{{currentView.title}}
May 31, 2023
Ukraine Invasion Updates May 2023
This page collects the Critical Threats Project (CTP) and the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) updates on the invasion of Ukraine for May 2023. Full list of Ukraine invasion updates are available here.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 31, 2023
The Russian military command has likely ordered Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov’s forces to begin offensive operations in Ukraine following the withdrawal of Wagner Group forces from Bakhmut. Kadyrov claimed on May 31 that Chechen forces received a new order and assumed responsibility over the Donetsk Oblast frontline. Kadyrov claimed that Chechen units need to start “active combat activities” and “liberate a series of settlements.” Kadyrov added that Chechen “Akhmat” Special Forces (Spetsnaz) and the “Sever-Akhmat” Special Purpose Regiment transferred to the Marinka direction southwest of Donetsk City. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) also claimed that assault detachments of the 5th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade of the 1st Army Corps and Akhmat Spetsnaz conducted offensive operations in the Marinka direction. Kadyrov noted that the Russian military command ordered Russian, Rosgvardia (Russian National Guard), and Chechen Akhmat forces to begin offensive actions along the front line in Zaporizhia and Kherson oblasts as well. Kadyrov claimed that these units have already begun tactical preparations for these offensive actions and claimed that “Akhmat” units’ offensive operations began before Ukrainian forces launched a counteroffensive. ISW has observed no indications of Chechen offensive operations in Zaporizhia or Kherson as of this writing.
The claimed return of Chechen forces to offensive operations would break Kadyrovites from a nearly yearlong hiatus from participating in high-intensity combat operations. Chechen forces have been largely operating in the rear after participating in the battles for Mariupol, Severodonetsk, and Lysychansk - with the exception of some offensive activities around Bilohorivka, Luhansk Oblast. ISW also observed Kadyrov’s forces operating as a police force in the rear in southern Ukraine and performing localized reconnaissance-in-force operations in Zaporizhia Oblast. Kadyrov also claimed that 3,300 personnel of the “Sever-Akhmat” Regiment were in Chechnya as of May 8, and ISW assessed that Kadyrov may have been conserving his forces instead sending them to the frontlines. Chechen units’ limited participation on the frontlines alongside Kadyrov’s heavy emphasis on recruitment may suggest that Kadyrov is hesitant to commit his forces to grinding offensive operations in Ukraine despite his ultranationalist narratives.
The Kremlin may be attempting to reintroduce Kadyrovites as the main offensive force following the culmination of Wagner forces and their withdrawal from the frontlines. ISW had previously assessed that Russian President Vladimir Putin had been attempting to pressure Kadyrov into increasing the role of Chechen fighters in combat operations since at least Putin's public meeting with Kadyrov on March 13. Kadyrov also claimed on May 20 to have met with Putin in Pyatigorsk, Stavropol Krai, around the time of Wagner Group’s claimed victory in Bakhmut. The Kremlin did not publish a readout from this meeting, and Kadyrov claimed that he boasted to Putin that there are seven Chechen regiments and four battalions operating in Ukraine. Kadyrov later clarified on May 26 that there are 7,000 Chechen personnel in Ukraine. The Russian MoD’s mention of “Akhmat” operations in the Marinka direction a day prior to Wagner’s initial claimed withdrawal date on June 1 indicates that Putin may have coerced Kadyrov into assuming an offensive role in the war to compensate for Wagner’s likely culmination. The Kremlin may perceive Chechen units as an untapped assault force that can restore Russia’s ability to sustain simultaneous offensive efforts on multiple axes of advance. If Kadyrov’s claims that he has 7,000 troops in Ukraine are close to accurate his forces will not be able to mount multiple significant offensive operations successfully.
The Kremlin may also be attempting to sever Kadyrov’s relationship with Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and re-emphasize federal authority over Chechen forces. Prigozhin responded on May 31 to reports of Chechen forces transferring to occupied Donetsk Oblast, stating that he is confident that Kadyrov’s forces will be successful in capturing some settlements in the region but emphasized that Kadyrov was not tasked with capturing the entirety of Donetsk Oblast. Prigozhin also noted that he is not aware of Chechen units’ new positions as this information is secret. Kadyrov participated in Prigozhin’s blackmail attempt in early May aimed at coercing the Russian MoD to allocate additional military supplies to Wagner in Bakhmut. Kadyrov claimed that his forces would relieve Wagner forces on May 6 and even directly asked Putin to authorize the transfer of Chechen forces from other directions to Bakhmut. Putin may have perceived Kadyrov’s behavior as a threat to his control given that Kadyrov and Prigozhin had conducted a successful joint information campaign in early October 2022 to facilitate military command changes. Putin or the Russian military command may have ordered Kadyrov to increase the presence of his units on the battlefield in retaliation for Kadyrov’s blackmail attempt.
The official Russian responses to recent attacks against Russia remain likely insufficient to satisfy the Russian ultranationalist information space’s desire for escalation in the war. Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov called on Russian forces on May 29 to capture Kharkiv City and Kharkiv Oblast to create a barrier between Belgorod Oblast and Ukraine. Gladkov later announced on May 31 the evacuation of children from the border areas of Shebekino and Grayvoron raions — including 300 children relocated to Voronezh Oblast — in response to the “deteriorating” border situation. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov refused to comment on Gladkov’s statements on May 29, igniting some ire in the Russian information space. Former Russian officer and ardent nationalist Igor Girkin criticized Peskov, Russian President Vladimir Putin, and Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu for their reluctance to address attacks against Russian territory. Russian milbloggers have complained about the lack of Russian military escalation to secure border areas in Belgorod and Kursk oblasts since at least September 2022, often criticizing the Kremlin for underreacting to attacks against Russian territory and failing to fully dedicate itself to the war effort. The evacuations and Peskov’s comments are largely consistent with Putin’s unwillingness and inability to meaningfully escalate the war short of full-scale general and economic mobilization, as ISW has previously assessed.
Key Takeaways
- The Russian military command has likely ordered Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov’s forces to begin offensive operations in Ukraine following the withdrawal of Wagner Group forces from Bakhmut.
- The claimed return of Chechen forces to offensive operations would break Kadyrovites from a nearly yearlong hiatus from participating in high-intensity combat operations.
- The Kremlin may be attempting to reintroduce Kadyrovites as the main offensive force following the culmination of Wagner forces and their withdrawal from the front lines.
- The Kremlin may also be attempting to sever Kadyrov’s relationship with Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and re-emphasize federal authority over Chechen forces.
- The official Russian responses to recent attacks against Russia remain likely insufficient to satisfy the Russian ultranationalist information space’s desire for escalation in the war.
- Russian forces conducted ground attacks northwest of Svatove and south of Kreminna.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks around Bakhmut and along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces continue to concentrate in southern Ukraine.
- The Russian State Duma appears to be considering measures to legalize the military recruitment of current or formerly incarcerated Russian men.
- Ukrainian Verkhovna Rada Human Rights Commissioner Dmytro Lyubinets announced that Ukraine has a new avenue to repatriate Ukrainian children abducted to Russia.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 30, 2023
Russia claimed that Ukraine conducted a series of drone strikes against Moscow on May 30 as Russia again targeted Ukraine with Iranian-made Shahed drones. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) accused Ukraine of attacking Moscow with eight drones on the morning of May 30, and claimed that Russian forces shot down five of the drones and suppressed three drones with electronic warfare systems.[1] Russian propagandist Vladimir Solovyev, however, claimed that Ukraine launched 32 drones of which some targeted the prestigious neighborhood of Rublyovka in Moscow Oblast.[2] A Russian independent outlet claimed that the drone strikes predominantly targeted areas near Russian President Vladimir Putin’s residence in Novo-Ogaryovo and other elite neighborhoods in Moscow Oblast.[3] Moscow Mayor Sergei Sobyanin stated that several buildings in Moscow suffered minor damage, and Russian sources amplified footage of a minor explosion in the Novaya Moskva neighborhood.[4] A Russian milblogger claimed that drones flying over Moscow resembled Ukrainian attack drones.[5] Geolocated footage shows Russian forces shooting down drones identified as Ukrainian by OSINT accounts in several different areas of Moscow and Moscow Oblast.[6] Ukrainian presidential aide Mykhailo Podolyak denied that Ukraine was directly involved in the drone strike but forecasted that there could be an increase in such attacks in the future.[7]
Russian forces conducted another Shahed 131 and 136 drone strike against Kyiv overnight on May 29 to May 30. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces shot down 29 of 31 Russian Shahed 131 and 136 drones that targeted Kyiv.[8] Senior Russian officials claimed that Russian forces struck high profile targets in Kyiv during recent strikes, likely to appear successful in retaliation for the recent Belgorod Oblast incursion.[9] Russian Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu claimed that Russian forces struck a Patriot air defense system in recent days.[10] Ukrainian Air Forces Spokesperson Colonel Yuriy Ihnat denied Shoigu’s claim, however.[11] Russian milbloggers’ recent complaints about the perceived lack of Russian escalation in response to the Belgorod border raid and Moscow drone strikes do not give Russian forces credit for the unprecedented scale of their air campaign against Kyiv. Many milbloggers, including high-profile voices like former Russian officer Igor Girkin and Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin have frequently and recently complained about the lack of full scale general and economic mobilization in Russia, the only feasible measure likely to satisfy the broader information space outcry.[12]
Russian President Vladimir Putin attempted to downplay the drone attack on Moscow to avoid exposing the limited options he has to retaliate against Ukraine. Putin claimed that Russian forces struck the Ukrainian military intelligence headquarters “two [to] three days ago” and claimed that the Russian Armed Forces continue to respond to Ukraine’s “war against Donbas” by striking Ukrainian military infrastructure.[13] Putin insinuated that the drone strike on Moscow was Kyiv’s response to Russian strikes, and the Russian MoD conveniently claimed on May 30 that Russian forces carried out “a group of strikes with long-range high-precision air-launched weapons at main decision-making centers” in Ukraine.[14] The Russian MoD did not claim that it had struck the Ukrainian military intelligence headquarters recently and there is no available confirmation of Putin’s claim.[15] Putin stated that Ukraine is trying to provoke a response and make Russia “mirror” its actions. Putin’s emphasis on past and ongoing missile strikes is likely an attempt to signal that Russia is already actively retaliating and does not need to respond to further Ukrainian provocations. Putin has consistently retaliated against genuine and purported Ukrainian actions by ordering massive missile and drone campaigns, likely due to Russian forces’ inability to achieve any decisive effects on the battlefield.[16]
Putin additionally pushed numerous Kremlin boilerplate narratives aimed at maintaining domestic support for the Russian war effort and villainizing the West. Putin also noted that, while the Moscow air defense systems “worked normally,” Russia still needs to “work” on improving these systems – a notable attempt to preempt criticism from Russian ultra-nationalists who have been criticizing Russia’s ineffective air defense systems in Moscow and along the Russian border regions with Ukraine.[17] Putin also accused Ukraine of threatening to destabilize the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) and using “dirty devices” – both default Russian false narratives that the Kremlin uses during Russian military failures.[18]
The drone attack on Moscow generated varied responses from the Russian information space. Moscow Duma Deputy Andrey Medvedev claimed that the Ukrainian forces hurriedly executed the drone attack as part of an information operation with negligible kinetic effects.[19] Some Russian milbloggers used the drone attacks to criticize the Russian withdrawal from Kyiv, Chernihiv, and Sumy oblasts in April 2022.[20] Igor Girkin used the strikes against Rublyovka to criticize Russian elites who he claimed have “never thought about the country and never will” and will not respond to Ukrainian attacks in Moscow, Belgorod Oblast, or Russian-occupied Ukraine.[21] Girkin also mocked Putin for continuing to assert that the war is a “special military operation,” despite drone attacks on the Russian capital.[22] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin reprimanded the Russian MoD and called on Russian officials to actually defend Russia instead of “sitting quietly.”[23] Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov threatened the European countries, claiming that, if they continue to supply Ukraine with weapons, they will not have the weapons needed to defend themselves when Russia “knocks on their doors.”[24]
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) is likely attempting to conceal the high Russian losses in Ukraine by artificially inflating Ukrainian casualties in the war. Defense Minister Shoigu claimed on May 30 that Russian forces had destroyed an absurdly high number of Western-provided Ukrainian weapons, including long range missiles, in the past month.[25] Shoigu celebrated claimed successes and training efforts, including by awarding Russian formations and bragging about the upcoming summer military exercises. A Wagner Group-affiliated milblogger criticized Shoigu, implying that Shoigu’s statements are so unrealistic that they appear to be fake to readers.[26] Dutch open-source group Oryx reported on May 29 that it confirmed that Russia has lost over 2,000 tanks and 2,366 infantry fighting vehicles (including over 850 BMPs) since the war began.[27]
EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs Josep Borrell stated that Russia will not enter negotiations while trying to win the war, supporting ISW’s assessment that Russian statements expressing willingness to negotiate are part of an ongoing information operation intending to weaken Western willingness to aid Ukraine.[28] Reuters reported on May 29 that Borrell said that Russia has repeatedly signaled that it would not end the war until it achieved its military goals and that it has over 300,000 personnel in Ukraine — twice as many as when the invasion started.[29]
Key Takeaways
- Russia claimed that Ukraine conducted a series of drone strikes against Moscow on May 30 as Russia again targeted Ukraine with Iranian-made Shahed drones.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin attempted to downplay the drone attack on Moscow to avoid exposing the limited options he has to retaliate against Ukraine.
- The drone attack on Moscow generated varied responses from the Russian information space.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) is likely attempting to conceal the high Russian losses in Ukraine by artificially inflating Ukrainian casualties in the war.
- EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs Josep Borrell stated that Russia will not enter negotiations while trying to win the war.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and northwest of Svatove, and Russian sources claimed that Russian forces conducted a ground attack south of Kreminna.
- The tempo of Russian and Ukrainian offensive operations in the Bakhmut direction remains low as of May 30.
- Russian forces made marginal advances amid continued ground attacks on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces did not conduct any confirmed ground attacks along the southern axis.
- Russian officials are establishing domestic veteran support programs which likely aim to advertise the perks of military service in Russia.
