positions immediately ahead and further south of the Ukrainian advance may be less challenging to Ukrainian forces.
- Ukrainian military officials particularly noted that advancing Ukrainian forces can operate more freely in areas with sparser Russian minefields.
- Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations and advanced near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast on September 3.
- Several Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces continue to operate on the left (east) bank of the Dnipro River in occupied Kherson Oblast.
- Russian forces conducted a series of drone strikes targeting Ukrainian port infrastructure in Odesa Oblast on September 3.
- The Russian military appears to be recruiting personnel at scale through ongoing crypto-mobilization efforts, although the quality and allocation of these new servicemembers remains unclear.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in western Donetsk, in the western Donetsk–eastern Zaporizhia border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 3.
- Russian law enforcement is patrolling and guarding polling stations in occupied Ukraine to prevent citizens from expressing opposition to the elections and recording the voting process.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 2, 2023
Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly advanced on September 2. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations in the Melitopol (western Zaporizhia Oblast) direction.[1] Russian milbloggers who have recently maintained that Russian forces hold positions in the southern part of Robotyne claimed that Russian forces withdrew from the southern outskirts of the settlement to unspecified positions further south.[2] Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated on September 1 that Ukrainian forces have overcome the Russian “first line of defense” in some areas of the Zaporizhia direction, but that the situation remains difficult due to additional Russian concrete fortifications and dense minefields.[3]
The New York Times reported on September 2 citing Ukrainian military personnel that Russian forces are spreading inflammable agents on mined fields and igniting them with drone-launched grenades while Ukrainian forces clear mines from the areas in an effort to hinder Ukrainian mine clearing efforts that have allowed Ukrainian forces to advance in certain areas.[4] Estonian Defense Forces Intelligence Center Commander Colonel Margo Grosberg reported on September 1 that Ukrainian artillery capabilities are “equal or even better” than those of Russian forces and have been able to push Russian artillery units back from the frontline, preventing them from supporting Russian forces.[5] This observation is not universally true across the frontline, as Ukrainian units regularly report coming under heavy Russian artillery fire corrected by Russian drones. Grosberg also stated that Ukrainian forces have been successful at severely damaging Russian artillery radars since July.[6] Russian sources have repeatedly expressed concerns since mid-July over the lack of Russian counterbattery artillery capabilities, particularly in southern Ukraine.[7]
Select Russian sources claimed that Russian officers of the 58th Combined Arms Army (CAA) defending in Zaporizhia Oblast contacted former 58th CAA commander Major General Ivan Popov due to the worsening situation at the Russian frontline. Russian milbloggers claimed that Popov has maintained contact with his former subordinates in western Zaporizhia Oblast, and a Russian insider source claimed that these officers turned to Popov for help instead of their new commander.[8] The Russian military command dismissed Popov as the commander of the 58th CAA (Southern Military District) in early July after he engaged in clear insubordination by attempting to bypass Chief of the Russian General Staff Army General Valery Gerasimov and bring his complaints about poor counterbattery capabilities, heavy losses, and a lack of rotations directly to Russian President Vladimir Putin.[9] Russian sources have routinely expressed concern about the issues that Popov highlighted and their detrimental impacts on the Russian defensive effort in southern Ukraine.[10] Popov partially established a precedent for insubordination, and his conduct reportedly prompted the Russian military command to begin removing similarly insubordinate commanders from frontline units, although not all reports of commanders removed were confirmed.[11] Russian sources claimed that Popov encouraged his former subordinates to report the truth about the front to the higher Russian command, possibly encouraging them to replicate his insubordination.[12] Popov’s contact with his former subordinates, if true, suggests that Popov’s replacement has not won the trust of his subordinates either because he is less competent or because he is less forthright with senior Russian leadership about continuing challenges facing the Russian defense in western Zaporizhia.