- Russian occupation officials continue to deport Ukrainian children to Russia under the guise of providing pediatric healthcare.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 29, 2023
Russian forces conducted another series of strikes against Ukraine with cruise missiles and Iranian-made drones overnight on May 28 to 29 and during the day on May 29. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces launched 40 Kh-101/Kh-555 air-based cruise missiles and 38 Shahed-131/136 drones on the night of May 28 to 29 and 11 Iskander-M/K missiles during the day on May 29.[i] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian air defenses destroyed in all 36 Kh-101/Kh-555 cruise missiles, 30 Shahed drones, and all 11 Iskander missiles.[ii] Ukrainian officials reported that Ukrainian forces intercepted all 11 Iskander missiles, and 40 cruise missiles and Shahed drones that targeted Kyiv City and Kyiv Oblast.[iii] Ukrainian sources reported that Ukrainian forces also intercepted missiles and drones near the cities of Lviv, Mykolaiv, and Odesa, and that Russian forces struck port infrastructure in Odesa City and a military infrastructure facility in Khmelnytskyi Oblast.[iv] Russian forces launched a relatively higher number of missiles than in recent series of strikes following the largest Russian series of Shahed strikes since the start of the full-scale invasion of Ukraine on May 28.[v] ISW previously assessed that Russian forces began a new limited air campaign in recent months to degrade Ukrainian counteroffensive capabilities, but that the Russian prioritization of targeting Kyiv is likely further limiting the campaign’s ability to meaningfully constrain potential Ukrainian counteroffensive actions.[vi]
Russia deployed more S-400 air defense systems (probably at least a battery) to Belarus on May 28. The Belarusian Ministry of Defense released video on May 28 showing a train with S-400 systems deploying to an unspecified area in Belarus.[vii] Independent Belarusian monitoring organization The Hajun Project reported that the train with S-400s arrived at the 25th Missile Arsenal near Stoubtsi (about 60 km southwest of Minsk).[viii] It is unclear whether these S-400s will enter service near Stoubtsi or deploy further to a different location. These systems will likely enter service with the Belarusian military but under Russian operational control. Russia’s and Belarus’ Joint Regional Air Defense System (established in 2009 and operational in 2016) effectively subordinates Belarus’ air defense assets to the Russian Western Military District.[ix] Belarusian officials confirmed that Russian-provided S-400 in Belarus became operational and deployed on combat duty on December 25, 2022.[x] ISW forecasted in 2020 that Russia would deploy S-400s to Belarus.[xi]
Former Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev confirmed that he is now operating as deputy commander of the Wagner Group. A Kremlin-affiliated milblogger published an interview on May 29 in which Mizintsev confirmed previous claims that he assumed the position.[xii] Mizintsev stated that he has maintained good relations with Wagner for the previous 10 years, further substantiating reports that Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin used close connections with Mizintsev to secure resources for Wagner while Mizintsev was in the Russian MoD.[xiii] Mizintsev claimed to be in Bakhmut overseeing the ongoing relief-in-place operation and claimed that Wagner is conducting an organized withdrawal.[xiv] Mizintsev praised the Wagner commanders and advocated that Wagner’s structure and management become a model for the total war that Russia needs to be fighting.[xv] Mizintsev declined to comment about feuds between the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and Wagner but highlighted that the Russian military has struggled with ammunition provisions and conducting a large-scale mobilization of the Russian nation to win in Ukraine.[xvi] ISW previously assessed that Prigozhin likely appointed Mizintsev as Wagner deputy commander in an effort to retain Wagner’s access to supplies, and Prigozhin has since promoted Mizintsev as his preferred replacement for Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu.[xvii] Mizintsev’s publicized confirmation of his position and adulation of Wagner is likely part of Prigozhin’s wider effort to advocate for more influence following the capture of Bakhmut.[xviii]
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin denied former Russian officer Igor Girkin’s May 27 accusation that Prigozhin could stage a military coup against the Kremlin by arguing that Wagner lacks the personnel needed to start a coup. Prigozhin stated on May 29 that there are different types of coups across the globe – including a “chaotic military coup” in Sudan – which take too long and result in major conflicts.[xix] Prigozhin argued that Wagner does not have a large enough army required to carry out a coup and claimed that Wagner has good relations with Russian President Vladimir Putin. Prigozhin vaguely implied that Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu could stage a coup as he has access to the Russian Special Forces. Prigozhin added that while some individuals in Russia are expecting a revolution Wagner is only advocating for select corrections to the Russian system. Prigozhin’s response to Girkin notably follows his response to a media inquiry in which he hypothesizes about who could have authorized the reported ban on mentions of Wagner on the Russian state media, and even considered Putin.[xx] Prigozhin then stated that there is an effort in Russia to avoid recognizing the legitimate heroes of this war and that “the officials-bureaucrats who run the Russian state today must remain the heroes and they are the only ones who can be thanked.” He added that “if they aren’t thanked, then they say, ‘Fine, heck with it, praise the president,’” implying that Putin is receiving unearned praise and thanks because of the unwillingness of Russian bureaucrats to honor those who truly deserve it. Prigozhin has dramatically increased the number of direct references to Putin since May 9 – after he indirectly criticized Putin during the Victory Day holiday.[xxi]
Chinese Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Mao Ning denied a Wall Street Journal report that Chinese Special Representative for Eurasian Affairs Li Hui urged European officials to end the conflict in Ukraine before it escalates.[xxii] Mao claimed that European officials acknowledged China’s “positive role in promoting peace talks” and appreciated China’s “calling for sovereignty and territorial integrity.”[xxiii] Mao claimed that the war in Ukraine is “now at a critical juncture” and that China continues to attempt to work with all parties to resolve the “crisis.” Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba stated that European officials did not confirm reports that Li urged them attempt to end the war or consider recognizing Russian-occupied areas of Ukraine as Russian territory.[xxiv] Kuleba also stated that Ukraine will continue to engage with China on the basis of three principles: mutual respect for territorial integrity, no proposals of territorial concessions, and no suggestions of freezing the conflict.
Russian authorities continue to forcefully integrate dioceses of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate (UOC MP) in occupied Zaporizhia Oblast into the Russian Orthodox Church (ROC) demonstrating the integral connection of the ROC with the Russian state. Zaporizhia Oblast occupation official Vladimir Rogov claimed that the Russian Bishop of Bronnitsky, Luka, held the first liturgy of the Russian Orthodox Church in Berdyansk Cathedral, which the Russian Orthodox Church had taken control over on May 16.[xxv] Rogov claimed that Russian Orthodox Church Head Patriarch Kirill appointed Bishop of Bronnitsky Luka as head of the Berdyansk and Prymorsk dioceses of the ROC. The Berdyansk and Prymorsk dioceses were previously part of the Russian-affiliated UOC MP, and their forced integration with the ROC emphasizes the close relationship between the ROC and the Russian state.[xxvi]
Key Takeaways
- Russian forces conducted another series of strikes against Ukraine with cruise missiles and Iranian-made drones overnight on May 28 to 29 and during the day on May 29.
- Russia deployed more S-400 air defense systems (probably at least a battery) to Belarus on May 28.
- Former Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev confirmed that he is now operating as deputy commander of the Wagner Group.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin denied former Russian officer Igor Girkin’s May 27 accusation that Prigozhin could stage a military coup against the Kremlin by arguing that Wagner lacks the personnel needed to start a coup.
- Chinese Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Mao Ning denied a Wall Street Journal report that Chinese Special Representative for Eurasian Affairs Li Hui urged European officials to end the conflict in Ukraine before it escalates.
- Russian authorities continue to forcefully integrate dioceses of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate (UOC MP) in occupied Zaporizhia Oblast into the Russian Orthodox Church (ROC) demonstrating the integral connection of the ROC with the Russian state.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- The tempo of Russian offensive operations in and around Bakhmut remains notably low.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City front, particularly focusing on Marinka.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks in western Donetsk Oblast and are expanding fortifications in Mariupol.
- Russian sources claimed that Russian forces repelled limited Ukrainian reconnaissance in force operations in Zaporizhia Oblast.
- The Russian military command appears to be introducing doctrinal organization to some of its irregular formations.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law on May 29 that will further strengthen the martial law regime in occupied areas of Ukraine.
- Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko is likely not hospitalized as of May 29.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 28, 2023
Russian forces conducted the largest Shahed drone strike against Ukraine since the start of the war overnight on May 27-28. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces launched 59 Shahed-131/136 drones, of which Ukrainian forces shot down 58. Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Colonel Yuriy Ihnat characterized this strike as the largest drone strike since the start of the war and stated that Russian forces chiefly targeted Kyiv. Zhytomyr Oblast Head Vitaliy Bunechko reported that Russian drones struck an unspecified infrastructure facility in the oblast. The Russian allocation of aerial munitions to targeting Kyiv rather than prioritizing infrastructure or military facilities continues to constrain this limited Russian air campaign’s ability to meaningfully degrade Ukrainian offensive capabilities for the upcoming counteroffensive, as ISW has previously assessed.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that the Russian relief in place operation in Bakhmut may continue past his initial June 1 deadline and last until June 5. Prigozhin stated on May 28 that Wagner’s withdrawal from the city may take a few more days because Wagner is not able to transfer all equipment in good condition by June 1. Prigozhin stated that Wagner forces intend to fully withdraw from Bakhmut to rear field camps by June 5. The Washington Post reported on May 28 that Ukrainian personnel in the Bakhmut area have observed Wagner forces leaving Bakhmut City itself and regular Russian personnel taking responsibility for Wagner’s previous positions in the city. The Ukrainian personnel reportedly stated that they cannot confirm that regular Russian forces are replacing Wagner throughout Bakhmut City, however. Russian sources amplified footage on May 27 and 28 purporting to show elements of the ”Nevsky” volunteer battalion and the irregular 1st ”Wolves” Sabotage and Reconnaissance Brigade operating on the flanks in the Bakhmut area. ISW has previously assessed that the “Wolves” Sabotage and Reconnaissance Brigade was operating in the Avdiivka area, further suggesting that Russian forces may be transferring irregular forces and Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) elements from around Avdiivka to the Bakhmut area. ISW previously assessed that the Russian transfer of these elements to Bakhmut may decrease the tempo of Russian offensive operations on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City front.
The tempo of Russian operations around Bakhmut remains notably low. The Ukrainian General Staff reported on May 28 that Russian forces conducted unsuccessful offensive operations near Orikhovo-Vasylivka (11km northwest of Bakhmut), west of Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut), and in the direction of Ivanivske (6k west of Bakhmut). Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty reported on May 28 that only one combat clash occurred near Bakhmut City in the past 24 hours. Geolocated footage published on May 28 indicates that Russian forces made marginal gains west of Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut). Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian forces are counterattacking west of Klishchiivka but that Ukrainian forces maintain their current positions in the area. A Russian source claimed that Ukrainian forces continued counterattacks near Orikhovo-Vasylivka on May 27, where Russian sources claimed Ukrainian forces advanced up to one kilometer on May 26. Ukrainian personnel in the Bakhmut area reportedly expressed optimism that the decreased tempo of Russian operations around Bakhmut may facilitate further limited and localized Ukrainian counterattacks. ISW previously assessed that the decreased tempo of Russian offensive operations in the Bakhmut area and the ongoing relief in place operation are likely providing Ukrainian forces in the area the initiative to launch a new round of operations around the city if they so choose.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin appears to have again indirectly undermined Russian President Vladimir Putin’s authority and regime. Prigozhin responded to a journalist’s question about Russian state media banning any discussions about Wagner forces, stating that unnamed Russian bureaucrats will only benefit from such censorship in the near term of one to three months before the Russian people will push back and start hating the bureaucrats. Prigozhin stated that Russian officials would have been able to enjoy their historic ability to censor Russian society if Russia had not started the war in Ukraine. Prigozhin then gave advice to an unnamed official: “if you are starting a war, please have character, will, and steel balls - and only then you will be able to achieve something.” Prigozhin implied that accomplishing real achievements would let the official avoid lying about the construction of new buildings, metro stations, and bridges in an effort to look good. Prigozhin notably shifted the discussion from talking about unnamed Russian officials to directly addressing a single man. Prigozhin’s comments are likely targeted at Putin whom the Russian state media has routinely portrayed as a leader minutely involved with small infrastructure projects and the lives of ordinary Russian people. Putin used to host annual hours-long “Direct Line” press conferences with constituents in which he often responded to inquiries that are best suited for local governments, for example.
Prigozhin may be attacking Putin for failing to give Prigozhin some promised reward for seizing Bakhmut. Prigozhin’s previous attack on Putin’s character occurred on May 9 – a symbolic holiday that Putin may have wanted to use to portray Russia’s claimed victory in Bakhmut as an achievement equivalent to Soviet Union’s drive on Berlin in 1945. Kremlin state media compared the seizure of Bakhmut city to the Soviet victory in Berlin on May 21, which likely indicates that the Kremlin was preparing to associate the victory in Bakhmut with Victory Day. Prigozhin claimed that Wagner had effectively captured Bakhmut by May 10 and cleared the city by May 20, and attempted to blame the delay in Wagner’s capture of the city on the Russian Ministry of Defense’s (MoD’s) withholding of ammunition. Prigozhin also claimed that his ”Bakhmut meatgrinder” offensive operation killed half of the Ukrainian army, a statement that Russian ultranationalist Igor Girkin declared to be false. Prigozhin also claimed that Wagner opened a springboard for further offensive operations in Donbas and sarcastically noted that Russian regular forces subordinated under the Russian MoD will be able to reach the Dnipro River, capture the territories of the four annexed regions, and capture Ukrainian strongholds west and north of Bakhmut.
Prigozhin’s jabs at Putin and the Russian MoD - in combination with his bragging about Wagner’s accomplishments – may suggest that Prigozhin is frustrated that he did not receive some promised compensation for his victory in the Battle for Bakhmut. The Russian MoD may have deliberately sabotaged Prigozhin days or weeks prior to May 9th to prevent Wagner from capturing the remaining few blocks in western Bakhmut before Victory Day, as Prigozhin suggests. Putin may have deliberately overlooked such MoD sabotage efforts to avoid having to fulfill whatever promise Prigozhin thinks Putin had made to him. Prigozhin has previously stated that if he was given 200,000 personnel, Wagner would have made further great advances on the frontlines. Prigozhin’s May 28 statement and his previous behavior may indicate that he had envisioned expanding Wagner at the expense of Russian conventional forces or replacing Russian military officials with Wagner-affiliated personnel. ISW previously assessed that Putin is a risk averse actor who is concerned over the health of his regime and thus unlikely to fully satisfy Prigozhin’s radical demands.
The Wagner Group held a reportedly illegal pro-Wagner rally in Yekaterinburg on May 28 despite the reported banning of the rally by Yekaterinburg authorities. Approximately 100 to 150 cars of Wagner personnel and supporters held a procession from Yekaterinburg to a cemetery in Berezovsky, Sverdlovsk Oblast, where the supporters laid flowers at a Wagner monument. Some Russian opposition sources claimed that local authorities explicitly banned Wagner from holding the rally and that Wagner held the rally in direct defiance of the ban. Footage shows luxury cars participating in the procession, suggesting that some local elites may be supporting Wagner. Sverdlovsk Oblast is a notable Russian defense industrial base (DIB) hub, and Russian authorities recently conducted several prominent arrests there of individuals including Wall Street Journal correspondent Evan Gershkovich on charges of espionage. Gershkovich notably travelled to Yekaterinburg to report on Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin’s criticisms of the Yekaterinburg History Museum Director Igor Pushkarev. Prigozhin has also notably feuded with Russian regional officials over allowing dead Wagner personnel to receive burials equivalent to those of regular Russian military personnel.
Russian propagandist Vladimir Solovyov criticized former Russian officer and ardent nationalist Igor Girkin on May 27. Solovyov accused Girkin of discrediting the Russian military and stated that Russian authorities should have already imprisoned Girkin. Solovyov complained that authorities have prosecuted other Russian milbloggers for discrediting the Russian military but have not touched Girkin. Girkin responded on May 28, noting that Solovyov is criticizing him despite his extensive military experience. Girkin highlighted that Solovyov has not criticized Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin despite Prigozhin’s criminal record and control over a “mercenary army.” Rumors of an investigation into Girkin for discrediting the Russian military previously gained prominence in mid-April, during which Prigozhin may have tried to pressure Girkin and his patronage networks as part of an ongoing feud to compete for influence and patronage.
Key Takeaways
- Russian forces conducted the largest Shahed drone strike against Ukraine since the start of the war overnight on May 27-28.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that the Russian relief in place operation in Bakhmut may continue past his initial June 1 deadline and last until June 5.
- The tempo of Russian operations around Bakhmut remains notably low.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin appears to have again indirectly undermined Russian President Vladimir Putin’s authority and regime.
- Prigozhin may be attacking Putin for failing to give Prigozhin some promised reward for seizing Bakhmut.
- The Wagner Group held a reportedly illegal pro-Wagner rally in Yekaterinburg on May 28 despite the reported banning of the rally by Yekaterinburg authorities.
- Russian propagandist Vladimir Solovyov criticized former Russian officer and ardent nationalist Igor Girkin on May 27.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces conducted limited offensive operations along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City front.
- Russian forces continued to fire on areas in Southern Ukraine.
- The UK Ministry of Defense (MoD) asserted that Russia is now demanding that Russian citizens make additional sacrifices to support the war effort.
- Russian occupation officials continue to forcibly deport Ukrainian children to Russia under the guise of summer camps.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 27, 2023
Wagner Group mercenaries appear to be withdrawing from Bakhmut city to reconstitute and regroup in the rear as Russian offensive operations decrease in and around the city. Ukrainian military officials reported that Russian offensive operations had dramatically decreased to two skirmishes in the Bakhmut direction, and Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar attributed this decrease to the Russian relief-in-place and regrouping of forces in the area.[1] The Ukrainian General Staff reported on May 27 that Russian forces conducted unsuccessful offensive operations west of Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut) and in the direction of Predtechyne (15km southwest of Bakhmut).[2] Malyar stated that Ukrainian forces hold dominant elevated positions north and south of Bakhmut and that Ukrainian forces stopped combat operations on May 26 and 27 to fulfill other unspecified tasks.[3] Malyar also stated that Ukrainian forces continue to control positions in the southwestern outskirts of Bakhmut City.[4] A prominent Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces are not conducting active operations aimed at regaining positions in Bakhmut City itself despite the possible continuation of localized Ukrainian counterattacks northwest and southwest of the city.[5]
Ukrainian National Security and Defense Council Secretary Oleksiy Danilov stated that Wagner mercenaries are withdrawing from the city of Bakhmut and are “regrouping to another three locations.”[6] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin reiterated that Wagner forces continued to withdraw from Bakhmut city on May 27.[7] Prigozhin’s statements are likely true given the decrease in Russian offensive capabilities around Bakhmut and Ukrainian statements regarding the situation in Bakhmut.
Key Takeaways
- Wagner Group mercenaries appear to be withdrawing from Bakhmut city to reconstitute and regroup in the rear as Russian offensive operations decrease in and around the city.
- The Russian military command may be transferring Donetsk People’s Republic’s (DNR) forces to relieve Wagner Group forces in Bakhmut city.
- The Russian transfer of DNR elements to Bakhmut may decrease the tempo of Russian offensive operations on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- The Russian military command appears to be reinforcing Bakhmut’s flanks with regular formations, however.
- Former Russian officer and ardent nationalist Igor Girkin accused Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin of planning a coup against the current Russian leadership.
- Ukrainian officials denied Western reporting that suggested that a Chinese diplomat expressed interest in a negotiated ceasefire in Ukraine amidst the likely renewal of Russia’s information campaign surrounding negotiations.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations northeast of Kupyansk and south of Kreminna.
- Russian forces continued to launch unsuccessful offensive operations on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Ukrainian forces continued to strike rear logistics nodes in southern Zaporizhia oblast.
- The Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) warned on May 26 that Russian forces are preparing to conduct large scale provocations to create radiological danger at the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP).
- The Russian Ministry of Justice registered the civil society group “Council of Mothers of Wives” as a foreign agent on May 26, likely to curb resistance to ongoing and future Russian force generation efforts.
- Russian authorities are escalating efforts to portray Russia as a safe guardian of Ukrainian children.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 26, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 1:30pm ET on May 26. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 27 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that Wagner forces continue to hand over positions in Bakhmut to the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and withdraw from the city. Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed on May 26 that the MoD is fulfilling its agreement by actively deploying regular Russian units to Wagner-held positions in Bakhmut city.[1] Prigozhin claimed that Wagner is conducting an organized withdrawal from Bakhmut and reiterated that the Russian MoD will fully control the city and its surrounding areas by June 1.[2] A Russian milblogger published footage of Prigozhin visiting Russian rear positions where Wagner forces are allegedly withdrawing to.[3] ISW has not observed visual confirmation of regular Russian forces taking up Wagner positions in Bakhmut itself or that Wagner is leaving the city. ISW has recently observed footage purporting to show elements of the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) 123rd Brigade, likely previously deployed near Siversk, operating in the Bakhmut area, and DNR forces may be replacing Wagner formations.[4]
Ukrainian sources claim that Wagner forces are still present in Bakhmut and that the tempo of Russian offensive operations around the city continues to decrease. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar reported that regular Russian units have replaced Wagner units in Bakhmut’s suburbs, likely referring to areas on the flanks around Bakhmut.[5] Malyar claimed that Ukrainian forces still control positions on the southwestern outskirts of the city and that Wagner forces are still present in Bakhmut city itself.[6] Ukrainian sources continue to report that the tempo of Russian offensive operations around Bakhmut has declined since the claimed Russian capture of the city.[7] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces conducted unsuccessful offensive operations near Bakhmut and in the direction of Predtechyne (15km southwest of Bakhmut) on May 26.[8]
Continued successful limited Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks may complicate the Russian relief in place operation in Bakhmut. Russian milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted successful counterattacks near Orikhovo-Vasylivka (11km northwest of Bakhmut) and Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut).[9] A prominent milblogger claimed that Ukrainian counterattacks near Orikhovo-Vasylivka caused elements of the “Veterany” private military company (PMC) to retreat up to a kilometer from their previously held positions in the area.[10] Milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian forces captured elevated positions along the E40 (Bakhmut to Slovyansk) highway near Orikhovo-Vasylivka and that fighting is ongoing in the area.[11] A Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces advanced towards Klishchiivka and crossed the Siverskyi Donets Canal, possibly threatening to encircle the settlement and force Russian forces to retreat towards the east.[12] Geolocated footage published on May 24 and 25 indicates that Russian forces likely regained limited positions west of Klishchiivka, however.[13] ISW has previously assessed that Russian forces may struggle to conduct a relief in place of Wagner forces in Bakhmut, and successful limited and localized Ukrainian counterattacks will likely complicate their ability to do so.[14] The decreased tempo of Russian offensive operations in the Bakhmut area and the reported ongoing relief in place operation are likely further providing Ukrainian forces in the area the initiative to launch a new phase of operations around the city if they so choose.[15]
Russian forces conducted a large-scale missile and drone strike across Ukraine on May 25 and 26. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces launched ten Kh-101/555 air-based cruise missiles at Kyiv and Dnipropetrovsk oblasts and launched eight S-300/400 anti-aircraft guided missiles at Dnipro City.[16] Russian forces also reportedly launched 31 Shahed-131/136 drones from the southern and northern directions on the night of May 25 to 26. The Ukrainian General Staff stated that Ukrainian forces destroyed all ten Kh-101/555 missiles and 23 Shahed-131/136 drones.[17] The Kyiv Oblast Military Administration Head Ruslan Kravchenko stated that Russian forces have conducted 13 missile attacks on Kyiv Oblast since beginning of May.[18] Ukrainian sources reported that the Russian forces struck a civilian hospital and residential buildings in Dnipro in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast.[19]
The Kremlin is likely reviving its information campaign to coerce the West into forcing Ukraine to accept concessions and negotiate on terms favorable to Russia. The Kremlin claimed on May 26 that Russian President Vladimir Putin expressed “the openness of the Russian side to dialogue on the political and diplomatic track, which is still blocked by Kyiv and its Western sponsors” in a phone call with Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva.[20] Putin’s statement does not indicate that Russia is interested in pursuing negotiations with Ukraine, and the Kremlin has not established any serious grounds for negotiations nor abandoned its maximalist goals to force the Ukrainian government to capitulate. The Kremlin is likely attempting to intensify its false claims about its readiness to negotiate with Ukraine amidst the arrival of the Chinese Special Representative for Eurasian Affairs Li Hui in Moscow on May 26 to discuss a negotiated settlement to Russia’s war in Ukraine.[21] The Wall Street Journal (WSJ) reported that Li previously urged European officials to end the conflict in Ukraine before it escalates during his visit to European states in the past week.[22] The WSJ also reported that a (likely European, but unspecified) diplomat who spoke to Li explained that freezing the conflict was not beneficial to international interests and that Europe would not withdraw its support for Ukraine. The WSJ also reported that another (likely European, but unspecified) diplomat claimed that China’s main interests are ensuring Russian victory and ensuring that Russia does not use nuclear weapons. The claimed interaction likely indicates that China may be attempting to push the West to influence Ukraine into accepting a ceasefire. The Kremlin is likely amplifying its false interests in negotiations ahead of the planned Ukrainian counteroffensive in order to discourage continued Western aid to Ukraine. ISW has previously reported on Russia’s peace negotiation information operations to deter Western support for Ukraine.[23]
The Wagner Group reportedly exchanged 106 Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs) for an unspecified number of Russian POWs on May 25, suggesting that Wagner may have conducted the exchange independently of the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD). Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin published footage on May 25 showing Wagner forces conducting the exchange of Ukrainian POWs and Russian POWs.[24] Separate geolocated footage published on May 25 indicates that the exchange occurred near Bakhmut.[25] Ukrainian sources reported on May 25 that Ukraine received 98 soldiers and eight officers in the exchange.[26] Russian sources did not specify the number of returned Russian personnel but claimed that some were from the 155th Naval Infantry Brigade of the Pacific Fleet and unspecified Chechen Akhmat formations.[27] ISW previously reported that Wagner has purportedly conducted a prisoner exchange without the Russian MoD’s involvement.[28]
Key Takeaways
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that Wagner forces continue to hand over positions in Bakhmut to the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and withdraw from the city.
- Ukrainian sources claim that Wagner forces are still present in Bakhmut and that the tempo of Russian offensive operations around the city continues to decrease.
- Continued successful limited Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks may complicate the Russian relief in place operation in Bakhmut.
- Russian forces conducted a large-scale missile and drone strike across Ukraine on May 25 and 26.
- The Kremlin is likely reviving its information campaign to coerce the West into forcing Ukraine to accept concessions and negotiate on terms favorable to Russia.
- The Wagner Group reportedly exchanged 106 Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs) for an unspecified number of Russian POWs on May 25, suggesting that Wagner may have conducted the exchange independently of the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD).
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations along the Avdiivka-Donetsk front.
- Russian forces continued to target Ukrainian positions in southern Ukraine.
- Russian officials are continuing to form new volunteer formations to defend Russian regions that border Ukraine.
- Russian occupation officials continuing attempts to erase Ukrainian cultural heritage by looting Ukrainian artifacts.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 25, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 12pm ET on May 25. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 26 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin announced on May 25 that the Wagner Group began handing over its positions in Bakhmut to the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and claimed Wagner will entirely withdraw from the city on June 1. Footage posted on May 25 shows Prigozhin speaking with Wagner fighters in Bakhmut and announcing that Wagner began handing over their positions to the Russian MoD and withdrawing to rear areas of the city.[1] Prigozhin reminded some of the fighters that Wagner will withdraw from the city entirely and reconstitute, rest, and train following June 1.[2] Prigozhin also claimed that Wagner plans to leave behind ammunition and provisions for regular Russian troops if necessary and sardonically showed two Wagner fighters who he claimed he will leave behind for the Russian MoD.[3] ISW has previously reported that Prigozhin announced that Wagner would hand over its positions to the MoD starting on May 25 and withdraw from Bakhmut by June 1, but it remains unclear if Wagner will be able to withdraw the entirety of its contingent by June 1 and if Russian MoD troops will execute a successful relief in place.[4]
Russia and Belarus signed agreements formally advancing preparations to deploy Russian tactical nuclear weapons to Belarus as part of a longstanding effort to cement Russia’s de facto military control over Belarus, though Russia has not yet deployed nuclear weapons to Belarus and their possible deployment is highly unlikely to presage any Russian escalation. Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu and Belarusian Defense Minister Viktor Khrenin signed documents on the deployment of Russian non-strategic (tactical) nuclear weapons to Belarusian territory during a meeting of defense ministers of the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) in Minsk, Belarus on May 25.[5] Shoigu emphasized that Russia would retain control of the tactical nuclear weapons in the event of their deployment to Belarus and claimed that Belarusian aircraft are now capable of carrying nuclear weapons.[6] Russian President Vladimir Putin previously announced on March 25 that Russia would deploy tactical nuclear weapons to Belarus by July 1, likely to renew tired information operations about the potential for nuclear escalation over the war in Ukraine.[7] Russia has long fielded nuclear weapons that are able to strike any target that tactical nuclear weapons launched from Belarus could also hit, and ISW continues to assess that Putin is extraordinarily unlikely to use nuclear weapons in Ukraine or elsewhere.[8] Shoigu also announced that Russian forces will deploy additional military contingents to Belarus to develop military infrastructure, expand joint combat training, and conduct reconnaissance activities near the borders of the Union State.[9] The deployment of tactical nuclear weapons to Belarus requires both significant military infrastructure and Russian command and control over elements of the Belarusian Armed Forces. The Kremlin likely intends to use these requirements to further subordinate the Belarusian security sphere under Russia.
Russian President Vladimir Putin met with the leaders of the Eurasian Economic Union member states and several other post-Soviet heads of state at the Supreme Eurasian Economic Council in Moscow on May 25, likely to expand sanctions evasion opportunities. Armenian President Nikol Pashinyan, Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko, Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, and Kyrgyz President Sadyr Japarov attended the meeting alongside leaders of non-Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) members states, including Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev, Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev, and Tajik President Emomali Rahmon.[10] Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) Executive Secretary Sergei Lebedev and Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Secretary General Zhang Min also attended the meeting.[11] Putin, Pashinyan, and Tokayev all called on further development of the EAEU’s relationship with third-party countries, including the negotiation of free trade agreements with the United Arab Emirates, India, Egypt, Indonesia, Israel, and Iran.[12] Tokayev highlighted efforts to create new international transport routes to China, India, Pakistan, Iran, the Middle East, East Asia, and Southeast Asia.[13] Tokayev also offered to help Russia launch the 2873km Chelyabinsk-Bolshak-Iran high speed freight railway, a project similar to the recent agreement between Russia and Iran to build a segment of the North-South corridor railway project between Rasht and Astara in order to strengthen Russo-Iranian military-economic cooperation.[14] Putin also called for the EAEU to create technological alliances with third-party countries, likely aimed at securing critical components that Russia is struggling to produce or acquire itself.[15]
The Kremlin is likely attempting to convince EAEU members states and other post-Soviet countries to aid in the Kremlin’s ongoing sanctions evasion schemes with China, Iran, and others by facilitating the logistics of those schemes.[16] Putin called for an increase in the number of new joint ventures under the common trademark ”made in the EAEU,” a measure likely aimed at rebranding Russian products as being EAEU products to avoid Western sanctions on exports.[17] Lukashenko and Tokayev both specifically called for the creation of a full-fledged Economic Union with a functioning common market, and Lukashenko claimed that EAEU representatives are discussing the creation of a common market for gas, oil, and petroleum products.[18] Belarus and Kazakhstan are likely both heavily involved in helping Russia evade sanctions, and the Kremlin is likely seeking to expand and formalize those relationship with the wider EAEU.[19] ISW previously assessed that the Kremlin appears to be leveraging its dominance in the CSTO to court member states to procure dual-use technologies that Russia cannot directly purchase due to Western sanctions, and it appears that the Kremlin is attempting to similarly leverage its role in the EAEU.[20]
Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov announced that Russian officials have created seven territorial defense battalions in Belgorod Oblast as of May 24, likely in order to posture his personal engagement in the defense of Russian border areas following the May 22 all-Russian pro-Ukrainian raid into Belgorod Oblast.[21] Gladkov stated that the seven battalions comprise 3,000 people in total, noting that they are already combat-ready units.[22] Gladkov previously announced the creation of several territorial defense battalions in December 2022, and has likely re-upped discussion of them in response to increased anxiety in border areas following the May 22 raid.[23] A prominent Russian milblogger claimed on May 24 that these battalions have a strong presence but are severely hindered by an inadequate weapons supply.[24] The milblogger claimed that United Russia Secretary General Andrey Turchak had urged President Putin to address the legal issues associated with providing weapons to the battalions a month ago.[25] These battalions, if left unfunded and unequipped, are very unlikely to have a substantial positive effect on the security of Russian border areas, however. The publicization of these formations is also likely meant to support ongoing Russian information operations that aim to generate support for a protracted war by portraying Ukraine as existentially threatening Russia.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin held a meeting with representatives of Russian oblasts bordering Ukraine to discuss fortifying border areas on May 24. Prigozhin proposed the creation of additional trenches, dugouts, and fire support along the Russia-Ukraine border, arguing that these structures can provide significant protection against possible military threats.[26] Prigozhin also emphasized the need to strengthen the presence of Russian forces along the border, expand the armament of border guards, and retrain them from using machine guns to grenade launchers.[27] Prigozhin stated that the May 22 raid of Belgorod Oblast by all-Russian pro-Ukrainian forces exposes how Russia lacks the rapid reaction forces needed to protect its borders against military threats.[28] Prigozhin stated that a general mobilization of the Russian population is inevitable, emphasizing the fact that Russian leadership can no longer snap its fingers to fix manpower shortcomings.[29] Prigozhin stated that a general mobilization should begin now in order to provide the people with the necessary training, a process that typically takes at least a minimum of four to six months.[30]
Wagner and Russian forces have notably engaged in previous efforts to fortify border areas, and the recent Belgorod Oblast raid exposed major shortcomings in these efforts. Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov reported on March 9 that Russian authorities spent 10 billion rubles (about $132 million) to construct the “Zasechnaya Line” of fortifications along Belgorod Oblast’s border with Ukraine.[31] Prigozhin announced the construction of a set of fortifications called the “Wagner Line” throughout Luhansk, Donetsk, and Belgorod oblasts in October 2022, and directly criticized the Russian bureaucracy for not supporting the construction of the line.[32] New calls to fortify Russian regions along the Russia-Ukraine border will likely have little substantial effect, with Russian and Wagner forces misallocating manpower that would be better suited supporting active offensive operations (or defenses in occupied Ukraine itself) by manning these fortifications. Existing fortifications and defensive preparations did little to thwart the limited May 22 raid into Belgorod. Prigozhin is likely taking advantage of information space anxieties surrounding this reality following the raid to build out his own domestic influence.