The Russian ultranationalist information space response to a Russian critique of anti-Western mindsets and Russian propaganda demonstrates that the ultranationalist community retains the ability to coalesce around certain issues. Director of the Russian think tank the Institute for the Study of the USA and Canada, Valery Garbuzov, published an article on August 29 criticizing Russian ruling elites who, he argues, have created and perpetuated a series of “utopian myths” about Russian hegemony, the “crisis of capitalism,” and Russia’s claimed leadership of a global anti-Western coalition.[13] Prominent voices within the Russian ultranationalist information space levied largely coherent criticisms against Garbuzov’s article on September 2, criticizing Garbuzov’s argument and the Russian political and informational structures that allowed Garbuzov to hold a prominent position in the Russian political sphere.[14] One prominent Russian milblogger claimed that Russian Telegram channels have filled an analytical gap in the Russian information space following the onset of the war in Ukraine that think tanks should fill and continue to do so 18 months later.[15]
Prominent Russian milbloggers likely have a monetary incentive to regularly report information about the war in Ukraine that is uncritical of Russian authorities. BBC reported on September 1 that prominent Russian milbloggers claimed that they can make between about 48,000 and 188,000 rubles (about $500 to 1,950) per advertisement on their Telegram channels.[16] BBC reported that an advertising agent working with Wagner-affiliated channels claimed that a prominent Wagner Group-affiliated source made around 31,500 rubles (about $330) per advertisement.[17] The advertising agent told BBC that several employees of RIA FAN, a now-shuttered media outlet affiliated with former Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin, received only about 10,500 to 21,800 rubles (about $108 to $226) per advertisement due to their lower subscriber count.[18] BBC noted that Russia’s average monthly salary is about 66,000 rubles (about $685). Prominent milbloggers’ monthly salaries are thus likely much higher than the Russian average. Russian milbloggers are likely economically incentivized to maintain and grow audiences through war reporting that is uncritical of Russian authorities, as criticism of the Russian authorities, resistance to attempted censorship, and potential legal problems could lead to a decrease in advertisements, although milbloggers who present themselves as telling unpleasant truths can also gain large followings. Alexander “Sasha” Kots, a prominent milblogger who also serves on the Kremlin’s Human Rights Council, claimed that milbloggers have a “direct channel to privately communicate information” to the Russian MoD.[19]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian forces continued counteroffensive operations in western Zaporizhia Oblast and reportedly advanced on September 2.
- Select Russian sources claimed that Russian officers of the 58th Combined Arms Army (CAA) defending in Zaporizhia Oblast contacted former 58th CAA commander Major General Ivan Popov due to the worsening situation at the Russian frontline.
- The Russian ultranationalist information space response to a Russian critique of anti-Western mindsets and Russian propaganda demonstrates that the ultranationalist community retains the ability to coalesce around certain issues.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and advanced in some areas on September 2.
- Ukrainian forces conducted offensive operations along at least one sector of the front on September 2 and advanced near Bakhmut, in western Donetsk Oblast, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- The Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) has formed its own Rosgvardia (Russian National Guard) units, elements of which reportedly operate both on the front line and in far rear areas of occupied Ukraine.
- Russian and occupation authorities are encouraging residents of occupied Ukraine who are residing in Russia to vote in the occupation regional elections, likely to increase voter turnout and the perception of electoral legitimacy.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, September 1, 2023
Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence (GUR) Head Kyrylo Budanov reported that the Russian military deployed elements of a newly created “reserve army” (the 25th CAA) to enable units currently on the frontline in Luhansk Oblast to laterally redeploy to defend against the Ukrainian counteroffensive in southern Ukraine. Budanov stated on August 31 that the Russian military deployed elements of the newly formed 25th Combined Arms Army (reportedly formed under the Eastern Military District) to replace elements of the 41st Combined Arms Army (Central Military District) in the Kupyansk direction, and that these elements of the 41st Combined Arms Army (CAA) began a “slow” redeployment to an unspecified area in southern Ukraine.[i] Elements of the 41st CAA’s 35th Separate Guards Motorized Rifle Brigade and 90th Tank Division participated in the failed Russian winter 2023 offensive operation in Luhansk Oblast and have continued limited offensive activity along the Svatove-Kreminna line through now.[ii] These units are likely degraded and have been operating without brigade and regiment level rotations like many frontline Russian units throughout the theater. ISW previously assessed that a lack of operational reserves would force the Russian command to conduct further lateral redeployments and make tough decisions about what sectors of the front to prioritize.[iii] The Russian military command appears to have deployed elements of the newly formed and likely low quality or understrength 25th CAA to Luhansk Oblast to free up the relatively more effective 41st CAA elements for southern Ukraine. Budanov added that elements of the 25th CAA are already participating in hostilities in Luhansk Oblast.[iv]
The 25th Combined Arms Army is unlikely to be combat effective at scale given its rushed deployment, ahead of a previously reported intended deployment date of December 2023. Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) formed a “reserve army” at the end of June, likely referencing the 25th CAA, which began recruiting personnel from the Russian Far East in mid-May.[v] The 25th CAA will reportedly consist of 30,000 contract personnel in two motorized rifle divisions as well as an unspecified number of tank and artillery battalions, although it is unclear what elements have actually formed to date.[vi] Budanov stated that Russian forces formed the 25th CAA as a ”strategic“ reserve and did not intend for the formation to be combat ready before October or November 2023.[vii] A Russian administrator in Dalnegorsk, Primorsky Krai posted a recruitment ad for the 25th CAA on June 5 that claimed that the 25th CAA would train personnel from September 1 to December 1 and then deploy to either Zaporizhia or Kherson Oblast - ISW has not independently observed reporting of the October or November date Budanov cited but has no reason to question this statement.[viii] Ukrainian Deputy Chief of the Main Operational Department Oleksii Hromov stated on July 5 that the 25th CAA would not be combat ready until at least 2024.[ix] Budanov noted that the 25th CAA elements that have arrived in Luhansk Oblast are understaffed and lack training, unsurprising due to their accelerated deployment.[x] ISW cannot yet independently verify that elements of the 25th CAA are operating in Luhansk Oblast, and the scale of the 25th CAA’s commitment is unclear from Budanov’s comments. The current size and capabilities of the elements of the 25th CAA deployed to Ukraine five months prematurely are unclear. The formation is likely either severely understaffed and not near the paper strength of two divisions, or is poorly trained much like initial Russian mobilized units in fall 2022, or both.