Russian political strategist Konstantin Dolgov claimed on May 25 that he was fired as a result of his May 23 interview with Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin. Dolgov published a post to his Telegram channel alleging that he was fired from his position with Russian propaganda platform Telega Online “because of an interview with Prigozhin” and refuted claims that he had previous plans to leave.[33] Prigozhin used his interview with Dolgov to highlight the massive scale of losses suffered by the Wagner Group during the Battle of Bakhmut, mount scathing critiques against Defense Minister Shoigu and Chief of the Russian General Staff Army General Valery Gerasimov, attack the families of Russian elites, and vaguely threaten violence against the broader Russian military establishment.[34] Dolgov complained that he is being personally punished for Prigozhin’s replies because Russian authorities cannot do anything about Prigozhin himself and suggested that Russia President Vladimir Putin would disagree with his firing.[35] Dolgov’s firing may be part of a larger informational campaign pushed by Russian authorities that is aimed at quietly disenfranchising Prigozhin in an attempt to counterbalance Prigozhin’s ever-growing platform, which continues to deprive Russian military officials of informational oxygen.
Russia conducted another massive Shahed-131/136 drone strike across Ukraine on the night of May 24 to 25. Ukrainian military sources reported that Russian forces launched 36 Shahed-131/136 drones at Ukraine from the northern and southern directions and that Ukraine shot down all 36 of the drones.[36] Russian milbloggers claimed that some of the drones reached their intended targets through rear areas of Ukraine, including Kyiv Oblast.[37] Ukraine’s Southern Operational Command noted on May 25 that Ukraine has destroyed 357 Shahed-type drones since Russia began using them in 2022.[38] The White House reported on May 15 that Russia has purchased over 400 drones (primarily Shaheds) from Iran since August 2022.[39] The suggestion that Ukraine has shot down 357 Shahed drones since August 2022 is likely inflated—Ukrainian officials may sometimes count drone crashes due to user error or technical malfunction as official shoot downs, so the actual number is likely to be somewhat lower.
Russian President Vladimir Putin continued attempts to portray Russia as an effective international mediator by mediating negotiations between Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan and Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev. Kremlin newswire RIA Novosti reported on May 25 that Pashinyan stated that Armenia and Azerbaijan have agreed on a mutual recognition of territorial integrity.[40] Aliyev noted that Armenia and Azerbaijan could reach a peace agreement now that Armenia recognizes Nagorno-Karabakh as part of Azerbaijan. Kremlin newswire TASS reported that Pashinyan qualified that statement on May 22 and emphasized that Armenia would recognize Nagorno-Karabakh as a part of Azerbaijan on the condition that Azerbaijan ensures the security of Nagorno-Karabakh’s Armenian residents.[41] Russian media reported that Putin noted the importance of the agreement and facilitated bilateral talks with Pashinyan and Aliyev before holding a trilateral meeting.[42] European Council President Charles Michel has also held talks to normalize Armenian-Azerbaijani relations, and Putin is likely seeking to act as a diplomatic counter-balance to the European involvement in Eurasian affairs.[43]
Key Takeaways
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin announced on May 25 that the Wagner Group began handing over its positions in Bakhmut to the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and claimed Wagner will entirely withdraw from the city on June 1. It remains unclear if Wagner will be able to withdraw the entirety of its contingent by June 1 and if Russian MoD troops will execute a successful relief in place.
- Russia and Belarus signed agreements formally advancing preparations to deploy Russian tactical nuclear weapons to Belarus as part of a longstanding effort to cement Russia’s de facto military control over Belarus, though Russia has not yet deployed nuclear weapons to Belarus and their possible deployment is highly unlikely to presage any Russian escalation.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin met with the leaders of the Eurasian Economic Union member states and several other post-Soviet heads of state at the Supreme Eurasian Economic Council in Moscow on May 25, likely to expand sanctions evasion opportunities.
- Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov announced that Russian officials have created seven territorial defense battalions in Belgorod Oblast as of May 24, likely in order to posture his engagement in the defense of Russian border areas following the May 22 all-Russian pro-Ukrainian raid into Belgorod Oblast.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin held a meeting with representatives of Russian oblasts bordering Ukraine to discuss fortifying border areas on May 24.
- Wagner and Russian forces have notably engaged in previous efforts to fortify border areas, and the recent Belgorod Oblast raid exposed major shortcomings in these efforts.
- Russian political strategist Konstantin Dolgov claimed on May 25 that he was fired as a result of his May 23 interview with Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin.
- Russia conducted another massive Shahed-131/136 drone strike across Ukraine on the night of May 24 to 25.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin continued attempts to portray Russia as an effective international mediator by mediating negotiations between Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan and Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev.
- Russian forces continued limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and south of Kreminna.
- Russian forces continued limited ground attacks around Bakhmut as Wagner Group forces reportedly began their withdrawal from frontline areas the city.
- Russian forces continued ground attacks along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian sources claimed that Russian forces shot down six drones over Crimea.
- Russian forces are reportedly continuing to recruit personnel with various diseases.
- Russian occupation officials continue to announce partnerships with various local Russian officials to improve the standard of living in occupied territories.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 24, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 12 pm ET on May 24. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 25 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Discussions regarding reported Russian losses in Bakhmut have saturated the pro-war information space and are drowning out any remaining positive informational effect resulting from the city’s capture. Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed during an interview with Russian political strategist Konstantin Dolgov on May 23 that Wagner lost 10,000 convict recruits and 10,000 full-time professional Wagner fighters killed in action over the course of the Battle for Bakhmut.[1] Prigozhin specifically noted that Wagner had recruited 50,000 prisoners, 20 percent of whom (10,000) died in fighting for Bakhmut.[2] Russian milbloggers immediately seized on the reported losses, shifting the overall Russian conversation away from discussions of the significance of the capture of Bakhmut and amplifying speculation surrounding the reported losses. The nationalist pro-war faction, exemplified by the views of former Russian officer Igor Girkin, commented on the massive scale of the reported losses and speculated that real losses may be much higher. Russian politician Viktor Alksnis simply remarked that the Soviet Army lost far fewer soldiers (15,051) in nine years in Afghanistan.[3] Girkin stated that he believes that Wagner’s actual losses could be more than 1.5 times higher than Prigozhin’s claims and pointed out that of the 50,000 recruits Wagner received from prisons, 10,000 died in action and 26,000 reportedly received pardons and returned to Russia, leaving 14,000 prison recruits unaccounted for.[4] Girkin suggested that a large portion of these 14,000 unaccounted-for prison recruits may have also been killed in action and claimed that Wagner has likely suffered more than 40,000 killed in action.[5] Girkin suggested that Prigozhin “keep [his] mouth shut” and stop talking about “wild losses for a very insignificant result.”[6] Another Russian milblogger, by contrast, praised Prigozhin for being open about the scale of losses and stated that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) would have hidden such figures.[7]
Key Takeaways
- Discussions regarding reported Russian losses in Bakhmut have saturated the pro-war information space and are drowning out any remaining positive informational effect resulting from the city’s capture.
- The overall Russian information space response to the capture of Bakhmut has fixated on attributing responsibility for its capture and speculating on the associated costs of the operation, thus depriving the Russian MoD of the oxygen necessary to positively frame the city’s capture.
- Prigozhin is likely using his heightened profile following the capture of Bakhmut to intensify his attacks against the Russian military establishment and elites. Prigozhin is also using the perception that Wagner is responsible for the capture of Bakhmut to advocate for a preposterous level of influence over the Russian war effort in Ukraine.
- The Kremlin continues efforts to portray Russia as having significant diplomatic partnerships.
- Russian sources continued to respond to the limited all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and the Freedom of Russia Legion (LSR) raid into Belgorod Oblast.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces continued limited ground attacks on the outskirts of Bakhmut and along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces continue to target Ukrainian positions in southern Ukraine with FAB-500 aerial bombs.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu claimed on May 24 that more than 120,000 Russian personnel have undergone training since the start of the full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine.
- The Russian Federation Council approved a law on holding elections in territories under martial law on.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 23, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 4pm ET on May 23. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 24 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Russian authorities ended the “counterterrorism” operation in Belgorod Oblast and claimed to have defeated the all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and the Freedom of Russia Legion (LSR) in the region on May 23. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Western Military District (WMD) Border Guards units defeated the raid and expelled all “saboteurs” from Belgorod Oblast.[i] Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov announced that the “counterterrorism” operation had ended but called on civilians who evacuated to wait before returning to the border settlements.[ii] Russian authorities later announced on May 23 that authorities evacuated 100 civilians from nine border settlements in Belgorod Oblast on May 22 after Gladkov originally denied conducting formal evacuations.[iii] Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov stated that Russian President Vladimir Putin will not hold an emergency meeting of the Russian Security Council to discuss the Belgorod raid but will instead discuss the situation during the Security Council’s planned May 26 meeting, likely in an effort to project confidence about Russian handling of the situation.[iv]
Russian forces likely pushed the RDK and LSR forces at least to the Kozinka border settlement and possibly out of Russian territory as of May 23. Kozinka is located approximately 76km southeast of Sumy City. Russian sources amplified footage of Russian forces firing on RDK and LSR vehicle positions near the Kozinka border checkpoint overnight and claimed that Russian forces recaptured Kozinka and its border checkpoint in the morning.[v] Geolocated footage from Russian state media shows damaged and destroyed vehicles at the checkpoint.[vi] Some Russian sources claimed that RDK and LSR forces entrenched themselves in the Kozinka church but that preliminary reports suggest Russian forces may have ousted the Ukrainian forces by the evening.[vii] Russian sources claimed that Russian forces began clearing operations in Kozinka and Glotovo (immediately east of Kozinka) on May 23.[viii] Geolocated footage posted on May 23 shows the aftermath of shelling Gora Podol (about 6km northwest of Kozinka) and Russian infantry conducting patrols between Grayvoron (about 7km northwest of Kozinka) and Gora Podol, suggesting that RDK and LSR personnel no longer hold or never held positions in the settlement.[ix] It is unclear whether the RDK and LSR captured any villages on May 22 or May 23, however. The LSR claimed that LSR and RDK personnel continued to operate in Belgorod Oblast on May 23, however.[x]
Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted raids across the Kharkiv-Belgorod border on May 23, but ISW has observed no confirmation that these raids occurred. Some Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian and Ukraine-affiliated formations – including Azov Regiment, Kraken Regiment, Territorial Defense, and regular Ukrainian forces – and RDK personnel attempted additional raids near Gorkovsky, Bogun-Gorodok, and Tsapovka, and managed to cross the border south of Shchetinovka.[xi] Other Russian sources denied claims that sabotage groups crossed the Kharkiv-Belgorod border.[xii]Russian sources also claimed that Ukrainian forces accumulated reserves less than 10 kilometers from the Kharkiv-Belgorod border and expressed fear about the threat of further raids.[xiii] One milblogger claimed that the Azov Regiment, Kraken Regiment, Territorial Defense, and regular Ukrainian forces all took part in a raid in Bryansk Oblast on May 22, but ISW has still not observed confirmation of this claimed raid.[xiv]
The Russian information space largely hyperfixated on speculated goals for the raids and on the conduct of the Russian response. Some Russian milbloggers amplified claims that a drone struck the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) building in Belgorod City and speculated that Ukrainian forces aimed to attack the FSB and Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) in the raid.[xv] Russian sources also amplified a photograph of Colonel General Alexander Lapin posing with a captured vehicle and claimed that Lapin led the counterterrorism operation alongside elements of the 3rd Motorized Rifle Division (20th Guards Combined Arms Army, Western Military District).[xvi] Many Russian sources praised Lapin for organizing Russian forces to conduct coherent counterterrorism operations after the Russian Border Service failed to repel the raids.[xvii] Some sources criticized the decision to give Lapin command and noted Lapin’s prior military failures such as the disastrous Siverskyi Donets river crossing near Bilohorivka, Luhansk Oblast in May 2022.[xviii] Lapin has notably returned to commanding Russian operations in eastern Ukraine after suffering intense criticism for commanding the operations to take Severodonetsk and Lysychansk, and Lapin has not received much praise in the information space since the campaign to undermine him led to Lapin’s dismissal in November 2022.[xix] The openness of Russian milbloggers to praise Lapin for commanding the defense against an extremely small and limited border incursion suggests that at least some milblogger factions are amenable to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s tendency to rotate old and disgraced commanders.[xx] The Russian reaction to the raid in the information space and in the reported military activities appears to be a highly disproportionate response to a very small and localized undertaking. Russian forces should not have required significant reinforcements—or the involvement of a colonel general—to repulse a raid conducted by reportedly 13 armored vehicles.[xxi]
Ukrainian officials stated that the pace of fighting in the Bakhmut direction has decreased amid continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks on May 23. The Ukrainian General Staff did not report fighting in Bakhmut City in its 1800 situational report for the first time since December 2022, suggesting that Wagner Group forces may have made further advances within the city. The General Staff also reported that Russian forces conducted unsuccessful offensive actions near Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut).[xxii] Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated that combat operations have decreased in and around Bakhmut and reiterated that Ukrainian forces maintain positions in a fortified area near the MiG-17 monument in western Bakhmut.[xxiii] A milblogger amplified video footage purportedly showing Wagner forces near the MiG-17 monument and claimed that there are no Ukrainian forces in the area, however.[xxiv] Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated that Ukrainian forces advanced 200 to 400 meters along the flanks of Bakhmut and still control a number of buildings and fortifications in southwestern Bakhmut.[xxv] A Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces advanced near Yahidne (1km northwest of Bakhmut) and that Russian forces unsuccessfully attacked near Hryhorivka (8km northwest of Bakhmut) and Ivanivske (immediately west of Bakhmut).[xxvi] Another milblogger denied reports that Ukrainian forces made gains during counterattacks northwest and southwest of Bakhmut and assessed that a Russian offensive from Bakhmut toward Ivanivske or Bohdanivka remains unlikely.[xxvii]
Key Takeaways
- Russian authorities ended the “counterterrorism” operation in Belgorod Oblast and claimed to have defeated the all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and the Freedom of Russia Legion (LSR) in the region on May 23.
- Russian forces likely pushed the RDK and LSR forces at least to the Kozinka border settlement and possibly out of Russian territory as of May 23.
- Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted raids across the Kharkiv-Belgorod border on May 23, but ISW has observed no confirmation that these raids occurred.
- Ukrainian officials stated that the pace of fighting in the Bakhmut direction has decreased amid continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks on May 23.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces continued offensive operations on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces continued defensive operations in southern Ukraine ahead of the planned Ukrainian counteroffensive.
- Pardoned Wagner Group convicts continue to commit crimes in Russia after finishing their military contracts with Wagner.