The Russian command likely views the deployment of a combat ineffective formation to Luhansk Oblast as a tolerable risk given the relatively lower tempo of operations along much of the Luhansk Oblast frontline. The recent lateral redeployment of elements of the 76th Guards Air Assault (VDV) Division from the Kreminna area in Luhansk Oblast to the Robotyne area in western Zaporizhia Oblast in late August further suggests that the Russian military command likely views this sector of the front as relatively safe.[xi] Ukrainian forces are conducting limited ground attacks in Luhansk Oblast compared to other areas of the front.
Additional Russian lateral redeployments and the immediate commitment of intended operational reserves suggest that short term reinforcement needs are impeding intended long-term reconstitution efforts. The redeployment of elements of the 41st CAA to southern Ukraine is the third major Russian lateral redeployment since the start of the Ukrainian counteroffensive in June and the second in recent weeks.[xii] Russian formations at the division level (and in some areas lower) defending in southern Ukraine have done so without rotation since the start of the Ukrainian counteroffensive, and these forces have committed substantial material, manpower, and effort to hold back Ukrainian advances.[xiii] The second lateral deployment in the span of a few weeks suggests an increasing Russian concern about the stability of Russian defenses in light of Ukrainian advances around Robotyne. The creation of the 25th CAA is likely a part of Shoigu’s long-term objective previously announced in January 2023 to form several new major ground forces formations, and the deployment of elements of the 25th CAA to avoid creating gaps in the Russian defense suggests that the immediate threat of a Ukrainian breakthrough is serious enough to supersede that effort.[xiv]
Russian “Vostok” Battalion commander Alexander Khodakovsky continues to highlight the impact of the lack of Russian counter-battery capabilities on Russian morale in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area. Khodakovsky claimed on September 1 that Russian forces continue to suffer from a lack of counter-battery capabilities in the Novomayorske-Novodonetske-Kermenchyk area (12km to 18km southeast of Velyka Novosilka), where Khodakovsky and the “Vostok” Battalion are reportedly defending.[xv] Khodakovsky insinuated that Russian forces are experiencing extreme physical and psychological stress in this area due to constant Ukrainian artillery fire and the Russian inability to return fire.[xvi] Khodakovsky expressed concerns about whether distressed and exhausted Russian forces will be able to defend against a future Ukrainian offensive in this sector of the front.[xvii]
Khodakovsky has previously highlighted similar concerns about the Russian defense in this area, although his recent comments are more negative and defeatist in tone.[xviii] Khodakovsky’s complaints about the lack of counter-battery capabilities in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area and concerns about its impacts on Russian morale are not necessarily indicative of a wider phenomenon in the Russian defense. However, Khodakovsky’s comments likely accurately reflect the situation in his limited but important sector of the frontline as well as the situation for often neglected proxy military formations such as Khodakovsky’s Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) “Vostok” Battalion. Khodakovsky noted on August 31 that Russian forces cannot lose sight of the daily fight against Ukrainian forces while fantasizing about "burying the enemy in the future.”[xix] Khodakovsky may believe that senior Russian commanders have done exactly this by letting the situation deteriorate to the point that Russian forces may be unable to defend against future Ukrainian offensives in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area.
Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and made some advances on September 1. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations south of Bakhmut, and geolocated footage shows that Ukrainian forces marginally advanced northwest of Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut).[xx] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces achieved unspecified success in the Novodanylivka-Novopokropivka direction (5km to 13km south of Orikhiv) in western Zaporizhia Oblast.[xxi] Russian sources claimed that Russian forces repelled Ukrainian attacks near Robotyne (10km south of Orikhiv) and Verbove (18km southeast of Orikhiv), however.[xxii] US National Security Council Spokesperson John Kirby stated on July 1 that the US has observed notable Ukrainian progress in the “Zaporizhia area” (likely meaning the western Zaporizhia Oblast direction) in the past 72 hours and that Ukrainian forces have achieved some success against the “second line of Russian defenses” in southern Ukraine.[xxiii] Kirby also stated that anonymous US officials’ criticisms of the progress of the Ukrainian counteroffensive are unhelpful.[xxiv]
Politico confirmed previously-reported numbers of refurbished US Abrams tanks set to arrive in Ukraine by mid-September. Politico confirmed that Ukraine will receive the first 10 of the 31 promised refurbished US Abrams tanks by mid-September following refurbishment in Germany, citing a US Department of Defense official and another source.[xxv] The US Army Europe and Africa Spokesperson Colonel Martin O’Donnell stated that the US remains committed to delivering the 31 Abrams during an unspecified timeframe in the fall.[xxvi] O’Donnell stated that 200 Ukrainian servicemen recently completed one of the final phases of Abrams training. Ukraine is unlikely to deploy the initial Abrams tanks (two platoons) until the entire brigade set is ready for operations.
Russian Deputy Defense Minister Colonel General Yunus-Bek Yevkurov is reportedly visiting multiple African countries as part of the Russian Ministry of Defense’s (MoD’s) continued effort to assume control over the Wagner Group’s operations in Africa. A Kremlin-affiliated milblogger claimed that Yevkurov is conducting a tour of various African countries including Burkina Faso and recently visited Libya and Syria in an attempt to replace “private military companies” (PMCs) with Russian MoD-controlled formations.[xxvii] The milblogger also claimed that the Russian MoD is forming a “volunteer corps” to function as an “expeditionary corps” that will include over 20,000 personnel.[xxviii] The “expeditionary corps” may be a reference to the “Rossiyskiy Ekpeditsionniy Korpus” (Russian Expeditionary Corps) PMC that Russian officials are allegedly creating to conduct operations abroad.[xxix] Bloomberg reported on August 31 that unnamed sources close to the Russian MoD and an unspecified PMC claimed that a Russian MoD-affiliated PMC is positioned to take control of Wagner’s operations in the Central African Republic.[xxx] ISW has continually observed claims since the Wagner rebellion on June 24 that the Russian MoD is attempting to consolidate control over Wagner operations in Africa.[xxxi]
A Russian public opinion poll indicates that there is likely little to no societal discontent around the Wagner Group or its financier Yevgeny Prigozhin’s death, and the true cause of the plane crash will have little impact on both Russian perceptions and the future of the Wagner Group. Independent Russian polling organization Levada Center found that roughly equivalent percentages of Russians believe that either Prigozhin’s death was accidental; Russian authorities intentionally orchestrated Prigozhin’s death; Prigozhin is still alive; or the cause of Prigozhin’s death is difficult to determine.[xxxii] Levada Center polls conducted on June 23 and August 23 found that Russians are almost evenly split between disapproving and approving of Prigozhin’s activities.[xxxiii] Public opinion on the death of Prigozhin (very likely a Kremlin-directed assassination) would only impact Kremlin or Ministry of Defense decision making if public opposition reached a far higher threshold, and the Kremlin likely in fact benefits from continued disagreement in Russian society over the circumstances of Prigozhin’s death.
A fringe Russian milblogger arrested on August 31 for allegedly discrediting the Russian military reportedly pled guilty on September 1.[xxxiv] Russian state media outlet TASS reported that Andrey Kurshin, administrator of the “Moscow Calling” Telegram channel, pled guilty to charges for knowingly disseminating false information about the Russian military and faces up to 10 years in prison.[xxxv] Russian media outlet Baza claimed that Russian officials charged Kurshin for posts made on September 14 and November 23, 2022 covering Russian shelling of Zaporizhia Oblast and a strike near a dam on the Inhulets River near Kherson City, respectively.[xxxvi] Kurshin, via the “Moscow Calling” channel, has actively criticized the Russian military, Ministry of Defense (MoD), and Kremlin throughout the war for poor Russian conduct, and these specific and older posts are unlikely to be the impetus for Kurshin’s arrest. Russian authorities reportedly arrested prominent ultranationalist Igor Girkin based on Telegram posts two months prior to his arrest but reportedly began investigating Girkin on the same day he levied especially harsh critiques against Russian President Vladimir Putin, as ISW has previously reported.[xxxvii]
Key Takeaways:
- Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence (GUR) Head Kyrylo Budanov reported that the Russian military deployed elements of a newly created “reserve army” (the 25th CAA) to enable units currently on the frontline in Luhansk Oblast to laterally redeploy to defend against the Ukrainian counteroffensive in southern Ukraine.