- Zaporizhia Oblast occupation officials announced the start of preliminary voting for the ruling United Russia party.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 22, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 4pm ET on May 22. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 23 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Elements of the all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and Freedom of Russia Legion (LSR) conducted a raid into Belgorod Oblast on May 22. Russian sources began reporting on the morning of May 22 that a detachment of the RDK and LSR consisting of two tanks, an armored personnel carrier, and nine other armored vehicles crossed the international border and captured Kozinka, a settlement in the Grayvoron region of Belgorod Oblast within 600 meters of the border with Sumy Oblast.[1] Several Russian sources claimed that the grouping then captured the settlements of Glotovo and Gora Podol (3km and 5km from the border, respectively), although some milbloggers disputed claims that the attack completely captured Glotovo or Gora Podol, instead reporting that RDK forces only got to the Glotovo House of Culture.[2] ISW has not yet observed geolocated confirmation that the RDK or LSR reached Glotovo or Gora Podol. Geolocated footage posted on May 22 does confirm that the RDK struck a border post near Kozinka before crossing the border with at least one tank.[3] The RDK also posted footage reportedly showing the body of a Russian border guard in a border station, likely from the border crossing near Kozinka.[4] Russian milbloggers later claimed that Russian troops retook control of all three settlements.[5] Some Russian sources additionally reported that Russian forces repelled pro-Ukrainian sabotage groups near Dronovka, about 22km northwest of Kozinka.[6] The RDK additionally posted footage reportedly outside two settlements near the border area in Bryansk Oblast, but the nature of this incursion is unclear and ISW has not observed additional evidence or discourse surrounding actions in Bryansk Oblast on May 22.[7]
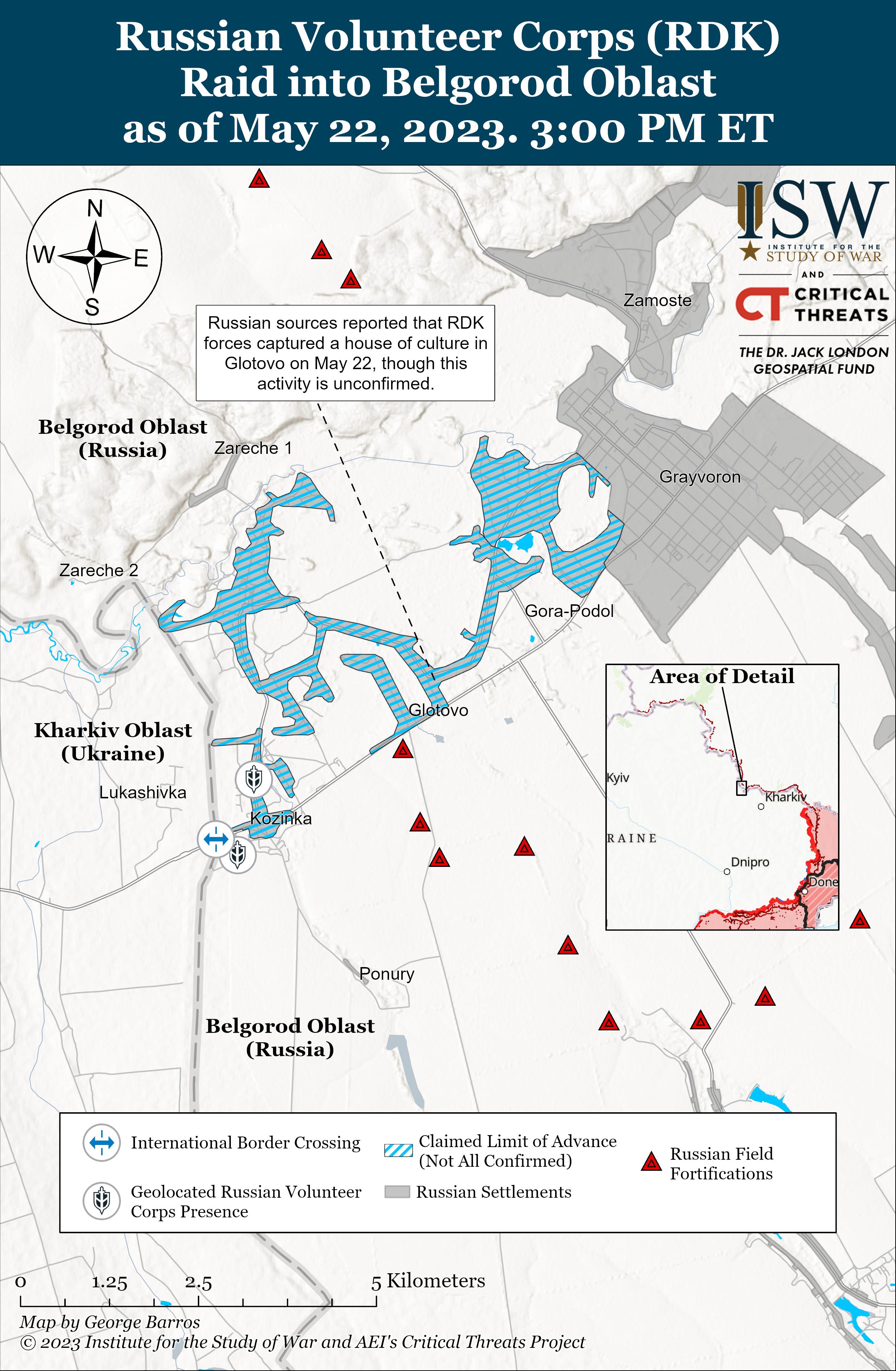
Ukrainian officials noted that they are aware of the attack but denied any direct involvement by the Ukrainian Armed Forces. Ukrainian Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Spokesperson Andriy Yusov noted that the RDK and LSR are comprised exclusively of Russian citizens and reported that the groups launched an operation in Belgorod Oblast to “liberate these territories...from the so-called Putin regime” and create a “security zone” by the border to protect Ukrainian civilians from further Russian shelling.[8] Advisor to the Head of the Ukrainian President’s Office Mykhailo Podolyak stated that Ukraine is observing and studying the situation but “has no direct relation to it,” noting that armed anti-regime Russian partisan movements are inevitable against the backdrop of the war.[9]
The raid prompted a slate of responses from local and federal Russian officials. Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov announced on May 22 the start of a counterterrorism operation regime in order to “ensure the safety of citizens in Belgorod Oblast.”[10] While some social media users posted footage claiming to show an official evacuation from the Grayvoron region, the Belgorod Oblast Ministry of Emergency Situations reported that it never announced an evacuation and suggested that some individuals may be leaving of their own accord.[11] Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov stated that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD), Federal Security Service (FSB), and Border Service reported to Russian President Vladimir Putin on an “attempt by Ukrainian saboteurs to break into Belgorod Oblast.”[12] Peskov also accused Ukraine of staging the incident in order to distract from the situation in Bakhmut.[13] A Russian milblogger additionally claimed that the Russian military leadership decided to deploy the 74th Motorized Rifle Brigade (41st Combined Arms Army, Central Military District) to the Belgorod Oblast border area in order to counter the attack.[14]
The Russian information space responded with a similar degree of panic, factionalism, and incoherency as it tends to display when it experiences significant informational shocks. Some milbloggers fixated on the fact that the RDK and LSR are comprised of mostly Russians and labeled them traitors to Russia, baselessly accusing them of working under the GUR.[15] Several milbloggers additionally speculated that the attack was a purposeful information operation intended to distract from the recent Russian capture of Bakhmut and to instill panic in the Russian information space in advance of a potential Ukrainian counteroffensive.[16] Former Russian officer and ardent nationalist milblogger Igor Girkin remarked that he has long warned that such cross-border raids may be part of a wider Ukrainian counteroffensive strategy.[17] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin took advantage of the incident to accuse the Russian government and its bureaucratic inertia of contributing to the attack and criticized the Russian MoD for being unable to strengthen Russian borders and defend Russia.[18] The first observed line of Russian defensive fortifications notably runs 2km in from of Gora Podol, and the suggestion that RDK forces managed to penetrate the defensive line emphasizes the weakness of such fortifications at least when not fully manned by well-prepared and well-equipped soldiers. While the majority of milbloggers responded with relatively varied concern, anxiety, and anger, the information space did not coalesce around one coherent response, which indicates first and foremost that the attack took Russian commentators by surprise.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that Wagner forces will withdraw from the entire frontline in Ukraine after June 1 in order to reconstitute and train for about two months. Prigozhin claimed on May 21 – one day after he declared victory in Bakhmut City – that Wagner forces will give Russian conventional forces control of Bakhmut on May 25 and completely withdraw from the entire frontline by June 1 to rest and reconstitute over a two-month period.[19] Prigozhin also claimed that any reports of Wagner assault operations during that two-month period are fake unless he says otherwise. ISW previously assessed that Wagner forces are unlikely to continue fighting beyond Bakhmut due to severe depletion and the culmination of their offensive capabilities.[20] The two-month reconstitution period Prigozhin has announced could have Wagner forces sitting out key parts of the Ukrainian counter-offensive depending on when and how it begins.
Ukrainian officials stated that limited fighting continued in and around Bakhmut on May 22. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that fighting continues in Bakhmut and that Russian forces conducted unsuccessful ground attacks near Hryhorivka (8km northwest of Bakhmut) and south of Ivanivske (immediately west of Bakhmut).[21] Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar reiterated that Ukrainian forces maintain positions in a fortified area in western Bakhmut and that fighting for heights north and south of Bakhmut continues.[22] Geolocated footage published on May 21 shows that Wagner forces advanced towards the T0504 entrance to southwestern Bakhmut.[23] A prominent Russian milblogger claimed that fighting is ongoing just west of Bakhmut near Khromove as of May 21.[24] Another milblogger claimed on May 22 that Russian forces attempted a limited ground attack south of Bakhmut near Bila Hora.[25] Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) Head Denis Pushilin, Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin, and other Russian sources claimed that Russian forces began clearing and demining operations on the western outskirts of Bakhmut.[26]
The Russian informational response to the capture of Bakhmut has thus far focused on competing for responsibility for the victory rather than discussing the resulting military situation. Prominent Russian milbloggers amplified a document allegedly from the Russian MoD that would grant state awards for the capture of Bakhmut to Russian Deputy Chief of the General Staff Colonel General Alexey Kim, MoD deputies Tatyana Shevtsova and Ruslan Tsalikov, and Ksenia Shoigu, the daughter of Russian Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu – notably omitting Wagner Group personnel and its affiliates, such as Prigozhin and Army General Sergey Surovikin.[27] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that DNR Head Pushilin announced the creation of a specific award commemorating the Battle of Bakhmut but complained that Russia should not hand out the medal to those who did not actually fight in Bakhmut.[28] Prigozhin complained that Russia has not issued state awards to dead Wagner fighters for the Bakhmut effort, and that the MoD had never even awarded Wagner fighters medals commemorating the capture of Palmyra, Syria.[29] Russian milbloggers amplified footage showing a Wagner commander awarding personnel with Wagner’s own internal award commemorating Bakhmut, likely attempting to beat the Russian MoD in solidifying its claims in the capture of Bakhmut.[30] A Russian milblogger affiliated with the nationalist, pro-war Angry Patriots Club criticized Prigozhin for claiming sole responsibility for the capture of Bakhmut, claiming that conventional Russian forces defended Bakhmut’s flanks and that the 137th Airborne (VDV) Regiment (106th Guards Airborne Division, Western Military District) has supported Wagner forces since the early part of the Bakhmut effort.[31]
The hyperfocus on claiming victory in Bakhmut distracts from the precarious Russian military situation in and around Bakhmut, underscoring the weight of Prigozhin’s influence in the information space. The Russian military situation in Bakhmut is particularly vulnerable as the Russian offensive effort in the area has likely culminated, granting Ukrainian forces the opportunity to launch further counterattacks on Bakhmut’s already-weakened flanks.[32] Wagner’s withdrawal in contact will also likely result in the Russian MoD manning defensive lines with poorly trained and provisioned conventional units similar to those that retreated from their positions while defending against Ukrainian counterattacks earlier in May.[33] The Russian information space is largely ignoring these vulnerabilities, however. Girkin complained that the Russian focus on capturing Bakhmut was a “strategic failure” that resulted in an “unnecessary and Pyrrhic” victory.[34] Girkin criticized Prigozhin, Shoigu, and Chief of the General Staff Army General Valery Gerasimov for prolonging the effort to take Bakhmut and distracting from preparations to defend against a coming Ukrainian counteroffensive.[35]
Russian forces launched another large-scale drone and missile strike against Ukrainian infrastructure on the night of May 21-22. The Ukrainian General Staff reported on May 22 that Russian forces launched 21 Shahed drones at Ukraine and 21 missiles at Dnipro and Zaporizhzhia cities and Kharkiv Oblast, including four Kh-101/555 air-launched cruise missiles, five Kh-22 cruise missiles, two Iskander-M ballistic missiles, five S-300 missiles, and four other unspecified missiles.[36] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces shot down all of the Kh-101/555 missiles and Shahed drones. Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Yuriy Ihnat stated that Russian forces may have lost the desire to strike Chernihiv and Sumy oblasts from the northern direction with guided aerial bombs due to the downing of two Russian Mi-8 helicopters, one Su-34 aircraft, and one Su-35 aircraft in Bryansk Oblast on May 13.[37]
Key Takeaways
- Elements of the all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and Freedom of Russian Legion (LSR) conducted a raid into Belgorod Oblast on May 22.
- Ukrainian officials noted that they are aware of the attack but denied any direct involvement by the Ukrainian Armed Forces. The raid prompted a slate of responses from local and federal Russian officials.
- The Russian information space responded with a similar degree of panic, factionalism, and incoherency as it tends to display when it experiences significant informational shocks.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that Wagner forces will withdraw from the entire frontline in Ukraine after June 1 in order to reconstitute and train for about two months.
- Ukrainian officials stated that limited fighting continued in and around Bakhmut on May 22.
- The Russian informational response to the capture of Bakhmut has thus far focused on competing for responsibility for the victory rather than discussing the resulting military situation. The hyperfocus on claiming victory in Bakhmut distracts from the precarious Russian military situation in and around Bakhmut, underscoring the weight of Prigozhin’s influence in the information space.
- Russian forces launched another large-scale drone and missile strike against Ukrainian infrastructure on the night of May 21-22.
- Russian forces continued limited ground attacks in the Kupyansk direction.
- Russian forces made marginal gains in the Avdiivka area and did not conduct any confirmed or claimed ground attacks in western Donetsk Oblast.
- The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant reportedly lost power for the seventh time since the beginning of the war.
- The Russian military is reportedly lowering the length of training for convicts in order to compensate for heavy losses.
- Russian occupation authorities announced that preliminary voting for the ruling United Russia Party has commenced in occupied territories.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 21, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 12:30pm ET on May 21. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 22 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Wagner Group mercenaries likely secured the western administrative borders of Bakhmut City while Ukrainian forces are continuing to prioritize counterattacks on Bakhmut’s outskirts. Ukrainian military officials reported that Ukrainian forces control an “insignificant” part of southwestern Bakhmut City around the T0504 highway — a tacit acknowledgement that Russian forces have secured the rest of western and northwestern Bakhmut, if not all of it.[1] These officials’ statements indicate that Ukrainian forces withdrew from the remaining areas in Bakhmut except those adjacent to the two highways into the city. Geolocated footage published on May 21 showed Wagner forces raising Russian and Wagner flags over a residential building in westernmost Bakhmut.[2] The Wagner Group’s likely capture of the last remaining small area of western Bakhmut does not impact ongoing Ukrainian counterattacks north or south of Bakhmut, nor does it impact Ukrainian control over the ground lines of communications (GLOCs) around Bakhmut that exhausted Wagner forces would need to reach in order to conduct further offensive operations. Russian forces will likely need additional reinforcements to hold Bakhmut City and its flanks at the expense of operations in other directions. ISW has observed artillery units of the 132nd Separate Guards Motorized Rifle Brigade (which was previously observed in the Avdiivka area) operating in the Bakhmut direction.[3]
Ukrainian military sources reported that Russian forces lost part of the dominant heights around Bakhmut and noted that sustained Ukrainian advances could lead to a tactical encirclement of Wagner forces in Bakhmut.[4] The Ukrainian 3rd Separate Assault Brigade stated on May 20 that the brigade’s counterattacks have expanded the Ukrainian salient in the Bakhmut area to 1,750 meters wide by 700 meters deep in an unspecified area.[5] Geolocated footage showed the Ukrainian 3rd Separate Assault Brigade striking unspecified Russian forces south of Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut), and engaging with the Russian 200th Separate Guards Motorized Rifle Brigade of the 14th Army Corps (Northern Fleet) northeast of Bohdanivka (5km northwest of Bakhmut).[6] Russian conventional forces such as the 72nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade are unsuccessfully attempting to regain lost positions and respond to Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks, actions that are consistent with ISW’s assessment that Ukrainian forces regained the tactical initiative around Bakhmut.[7] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian conventional forces conducted unsuccessful offensive operations south of Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut), in the direction of Hryhorivka (about 6km northwest of Bakhmut), and in the direction of Bila Hora (12km southwest of Bakhmut), and Russian milbloggers also noted the failed Russian assaults on Bakhmut’s flanks.[8]
ISW previously forecasted that Wagner offensive operations would likely culminate after months of attritional urban combat, and it is unlikely that Wagner will continue fighting beyond Bakhmut at its current depleted state. ISW assessed that Wagner forces were nearing culmination when they decided to fight though Bakhmut City. Wagner forces were enabled to continue offensive operations past that culmination point as Russian regular forces took responsibility for Bakhmut’s flanks, allowing Wagner to concentrate on the urban fight. Wagner forces began showing signs that they would be unable to pursue offensive operations beyond Bakhmut City from at least late December 2022.[9] A Russian milblogger claimed on May 21 that Wagner forces have not directly attacked Khromove and Ivanivske — settlements immediately west and southwest of Bakhmut — since capturing Bakhmut.”[10] Commander of the Vostok Battalion Alexander Khodakovsky stated that, “driven in [their] head by the inertia of the offensive, [Russian forces] did not want to promptly recognize the depletion of [Russian] offensive potential and did not take care to set up necessary defenses” in captured areas.[11] Former Russian officer Igor Girkin stated that all Russian forces are now exhausted after decisively committing to win an unnecessary battle for Bakhmut and claimed that exhausted Wagner mercenaries stopped immediately at the outskirts of Bakhmut “as they crawled” to the city’s administrative border.[12] Russian regular forces situated on Bakhmut’s northern and southern flanks are also unlikely to push west towards Kostyantynivka or north towards Slovyansk amid Ukrainian counterattacks in the Bakhmut area any time soon. Russian conventional forces will be even more unlikely to pursue offensive operations if Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin delivers on his stated intent to withdraw Wagner personnel from Bakhmut City on May 25.[13] It is currently unclear if Prigozhin will actually withdraw his forces from Bakhmut, but some milbloggers are speculating that Prigozhin will commit Wagner to a different “critical” frontline at the end of the month.[14] Russian forces faced a similar culmination following highly attritional infantry attacks in Severodonetsk and Lysychansk in June–July 2022.
Russian President Vladimir Putin congratulated the Wagner Group and the Russian military on May 21 for capturing Bakhmut.[15] Putin directly attributed the capture of the city to Wagner mercenaries, while noting that Russian regular forces provided “necessary support and flank protection” for the Battle of Bakhmut. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) similarly announced that Russia captured Bakhmut because of Wagner assaults in the city and aviation and artillery support from the Russian Southern Grouping of Forces.[16] Putin and the MoD likely directly acknowledged Wagner’s responsibility for the capture of Bakhmut to avoid a repetition of the backlash that followed their immediate failure to do so when Wagner captured Soledar on January 12.[17] Putin’s acknowledgement of Wagner’s role in Bakhmut is the first time that he himself has directly credited Wagner with a battlefield victory. Putin likely took this step because Prigozhin has thoroughly established Wagner’s responsibility for operations in Bakhmut within the Russian information space. Putin and the MoD likely sought to mitigate Prigozhin’s ability to claim sole responsibility for the capture of Bakhmut by emphasizing that regular Russian forces aided in the effort.
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin predictably claimed the victory over Bakhmut City entirely for himself and his forces. Prigozhin stated on May 21 that “it is a total lie” that Russian Airborne Forces (VDV) helped Wagner capture the city and said that no one from the Russian MoD was in Bakhmut.[18] Prigozhin claimed that Wagner practically received no help from the Russian military except from former overall theater commander Army General Sergey Surovikin and Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics-turned-Wagner-Group-deputy-commander Colonel General Mikhail Mizinstev.[19] Prigozhin claimed that that the 305th Artillery Brigade (5th Combined Arms Army, Eastern Military District) helped Wagner after being subordinated to Wagner’s command. Prigozhin also acknowledged that the 57th Motorized Infantry Brigade (5th Combined Arms Army, Eastern Military District) played a ”satisfactory” role in controlling one of the flanks around Bakhmut.[20] Prigozhin argued that the Russian command will attempt to claim the victory over Bakhmut when Wagner transfers the city to regular Russian forces and stated that the situation will be similar to how the MoD took much of Wagner’s alleged credit for capturing Palmyra, Syria, in 2016.[21]
Prigozhin is likely attempting to solidify Wagner as solely responsible for Bakhmut’s capture before the Kremlin and the MoD can craft a response. Russian sources widely congratulated Wagner for the capture of Bakhmut and accepted Prigozhin’s May 20 claim — rather than Putin’s statement — as the official announcement of the city’s capture.[22] Russian sources also amplified footage of Wagner forces placing a Wagner Group flag — not a Russian flag — at the highest point in Bakhmut, likely an intentional snub of the MoD.[23] Prigozhin will likely use Wagner’s perceived responsibility for Bakhmut’s alleged capture to advocate for more supplies, responsibilities, and privileges for Wagner as he did following Wagner’s involvement in the capture of Popasna in May 2022.[24] Prigozhin will also likely use Wagner’s role in the alleged capture of Bakhmut to intensify his efforts to establish himself as the central figure of the Russian ultranationalist community.
Russian reactions to the claimed capture of Bakhmut illustrate an increasingly growing divide between the Kremlin’s domestic presentation of the war and the ultranationalist milblogger community’s coverage of Russian operations in Ukraine. Russian state television portrayed the alleged capture of Bakhmut as a seminal historic event and claimed that the city’s capture would facilitate Russian operations to capture Slovyansk (41km northwest of Bakhmut) and Kramatorsk (35km northwest of Bakhmut) and even Dnipro City (roughly 215km west of Bakhmut).[25] The Kremlin likely attempted to oversell the significance of the capture of Bakhmut as a historical victory due to the continued lack of tactical success in Ukraine, with one Russian state media outlet outrageously commenting that Wagner personnel in Bakhmut must feel like “their grandfathers in Berlin.”[26]
Russian ultranationalist milbloggers celebrated the alleged capture of Bakhmut but emphasized that “Bakhmut is not Berlin” and that the capture of the city would be simply another step in ongoing difficult operations to achieve Russian objectives in Ukraine.[27] Russian milbloggers responded to the alleged capture of Bakhmut by discussing more immediate possible Russian operations to capture Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut), Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut), and Chasiv Yar (12km west of Bakhmut).[28] Other prominent Russian milbloggers responded to the capture of Bakhmut by focusing on possible imminent Ukrainian counteroffensive operations instead of possible future Russian offensive operations.[29] Russian milbloggers shifted to more conservative expectations of Russian operations as the attritional offensive to capture Bakhmut continued from winter into spring of 2023, and they have largely abandoned their previous high expectations that the capture of Bakhmut would lead to a collapse of Ukrainian lines in the area and Russian advances up to Slovyansk and Kramatorsk.[30] Russian milbloggers’ more realistic views about both Russian capabilities in Ukraine and the relevance of the Bakhmut offensive highlight the divergence between two very different segments of the pro-war Russian information space: the more optimistic presentation of the war offered by the Kremlin and the more informed presentation of the war offered by milbloggers. These growing differences will likely continue to undermine the Kremlin’s ability to shape the Russian information space.
US President Joe Biden stated on May 21 that the US will train Ukrainian pilots on fourth-generation aircraft, including F-16s, to augment Ukraine’s defense capabilities in the long term. Biden stated that Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky gave him a “flat assurance” that Ukrainian forces will not use Western-provided F-16s to strike Russian territory.[31] Biden reiterated that Ukraine will not use F-16s in its anticipated counteroffensive and framed the provision of F-16s as part of a longer-term effort to augment Ukraine’s defensive capabilities as Ukraine’s operational needs evolve.[32] Biden expanded on this argument, stating that the US did not pledge to send Ukraine tanks earlier because Ukraine did not need tanks earlier.[33] ISW has assessed that the need to send Ukraine Western tanks, including M1s, became apparent in June 2022.[34]
ISW previously assessed in January 2023 that delays in the provision to Ukraine of Western long-range fires systems, advanced air defense systems, and tanks have limited Ukraine’s ability to take advantage of opportunities for larger counter-offensive operations presented by flaws and failures in Russian military operations.[35] The inevitable delay between the pledge to send such systems and the Ukrainians’ ability to use them calls for the provision of such systems at the earliest indications that they will be required, not when the situation becomes dire.[36] Had Western leaders started setting conditions for Ukraine to use Western tanks in June 2022, when the first clear indicators appeared that Western tanks would be needed, Ukrainian forces would have been able to start using them in November or December. The continual delays in providing Western materiel when it became apparent that it is or will soon be needed have thus contributed to the protraction of the conflict.[37]
Former Russian officer Igor Girkin’s “Club of Angry Patriots” social movement opened a St. Petersburg chapter with an inaugural event on May 21. The event’s speakers discussed their dissatisfaction with the way elements of Russia’s "military-political elite” are not trying to decisively defeat Ukraine and instead are focusing efforts on maintaining current Russian gains in Ukraine and holding negotiations with the West.[38] They also discussed how the Club of Angry Patriots is creating an “alternative center of power” that should help achieve the final destruction of the Ukrainian state and the further mobilization of the Russian nation to that end.[39] Speakers also discussed how the Russian elite that formed against the backdrop of the 1990s period of privatization and "the post-Soviet catastrophe” has “rotted.”[40]
The opening of the club in St. Petersburg is likely a continuation of Igor Girkin’s political feud with Prigozhin and the Wagner Group. The Wagner Group opened its first official national headquarters in St. Petersburg in November 2022.[41] The Angry Patriots Club accused Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin of supporting efforts to freeze the war in Ukraine in April 2023.[42] Girkin launched the “Club of Angry Patriots” social movement as a new effort in April 2023 likely aimed at protecting the influence of the Russian pro-war faction within the Kremlin.[43]
Key Takeaways
- Wagner Group mercenaries likely secured the western administrative borders of Bakhmut City while Ukrainian forces are continuing to prioritize counterattacks on Bakhmut’s outskirts.
- ISW previously forecasted that Wagner offensive operations would likely culminate after months of attritional urban combat, and it is unlikely that Wagner will continue fighting beyond Bakhmut at its current depleted state.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin congratulated the Wagner Group and the Russian military on May 21 for capturing Bakhmut.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin predictably claimed the victory over Bakhmut City entirely for himself and his forces
- Russian reactions to the claimed capture of Bakhmut illustrate an increasingly growing divide between the Kremlin’s domestic presentation of the war and the ultranationalist milblogger community’s coverage of Russian operations in Ukraine.
- US President Joe Biden stated on May 21 that the US will train Ukrainian pilots on fourth-generation aircraft, including F-16s, to augment Ukraine’s defense capabilities in the long term.
- Former Russian officer Igor Girkin’s “Club of Angry Patriots” social movement opened a St. Petersburg chapter with an inaugural event on May 21.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations northeast of Kupyansk and south of Kreminna.
- Russian forces continued offensive operations on the Donetsk City-Avdiivka frontline but have not made any verifiable territorial gains.
- Ukrainian forces reportedly conducted a deep strike against a Russian headquarters at an airfield in Berdyansk, Zaporizhia Oblast, with a Storm Shadow missile.
- Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov claimed that seven regiments and four battalions from Chechnya are operating in Ukraine as of May 20.
- Russian occupation authorities are reportedly intensifying filtration measures in occupied Ukraine to find Ukrainian partisans.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 20, 2023
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin declared victory in Bakhmut City on May 20 and announced his intent to withdraw from the city on May 25.[i] Prigozhin claimed that Wagner Group forces completely captured Bakhmut City on May 20, seizing the last multi-story apartment building in southwestern Bakhmut near the MiG-17 monument. Prigozhin announced that Wagner forces will establish defensive positions before transferring responsibility for the city to Russian conventional forces on May 25. Prigozhin effectively stated that Wagner forces will conduct an operational pause by resting and restoring combat power at field training camps in unspecified areas, presumably far from the frontline. ISW has not observed geolocated footage confirming Prigozhin’s claims as of this publication. Ukrainian officials reported that Ukrainian forces are still fighting in a small section of southwest Bakhmut as of May 20. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated that Ukrainian forces continue to hold positions near the MiG-17 monument as of May 20.[ii] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) has not commented on Prigozhin’s claims as of this publication.
Prigozhin’s claimed victory over the remaining areas in Bakhmut is purely symbolic even if true. The last few urban blocks of eastern Bakhmut that Prigozhin claimed that Wagner Group forces captured are not tactically or operationally significant. Their capture does not grant Russian forces operationally significant terrain to continue conducting offensive operations or any particularly strong position from which to defend against possible Ukrainian counterattacks.
Ukrainian forces continue pressuring Bakhmut’s northern and southern flanks. Ukrainian and Russian sources reported that fighting is ongoing on Bakhmut’s northern and southern flanks in the directions of Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut), Stupochky (13km southwest of Bakhmut), and Bila Hora (12km southwest of Bakhmut).[iii] Ukrainian forces reported on May 19 that they have recaptured approximately four square kilometers of additional territory near Bakhmut, and Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces continue conducting localized attacks near Klishchiivka (6km southwest of Bakhmut).[iv] Prigozhin’s claimed capture of the remaining blocks in Bakhmut is not strategically significant as it will not allow exhausted Wagner or conventional Russian forces to establish a meaningful springboard for further offensive operations. Ukrainian ongoing counterattacks north, west, and southwest of Bakhmut will complicate any further Russian advances beyond Bakhmut in the near term. Prigozhin’s withdrawal announcement, whether Wagner withdraws from the city or not, indicates that Prigozhin does not intend to continue an offensive effort to push directly west of Bakhmut.
Wagner forces are unlikely to successfully conduct a controlled withdrawal from Bakhmut while in contact with Ukrainian forces within five days without disrupting the Russian MoD’s efforts to prepare for planned Ukrainian counteroffensives. Wagner forces are unlikely to establish adequate defenses or consolidate recent gains in Bakhmut sufficient to forestall Ukrainian counterattacks by May 25 even if Prigozhin’s announcement of Wagner’s withdrawal is true. Ukrainian forces are still in Khromove and Ivanivske and are engaging Russian forces in and near Bakhmut. Ukrainian artillery can still target Russian forces in and around Bakhmut. Withdrawal in contact with the enemy is an exceedingly difficult task that the Wagner Group’s forces are unlikely to perform well within Prigozhin’s five-day time frame. Conducting a relief-in-place while in contact is also an extremely challenging maneuver that Russian forces would likely struggle to conduct even if the Russian MoD agrees to undertake it. Wagner units have shown poor coordination with Russian conventional forces, other irregular formations subordinated to the Russian MoD, and the Russian military command—factors that would hinder a smooth relief-in-place operation.[v] The Russian military command is unlikely to generate sufficient forces to relieve Wagner in Bakhmut and hold its flanks within the window Prigozhin has announced without redeploying Russian forces from other areas. Prigozhin’s statement of his intent to withdraw could be a crude attempt to mislead Ukrainian forces into conducting a counterattack through Bakhmut City.
Russian conventional forces likely will still need to transfer additional forces to the Bakhmut direction even if Wagner mercenaries remain in Bakhmut. Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated that Russian forces continue to transfer airborne, motorized rifle, and special forces elements to reinforce the Bakhmut flanks even as Wagner forces remain in Bakhmut City.[vi] The UK MoD also reported that the Russian military command likely redeployed several battalions in the last few days to reinforce Bakhmut despite only having few uncommitted combat units and that this redeployment suggests a substantial commitment to the Bakhmut effort by the Russian leadership.[vii] These additional forces could in principle be meant to participate in the relief-in-place of Wagner forces that Prigozhin has just announced, reducing but not eliminating some of the challenges considered above, but it is more likely that they are intended to secure Bakhmut’s threatened flanks.
Russian forces targeted Kyiv Oblast with Iranian-made Shahed drones on the night of May 19 to 20. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces launched 18 Shahed-136/131 drones at Kyiv Oblast, and that Ukrainian air defenses shot down all 18 of the drones.[viii] The Ukrainian General Staff also reported that Ukrainian forces destroyed two Russian Shahed drones in eastern Ukraine.[ix] Russian forces have targeted Kyiv heavily in the past month, likely to produce informational affects with both Russian and Ukrainian audiences. This hyperfocus on targeting Kyiv is at odds with the new limited Russian air campaign’s other target: alleged Ukrainian rear logistics.[x] These conflicting target sets likely further limit the campaign’s ability to degrade Ukrainian counteroffensive capabilities in the near term.[xi]
US National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan stated on May 20 that the United States may agree to transfer modern combat aircraft to Ukraine, including the F-16, on the condition that Ukraine does not use them to strike Russian territory. Sullivan stated the war in Ukraine has “evolved” and that F-16 fourth-generation fighter aircraft have now become “part of that mix” of weapons that Ukraine will need as part of a “future force to be able to deter and defend against Russian aggression as we go forward.”[xii] Sullivan stated that any F-16s given to Ukraine – like other Western weapons provided to Ukraine – will be provided under the condition that they do not strike Russian territory.[xiii] Sullivan also stated that training Ukrainian pilots to use F-16s is the “obvious first step” and that the next steps are to “determine how to do the actual provision of planes.”[xiv] US President Joe Biden informed G7 leaders on May 19 that Washington will support a joint effort to train Ukrainian pilots on F-16s and other fourth generation aircraft but did not pledge that the US will send Ukraine the F-16s.[xv]
Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar reported that Russian sources are falsely alleging that high-ranking Ukrainian military commanders have recently died, likely to demoralize the Ukrainian forces and to portray Russian forces as constraining Ukrainian counteroffensive capabilities. Malyar stated that these information operations allege that Russian strikes have recently killed Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces Commander General Ihor Tantsyura, Ukrainian Eastern Grouping of Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi, and Ukrainian Commander in Chief General Valeriy Zaluzhnyi.[xvi] Prigozhin also amplified the information operation alleging that Zaluzhnyi might be dead on May 20.[xvii] These information operations are particularly absurd given that Zaluzhnyi spoke with US Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Mark Milley on May 19 and that Syrskyi appeared on Ukrainian television on May 16.[xviii] Ukrainian officials have denied previous Russian claims that a May 10 strike on a Ukrainian command post in the Bakhmut area killed several high-ranking Ukrainian military officials and that Wagner forces killed Tantsyura while he was en route to Bakhmut on May 2.[xix] ISW has previously assessed that Russian ultranationalists are increasingly seeking to frame any Russian operations as delaying potential Ukrainian counteroffensive actions.[xx]
Key Takeaways
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin declared victory in Bakhmut City on May 20 and announced his intent to withdraw from the city on May 25.