- The 25th Combined Arms Army is unlikely to be combat effective at scale given its rushed deployment, ahead of a previously reported intended deployment date of December 2023.
- Additional Russian lateral redeployments and the immediate commitment of intended operational reserves suggest that short term reinforcement needs are impeding intended long-term reconstitution efforts.
- Russian “Vostok” Battalion commander Alexander Khodakovsky continues to highlight the impact of the lack of Russian counter-battery capabilities on Russian morale in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area.
- Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations near Bakhmut and in western Zaporizhia Oblast and made some advances on September 1.
- Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, near Bakhmut, along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line, in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, and in western Zaporizhia Oblast but did not make any confirmed gains.
- Russian occupation officials announced on September 1 that voting began for the Russian regional elections held in occupied Ukraine and will continue in various forms through September 10.
- Russian officials continue efforts to forcibly indoctrinate Ukrainian youth into Russian culture and identity by integrating schools in occupied Ukraine into the Russian educational system.
Previous Updates
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
Related Reads
In the winter of 2021-2022, CTP and ISW launched a forecast series in response to the Russian military build-up on Ukraine's border. The reports in this series are listed below. CTP and ISW have also maintained this indicators document with daily information on the crisis through February 17, 2022.
Putin’s Likely Course of Action in Ukraine - Part 3: Updated Course of Action Assessment
January 27, 2022
Russian President Vladimir Putin is using the crisis he created by mobilizing a large military force around Ukraine to achieve two major objectives: first, advancing and possibly completing his efforts to regain effective control of Ukraine itself, and second, fragmenting and neutralizing the NATO alliance. Russian military preparations can support a massive invasion of Ukraine from the north, east, and south that could give Putin physical control of Kyiv and other major Ukrainian cities, allowing him to dictate terms that would accomplish the first objective. Such an invasion, however, might undermine his efforts to achieve the second objective because it could rally the NATO alliance around the need to respond to such a dramatic act of aggression. An invasion would also entail significant risks and definite high costs. A Russian military action centered around limited military operations in southern and southeastern Ukraine coupled with a brief but widespread and intense air and missile campaign could better position Putin to achieve both aims as well as reduce the likely costs and risks to Russia.
Putin's Likely Course of Action in Ukraine - Part 2
December 11, 2021
Russian President Vladimir Putin is amassing a military force on and near Ukraine’s borders large enough to conduct a full-scale invasion. Western intelligence agencies have reportedly intercepted Russian military plans to do so by early February. Visible Russian military activities and these plans so clearly support preparations for an invasion that it seems obvious that Putin really might invade if his demands are not met.
Putin is rarely so obvious, however, and a massive Russian invasion of Ukraine would mark a fundamental transformation of the approach he has taken for two decades to advance his interests and respond to threats. We cannot dismiss the possibility that such a transformation has occurred. The United States, NATO, and Ukraine must seriously consider the risk of a Russian invasion of Ukraine and prepare military, diplomatic, and economic measures to deter and respond to that threat.
Putin's Likely Course of Action in Ukraine - Part 1
December 10, 2021
Russian President Vladimir Putin is amassing a large force near the Ukrainian border and reportedly has a military plan to invade and conquer most of unoccupied Ukraine. Western leaders are rightly taking the threat of such an invasion very seriously, and we cannot dismiss the possibility that Putin will order his military to execute it. However, the close look at what such an invasion would entail presented in this report and the risks and costs Putin would have to accept in ordering it leads us to forecast that he is very unlikely to launch an invasion of unoccupied Ukraine this winter. Putin is much more likely to send Russian forces into Belarus and possibly overtly into Russian-occupied Donbas. He might launch a limited incursion into unoccupied southeastern Ukraine that falls short of a full-scale invasion.
A full-scale Russian invasion of unoccupied Ukraine would be by far the largest, boldest, and riskiest military operation Moscow has launched since the 1979 invasion of Afghanistan. It would be far more complex than the US wars against Iraq in 1991 or 2003. It would be a marked departure from the approaches Putin has relied on since 2015, and a major step-change in his willingness to use Russian conventional military power overtly. It would cost Russia enormous sums of money and likely many thousands of casualties and destroyed vehicles and aircraft. Even in victory, such an invasion would impose on Russian President Vladimir Putin the requirement to reconstruct Ukraine and then establish a new government and security forces there more suitable for his objectives.