- Prigozhin’s claimed victory over the remaining areas in Bakhmut is purely symbolic even if true.
- Ukrainian forces continue pressuring Bakhmut’s northern and southern flanks.
- Wagner forces are unlikely to successfully conduct a controlled withdrawal from Bakhmut while in contact with Ukrainian forces within five days without disrupting the Russian MoD’s efforts to prepare for planned Ukrainian counteroffensives.
- Russian conventional forces likely will still need to transfer additional forces to the Bakhmut direction even if Wagner mercenaries remain in Bakhmut.
- Russian forces targeted Kyiv Oblast with Iranian-made Shahed drones on the night of May 19 to 20.
- US National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan stated on May 20 that the United States may agree to transfer modern combat aircraft to Ukraine, including the F-16, on the condition that Ukraine does not use them to strike Russian territory.
- Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar reported that Russian sources are falsely alleging that high-ranking Ukrainian military commanders have recently died, likely to demoralize Ukrainian forces and to portray Russian forces as constraining Ukrainian counteroffensive capabilities.
- Russian forces continued limited ground attacks in the Kreminna area.
- Russian forces continued to conduct ground attacks on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- The Washington Post reported on May 19 that a Ukrainian commander stated that Ukrainian Special Operations forces conduct raids in east (left) bank Kherson Oblast but that Ukrainian forces do not hold stable positions there.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) is incorporating mobilized and conscripted personnel into its own “Veterany” private military company (PMC), leading to discrimination and conflict.
- A Lithuanian official publicly accused Russia of attempting to hold international children hostage in occupied Crimea as “human shields” against a future Ukrainian counteroffensive.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 19, 2023
A Ukrainian official stated that Russian forces have concentrated most of their available reserves to the Bakhmut area and slowed Ukrainian counterattacks in the past 24 hours. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated on May 19 that Russian forces concentrated most of their reserves in the Bakhmut direction, which has slowed the rate of Ukrainian advances. Malyar also stated that Ukrainian forces continue to counterattack on the northern and southern outskirts of Bakhmut and advanced 500 meters on one flank and 1,000 meters on the other. Some Russian milbloggers celebrated the slowed Ukrainian rate of advance and claimed that the Ukrainian forces are unable to sustain prolonged localized counterattacks around Bakhmut. Russian forces on Bakhmut’s flanks likely remain weak, however; Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin continued to criticize the Russian 4th Motorized Rifle Brigade (2nd Luhansk People’s Republic Army Corps) on May 19 for retreating from defensive lines southwest of Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut). Ukrainian counterattacks near Bakhmut have notably likely eliminated the threat of a Russian encirclement of Ukrainian forces in Bakhmut and forced Russian troops to allocate scarce military resources to defend against a limited and localized offensive effort, as Ukrainian command likely intended.
Russian forces conducted another series of drone and missile strikes across Ukraine on the night of May 18 to 19. Ukrainian military sources reported that Russia launched six Kalibr cruise missiles and 22 Shahed-131/136 drones at Ukraine from the direction of the Black Sea. The Ukrainian General Staff noted that Ukrainian air defenses shot down 16 drones and three Kalibr missiles, despite the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD)’s claim that Russian forces struck all intended targets. Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Head Serhii Lysak reported explosions near Kryvyi Rih following Russian strikes in the area. Ukrainian Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) representative Vadym Skibitsky noted that the recent uptick in Russian drone and missile strikes, as well as artillery strikes along the entire frontline, are meant to disrupt Ukrainian counteroffensive plans and preparations. ISW previously assessed on May 14 that the recent increase in Russian strikes on Ukrainian rear areas is likely part of a new air campaign premised on degrading Ukrainian counteroffensive capabilities in the near term. Skibitsky additionally noted that Russia can only produce 25 Kalibr cruise missiles, 35 Kh-101s, two Kinzhals, and 5 ballistic 9M723 Iskander-Ms per month. Considering that Russian forces have launched missile strikes at rear areas of Ukraine on a near daily-basis thus far in May, it is likely that they are rapidly expending their stocks of precision munitions, potentially at a rate that exceeds production capabilities.
President Joe Biden reportedly informed G7 leaders on May 19 that Washington will support a joint effort to train Ukrainian pilots on F-16s and other fourth generation aircraft. This decision marks a sharp turn in US policy vis a vis fourth generation aircraft in Ukraine and follows Biden’s meetings with various G7 leaders in Hiroshima, Japan on May 19. Yahoo News relatedly reported on May 18 that Ukrainian pilots outperformed standard Pentagon expectations for F-16 training time in a flight simulator and would be able to operate F-16s in only four months as opposed to the anticipated 18 months, citing an internal US Air Force assessment.
The Kremlin reportedly spent 3.1 trillion rubles (approximately $38.7 billion) in an undisclosed section of the Russian budget in 2023, likely to fund the war and maintain occupied territories in Ukraine. Independent Russian news outlet The Bell reported that the Russian Ministry of Finance released data on May 16 on budget expenditures since the start of 2023 amounting to a total of 11.9 trillion rubles ($148.5 billion) with only 8.8 trillion rubles ($109.8 billion) accounted for in Russia’s public budget, leaving 3.1 trillion rubles – over a quarter of Russia’s expenditures – unaccounted for. The Bell reported that most undisclosed budget items account for defense, national security, and law enforcement, and that some may fall onto social and other expenditures in occupied Ukraine. The Bell also reported that the unspecified spending is higher than in the same time period in previous years. ISW continues to assess that the Russian economy will struggle to meet the needs of the large-scale war that the Russian military is fighting in Ukraine and to sustain its occupation of Ukrainian territories.
Moscow Mayor Sergey Sobyanin announced that he will run for reelection as a member of Russian President Vladimir Putin’s United Russia Party for the first time, prompting criticism from select Russian ultranationalists. Russian “Civil Solidarity” movement head Georgy Fedorov argued on May 19 that Sobyanin’s United Russia candidacy suggests that “all political processes in Russia are now only possible in the pre-existing political party system,” that Russia is set to experience “great turbulence,” and that Russia’s “non-systemic opposition has been crushed.” Former Russian officer and ardent ultranationalist Igor Girkin amplified Georgy’s statements and sarcastically called United Russia the “party of crooks and thieves,” a well-known slogan used by Russian opposition figure Alexey Navalny. Sobyanin has held the post of Moscow Mayor nominally as an independent since 2010, although his United Russia candidacy is likely simply a public formalization of his longstanding relationship with United Russia, as Sobyanin has been a member of the party since 2001. United Russia likely seeks to buttress its own popularity (which stands around 45% in Moscow) with that of Sobyanin, who has polled at 74%. These select ultranationalists likely responded to Sobyanin’s announcement to critique what they view as United Russia’s attempt to monopolize support amongst the Russian ultranationalist constituency and were likely not genuinely reacting to the loss of an independent figure. The Kremlin may additionally have publicly linked Sobyanin to United Russia to remove a nominally independent figure, regardless of his actual independence. ISW previously assessed that the Kremlin will likely attempt to solidify United Russia as the definitive pro-war party during elections in 2023 and 2024, and Russian ultranationalist communities with their own political ambitions may increasingly seek to undercut these efforts.
A Ukrainian source reported that elements of two spetsnaz brigades of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (GRU) have deployed to border areas of Kursk Oblast in order to conduct counter-sabotage activities and provocations. The Ukrainian Resistance Center stated on May 19 that the 3rd and 22nd Guards Special Purpose brigades have deployed to Tyotkino, Kursk Oblast to prevent cross-border Ukrainian partisan activities, carry out cross-border provocations, and raise the morale of Russian forces. ISW has previously assessed that such Russian deployments to border areas are likely an attempt to fix a portion of Ukrainian forces to border regions and disperse them from critical frontline areas. Elements of the 3rd Guards Special Purpose Brigade have been previously reported near the Kreminna area of Luhansk Oblast, while elements of the 22nd Guards Special Purpose Brigade were reportedly active in the Orikhiv area in western Zaporizhia Oblast. It is unclear why Russian leadership may have made the decision to remove such elements from active sectors of the frontline to Russian rear areas, and it may be possible that these units suffered previous losses in recent operations and have been withdrawn and redeployed in order to rest and refit. The deployment of these units to border areas is unlikely to have the desired informational or operational effects.
Key Takeaways
- A Ukrainian official stated that Russian forces have concentrated most of their available reserves to the Bakhmut area and slowed Ukrainian counterattacks in the past 24 hours.
- Ukrainian counterattacks near Bakhmut have notably likely eliminated the threat of a Russian encirclement of Ukrainian forces in Bakhmut and forced Russian troops to allocate scarce military resources to defend against a limited and localized offensive effort, as Ukrainian command likely intended.
- Russian forces conducted another series of drone and missile strikes across Ukraine on the night of May 18 to 19.
- President Joe Biden reportedly informed G7 leaders on May 19 that Washington will support a joint effort to train Ukrainian pilots on F-16s and other fourth generation aircraft.
- The Kremlin reportedly spent 3.1 trillion rubles (approximately $38.7 billion) in an undisclosed section of the Russian budget in 2023, likely to on fund the war and maintain occupied territories in Ukraine.
- Moscow Mayor Sergey Sobyanin announced that he will run for reelection as a member of Russian President Vladimir Putin’s United Russia Party for the first time, prompting criticism from select Russian ultranationalists.
- A Ukrainian source reported that elements of two brigades of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (GRU) have deployed to border areas of Kursk Oblast in order to conduct counter-sabotage activities and provocations.
- Russian sources claimed that Russian troops continued offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove line.
- Russian forces continued to conduct ground attacks in the Bakhmut area and slightly increased their tempo of ground attacks along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Ukrainian officials stated that Russian forces are preparing defenses by flooding fields in Russian occupied Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Russian Security Council Deputy Chairman Dmitry Medvedev claimed that the Russian military has recruited 117,400 contract personnel in volunteer formations since January 1, 2023.
- The Russian State Duma adopted the final reading of a draft law authorizing regional elections under martial law.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 18, 2023
Ukrainian forces have seized the tactical initiative and made tactically significant gains around Bakhmut in counter-attack operations on May 18. These operations are a continuation of the localized counter-attacks Ukrainian forces have been conducting for some days and do not reflect the start of a major new operation. Multiple Russian milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian forces drove through the Russian defensive lines south and southwest of Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut) and northwest of Klishchiivka (6km southwest of Bakhmut) from the northwest.[1] The milbloggers also claimed that Russian forces retreated from positions north of Sakko i Vantsetti (15km north of Bakhmut) to positions south of the settlement, but that Ukrainian forces have not yet entered the settlement. Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed that Russian forces yielded 570 meters of territory north of Bakhmut, which is consistent with Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar’s statement that Ukrainian forces had advanced 500 meters north of Bakhmut and 1,000 meters south of Bakhmut.[2] Ukrainian Eastern Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated that Ukrainian forces advanced up to 1,700 meters in the past day, and the Ukrainian 3rd Separate Assault Brigade stated that the brigade’s counterattacks expanded the Ukrainian salient in the Bakhmut area to 2,000 meters wide by 700 meters deep.[3]
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 17, 2023
Russian and Ukrainian officials acknowledged continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks near Bakhmut on May 17. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated that Ukrainian forces are advancing in unspecified areas on Bakhmut’s flanks. Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated that Ukrainian forces advanced up to 500 meters in the Bakhmut direction in the past day and continue to attack Russian flanks. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian Airborne Forces (VDV) made marginal advances but acknowledged continued Ukrainian counterattacks against Bakhmut’s flanks near Bohdanivka (5km northwest of Bakhmut) and Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut). Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin denied the MoD’s claim of territorial gains, however, and criticized the MoD for falsely portraying a retreat as capturing new positions. One prominent milblogger complained that Russian forces must now react to Ukrainian actions, implying that Russian forces are losing the initiative in the Bakhmut area despite the limited nature of Ukrainian counterattacks in the area.
Ukrainian officials reported that terrain features constrain Ukrainian offensive operations across the Dnipro River in Kherson Oblast. Ukrainian Southern Forces Joint Press Center Head Nataliya Humenyuk acknowledged that the width of the Dnipro River hinders Ukrainian territorial advances in Kherson Oblast and called for the information space to “forget” about Ukrainian offensive activities in the Kherson direction. Ukrainian Security Services (SBU) Colonel Roman Kostenko stated on May 14 that the Ukrainian forces pushed Russian forces back from the islands close to Kherson City and stated that the islands have poor terrain, no trenches, limited shelter, and that the ground is always wet.
US officials reported that a Patriot air defense system is operational after Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian missile strikes on Kyiv destroyed the system on May 16. CNN cited three US officials as stating that a Patriot air defense system is still operational despite the Russian MoD claims that a Kinzhal missile destroyed it. An unidentified US defense official had previously told CNN that the Patriot system likely suffered damage, but three officials specified that the system suffered minimal damage that does not impede its operations. Officials did not specify if Russian missiles or debris caused the damage.
The Kremlin reportedly accused three hypersonic missile scientists of treason. Employees of the Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Science published an open letter on May 15 in defense of three of their scientists — Anatoly Maslov, Alexander Shiplyuk, and Valery Zvegintsev — whom Russian authorities reportedly arrested in the past year under suspicion of committing “high treason.” The open letter also noted that these arrests deter the younger generation from pursuing careers in science, which contributes to a decrease in the quality of scientific research. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov claimed that the Kremlin was aware of the open letter and that Russian security services are involved.
Select Russian strongmen (siloviki) are likely attempting to signal to Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin that he must cease his political ambitions in Russia. Prigozhin responded to a media inquiry on May 17 about several allegations from Russian Telegram channels — which are reportedly affiliated with the Russian Presidential Administration and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) — about Prigozhin’s political aspirations in Russia. These channels claimed that Prigozhin is using the battle for Bakhmut and war in Ukraine to become a political figure in Russia rather than actually fighting for Russia’s interests. The journalist directly asked Prigozhin if he thinks that Russian siloviki are trying to signal to him via these Telegram channels. Prigozhin confirmed that he had an interaction with an unnamed Russian senior official “recently” who had accused Prigozhin of deliberately acting in his own self-interest. Prigozhin emphasized that this official was not Russian President Vladimir Putin but indirectly implied that these sentiments are widespread in the Russian Presidential Administration — noting that the Telegram posts reflect the collective opinion of the bureaucratic community.
The Russian siloviki may be intimidating Russian officials affiliated with Prigozhin to discourage their cooperation with Wagner. One of the Telegram channels mentioned in the media inquiry noted that Prigozhin is losing contact with Chairperson of the Russian State Duma Vyacheslav Volodin and had a fight with First Deputy Chief of Staff of the Russian Presidential Administration Sergey Kiriyenko who originally supported his initiatives. Volodin, for example, reportedly stopped pushing Wagner’s agendas to avoid a conflict with Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu. The channel observed that a member of the Russian Communist Party, Viktor Sobolev, originally supported a bill that favored Wagner only to later denounce Wagner as an “illegal armed formation” on May 15. The channel noted that Prigozhin still has contact with Putin’s administration via Chief of Staff of the Russian Presidential Executive Office Anton Vaino and noted that Prigozhin’s fate lies entirely in Putin’s hands. Shoigu is reportedly unsuccessfully attempting to convince Putin to eliminate Prigozhin due to Prigozhin’s failure to secure battlefield victories — which likely indicates that Prigozhin’s bloody efforts to capture Bakhmut are in fact an attempt to compete with Shoigu for self-preservation.
The siloviki appear to be unsuccessful in their attempts to scare Prigozhin into obedience. Prigozhin stated that he is ready to take on the “bureaucrats” and accused them of attempting to gain more authority while using Wagner to fight the war. Prigozhin also accused unnamed officials of being apathetic about Russian deaths on the frontlines and sarcastically stated that the future Russian defense minister has been in Bakhmut for over a week when responding to a question asking if Shoigu had accepted his invitation to visit the Bakhmut frontline. Prigozhin had been recently publicizing his cooperation with former Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics-turned-Wagner-Group-deputy-commander Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev, and it is possible that Prigozhin may be attempting to promote Mizintsev as a replacement for Shoigu. Prigozhin is likely aware that Putin is not entirely convinced of Shoigu’s ability to win the war and may be hopeful that a decisive victory in Bakhmut would give him the leverage to replace Shoigu with Wagner-affiliated officials. Both Prigozhin and Shoigu likely perceive this feud as an existential matter.
Russian authorities continue to crack down against domestic anti-war dissent in an effort to strengthen domestic repressions and prepare Russian society for a long-term war effort. BBC’s Russia service reported on May 17, citing anonymous interlocutors, that the Russian General Prosecutor’s office and the Federal Service for the Supervision of Education and Science (Rosobrnadzor) conducted an unscheduled inspection at the European University in St. Petersburg as part of counterterror and counter-extremism measures. BBC noted that the investigators investigated the dissertation topics and personal files of undergraduate and graduate students as well as the publications and classes of faculty in at least four departments: anthropology, history, sociology, and political science. BBC stated that the investigation affected several dozen faculty members and hundreds of students. BBC reported that Russian authorities have been conducting similar inspections at three other Moscow universities since 2021. One of the interlocutors stated that Russian authorities regularly conduct these inspections, resulting in faculty and curricula changes.
The Astrakhan Oblast “A Just Russia” party faction voted out faction head and former Russian State Duma Deputy Oleg Shein on May 16 after Shein resigned from the post on April 18. Shein cited disagreements with federal “A Just Russia” faction co-leader Sergey Mironov — who is notably connected with Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin — for the Astrakhan faction’s vote and claimed that the party forced him out of his role due to his anti-war sentiment. Shein later quipped that the faction had not yet ”invented” the reason for his ousting.
Russian authorities are likely forcefully integrating Ukrainian Orthodox Church (UOC) dioceses in occupied Zaporizhia Oblast as part of a wider religious persecution campaign in occupied Ukraine. Russian Orthodox Church Patriarch Kirill and the Synod of the Russian Orthodox Church (ROC) announced the adoption of the Berdyansk and Prymorsk UOC dioceses into the ROC on May 16. The ROC claimed that Berdyansk and Prymorsk dioceses, clergy, and parishioners voted to join the ROC after UOC leadership “abandoned” the dioceses. ISW has previously reported on Russia’s religious oppression occupied Ukraine, including the detention or assassinations of at least 29 Ukrainian clergy or religious leaders since the start of the war.
Key Takeaways
- Russian and Ukrainian officials acknowledged continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks near Bakhmut on May 17.
- Ukrainian officials reported that terrain features constrain Ukrainian offensive operations across the Dnipro River in Kherson Oblast.
- US officials reported that a Patriot air defense system is operational after Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian missile strikes on Kyiv destroyed the system on May 16.
- The Kremlin reportedly accused three hypersonic missile scientists of treason.
- Select Russian strongmen (siloviki) are likely attempting to signal to Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin that he must cease his political ambitions in Russia.
- The Russian siloviki may be intimidating Russian officials affiliated with Prigozhin to discourage their cooperation with Wagner but appear to be unsuccessful in their attempts to scare Prigozhin into obedience.
- Russian authorities continue to crack down against domestic anti-war dissent in an effort to strengthen domestic repressions and prepare Russian society for a long-term war effort.
- Russian authorities are likely forcefully integrating Ukrainian Orthodox Church (UOC) dioceses in occupied Zaporizhia Oblast as part of a wider religious persecution campaign in occupied Ukraine.
- Russian and Ukrainian officials acknowledged continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks near Bakhmut on May 17.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces continued to make incremental gains in Bakhmut and conducted limited ground attacks on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces continued to target west (right) bank Kherson Oblast and islands at the Dnipro River delta out of fear of planned Ukrainian counteroffensives.
- The Kremlin continues crypto-mobilization efforts by recruiting regional volunteer battalions and criminals.
- The Russian State Duma adopted amendments to the martial law on May 16 that authorize the forced and controlled movement of citizens from territories under the martial law to the territories without marital law.
- Russian ultranationalists are speculating about the fate of Belarus’ independence in case of Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko’s severe illness or death.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 16, 2023
Russian forces have likely committed to reinforcing their tactical offensive effort in the Bakhmut area despite Ukraine’s apparent focus on limited and localized counterattacks. Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) Head Denis Pushilin claimed on May 16 that Russian forces have strengthened their forces in the Bakhmut area to stabilize the situation, and a prominent Russian milblogger claimed that four unspecified Russian battalions have deployed to the flanks around Bakhmut to prevent Ukrainian breakthroughs.[1] Russian claims about Russian reinforcements are consistent with Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar’s May 15 statement that Russian forces are deploying additional airborne (VDV) forces to defend Bakhmut’s flanks, presumably from other areas of the front.[2] Russian forces have continued to make marginal gains within Bakhmut itself as of May 16, and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) continues to claim that Russian forces around Bakhmut are focused on repelling Ukrainian counterattacks.[3] The Russian MoD claimed on May 16 that elements of the 4th Motorized Rifle Brigade (2nd Luhansk People’s Republic Army Corps) repelled 10 Ukrainian counterattacks near Ivanivske (6km west of Bakhmut).[4]
Ukrainian military officials continue to indicate that Ukraine is pursuing much more limited operations in the Bakhmut area than Russian forces, who appear to be committed to Bakhmut as a renewed main effort. Malyar stated on May 16 that while Ukrainian forces have liberated roughly 20 square kilometers of territory in recent days, Russian forces are continuing to make marginal gains within Bakhmut.[5] Ukrainian Eastern Grouping of Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi stated that Ukrainian forces are continuing to use the concept of “active defense” in conducting counterattacks in unspecified areas near Bakhmut.[6] Ukrainian Eastern Grouping of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty reiterated that the main objective of the Ukrainian defensive operation in the Bakhmut area is to exhaust Russian forces in the area.[7] ISW has geolocated footage published on May 16 of Ukrainian positions in southwestern Bakhmut that suggests that Ukrainian forces have recently made limited gains in the city itself.[8] Geolocated footage published on May 16 indicates that Ukrainian forces made marginal gains east of Orikhovo-Vasylivka (11km northwest of Bakhmut), although ISW has not observed any further Ukrainian gains around Bakhmut as of May 16.[9]
The reported Russian reinforcements to the Bakhmut area suggest that Russian forces are continuing to concentrate offensive capabilities there despite an assessed wider effort to reprioritize operations to prepare for potential Ukrainian counteroffensives. Russian forces have also recently transferred elements of the 6th Guards Motorized Rifle Division (20th Guards Combined Arms Army, Western Military District) to an unspecified area north of Bakhmut, likely from positions along the Svatove-Kupyansk line.[10] The movement of Russian forces from other sectors of the front to the Bakhmut area is likely a response to persisting Russian concerns about the stability of frontlines in the area amid Wagner Group’s continued degradation in the offensive to capture Bakhmut.[11] These concerns were likely more pronounced in recent days that saw limited Ukrainian gains around Bakhmut and may have prompted further Russian concentration on the tactical offensive effort in the area. The reinforcements are also likely meant to enhance Wagner’s ability to capture the remainder of Bakhmut rapidly and present a Russian tactical victory before possible setbacks during a Ukrainian counteroffensive operation. ISW assesses that the Russian military command likely decided to reprioritize operations and sustainment efforts in recent weeks to prepare for potential Ukrainian counteroffensive operations, although the continued concentration on Bakhmut may suggest that immediate tactical concerns could be undermining the larger effort.[12]
Russia conducted another large-scale drone and missile strike on the night of May 15 to 16. Ukrainian sources reported that Russian forces launched six Kh-47 Kinzhal air-launched ballistic missiles from six MiG-31K aircraft at Kyiv, as well as nine Kalibr cruise missiles and 10 land-based S-400 and Iskander-M missiles at other rear areas of Ukraine.[13] Ukrainian air defense shot down all missiles, including all six Kinzhals (repeatedly touted by Russian forces as unstoppable) and nine total drones, including six Shahed-131/136s.[14] It is unclear which systems Ukrainian forces used to shoot down the Kinzhals, but Ukrainian officials previously attributed the defeat of a Kinzhal missile to US-provided Patriot air defense system on May 4.[15] Ukrainian Joint Forces Commander Lieutenant General Serhiy Nayev noted that the missile strike on Kyiv is the eighth in the month of May alone.[16] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) notably claimed that one of the Kinzhals struck a Patriot air defense system in Kyiv.[17] An unidentified US defense official told CNN that the Patriot system has likely suffered damage but has not been destroyed and that the US is still assessing the extent of the damage.[18]
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin attempted to downplay his reported cooperation with Ukrainian intelligence on May 15. Prigozhin responded to a media inquiry about leaked US intelligence report published in The Washington Post that revealed that he attempted to disclose positions of Russian conventional forces to Ukrainian intelligence in exchange for Ukraine’s withdrawal from Bakhmut.[19] Prigozhin stated that ”in any war exchanges are made, and this is not a secret for the warring parties” in an attempt to downplay his reported connections with the Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR).[20] Prigozhin argued that information about troop positions is ”not secretive at all” in modern warfare due to the use of satellite imagery. Prigozhin also paradoxically attempted to deny the validity of the leaked US intelligence documents, claiming that a junior US officer would have not had access to such secret documents. GUR Spokesperson Andriy Yusov stated that Ukraine will not comment on the leaked document.[21]
The Wagner Group’s continued glorification and normalization of violence is evident in a widely circulated video purportedly showing a killed American volunteer in Bakhmut. A Wagner Group-affiliated Telegram channel posted footage on May 16 of Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and former Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics-turned-Wagner-Group-deputy-commander Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev showing the documents and body of an American volunteer serving with the Ukrainian military.[22] Prigozhin claimed that he would give the body to US authorities because he likely died a worthy death in war.[23] Prigozhin’s video emphasizes Wagner’s continual promotion of brutality and glorification of war, as the video appeared to showcase Wagner gloating over the death of an American and amplified the graphic nature of his death. ISW previously reported on Wagner’s promotion of violence through the use of widely-shared graphic video footage.[24] A US State Department spokesperson stated that the State Department is ”aware of the reports” and ”seeking additional information.”[25]
Russia and Iran continue efforts to strengthen bilateral military-economic cooperation. Iranian state-run news agency IRNA reported on May 16 that Iranian Ambassador to Russia Kazem Jalali announced that Russia and Iran will sign an agreement on the construction of the Rasht-Astara railway line during Russian Deputy Prime Minister Alexander Novak’s visit to Tehran on May 16 and 17.[26] This agreement will reportedly advance the completion of Iran’s North-South corridor project by completing a 162km link between the Iranian cities of Rasht and Astara and will create a connection between St. Petersburg and the Persian Gulf.[27] The completion of this sector has been a long-standing Iranian line of effort, partially aimed at strengthening Iran‘s domestic economy and facilitating sanctions evasion efforts. Both Russia and Iran are taking additional steps to further bilateral military cooperation. The White House reported on May 15 that Russia seeks to buy additional drones from Iran after having used most of the 400 Iranian drones purchased since August 2022 in attacks on Ukrainian infrastructure.[28] Iranian media also reported on May 13 that Iran will receive its first shipment of Russian Su-35 multi-role fighter aircraft in the coming week.[29] Moscow will likely continue to pursue mutually beneficial military-economic programs in order to ensure continued Iranian material support for Russian operations in Ukraine.
The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) proposed a draft regulatory act that would allow FSB officers to conduct searches without a court order, likely to support the Kremlin’s ongoing efforts to strengthen domestic repression. The draft regulatory legal act would allow FSB officers to conduct operational search activities not associated with an ongoing criminal case without a court order in instances “that are urgent and may lead to the commission of a serious ...crime.”[30] FSB officers would also be allowed to conduct searches without court orders in connection with ”events or actions that pose a threat to the state, military, economic, information, or environmental security of Russia.”[31] ISW has previously assessed that the FSB appears to be currently conducting an overhaul of domestic security organs, and the new regulatory act is likely meant to augment these efforts.[32] The Kremlin has recently supported laws strengthening punishments for trespassing at facilities run by certain federal bodies, for the misappropriation of Russian military assets, and for the discreditation of all Russian personnel fighting in Ukraine to expand pretexts for the arrests of Russian citizens and the removal of officials who have fallen out of favor.[33] The FSB’s involvement in ongoing overhauls and the increasingly broad regulations to conduct searches suggest that the Kremlin is preparing for the FSB to be the internal security organ that would conduct a wider domestic crackdown.
Russian forces reportedly shut down another Ukrainian evangelical Christian church in Mariupol likely as part of a wider systematic religious persecution campaign in occupied Ukraine. Ukrainian Mariupol Mayoral Advisor Petro Andryushchenko reported that Russian forces seized the Ukrainian Christian Evangelical Church of the Holy Trinity in Mariupol and are using the church to house 10 to 30 Russian servicemen.[34] ISW reported on April 9 that Protestants suffered two-thirds of all of the reported religious repression events in occupied Mariupol.[35] ISW identified that Russian occupation officials most commonly persecute members of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church and Protestants, particularly evangelical Baptists.[36]
Key Takeaways
- Russian forces have likely committed to reinforcing their tactical offensive effort in the Bakhmut area despite Ukraine’s apparent focus on limited and localized counterattacks.
- The reported Russian reinforcements to the Bakhmut area suggest that Russian forces are continuing to concentrate offensive capabilities there despite an assessed wider effort to reprioritize operations to prepare for potential Ukrainian counteroffensives.
- Russia conducted another large-scale drone and missile strike on the night of May 15 to 16.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin attempted to downplay his reported cooperation with Ukrainian intelligence on May 15.
- The Wagner Group’s continued glorification and normalization of violence is evident in a widely circulated video purportedly showing a killed American volunteer in Bakhmut.
- Russia and Iran continue efforts to strengthen bilateral military-economic cooperation.
- The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) proposed a draft regulatory act that would allow FSB officers to conduct searches without a court order, likely to support the Kremlin’s ongoing efforts to strengthen domestic repression.
- Russian forces reportedly shut down another Ukrainian evangelical Christian church in Mariupol likely as part of a systematic religious persecution campaign in occupied Ukraine.
- Russian forces are reportedly deploying additional manpower and equipment from Belarus to reinforce their positions in Luhansk Oblast.
- Russian forces continued unsuccessful offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kremmina line.
- Russian forces have made marginal gains within Bakhmut as of May 16 and continued limited ground attacks along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces are continuing to panic about maintaining their positions in the east (left) bank Kherson Oblast ahead of anticipated Ukrainian counteroffensives.
- The Kremlin continues to pass legislation that provides benefits to participants of the war and their families in order to incentivize military service.
- Russian authorities continue efforts to consolidate the economic subordination of occupied areas of Ukraine into the Russian economy.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 15, 2023
Leaked US intelligence accessed by The Washington Post indicates that Wagner Group financier Yevgeniy Prigozhin offered to disclose the locations of Russian positions to Ukrainian intelligence in exchange for Bakhmut.[1] The Washington Post reported on May 15 that Prigozhin offered the Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) information about Russian troop positions in exchange for a Ukrainian withdrawal from Bakhmut, and two Ukrainian unnamed officials confirmed that Prigozhin had spoken to GUR officials on numerous occasions. GUR officials reportedly rejected Prigozhin’s offer because they did not trust Prigozhin, and some documents indicate that Kyiv suspects that the Kremlin is aware of Prigozhin’s communication with Ukrainian intelligence. The Washington Post reported that Prigozhin urged Ukrainian officials to attack Russian forces and revealed the problems that the Russian forces are facing with morale and ammunition stocks. The Washington Post published an interview with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky on May 13 about GUR Chief Major General Kyrylo Budanov’s interactions with Prigozhin and his operatives in Africa in which Zelensky did not confirm Ukraine’s contacts with Prigozhin.[2]
The reports of Prigozhin’s offers to cooperate with Ukrainian intelligence triggered a mixed response within Russia. Prigozhin originally responded to Zelensky’s interview on May 14, sarcastically stating that he can “confirm this information” because Wagner “has nothing to hide from foreign special services” and that he and Budanov are “still in Africa.”[3] Prigozhin’s later accused The Washington Post of spreading fake information and claimed that unnamed figures warned him about the efforts to discredit him using fake information.[4] Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov dismissed the allegations on May 15 and stated that, although he cannot comment on the information, it “looks like yet another hoax.”[5] Russian milbloggers – including one of Prigozhin’s enemies, former Russian officer Igor Girkin – claimed that they do not believe that Prigozhin would cooperate with Ukrainian intelligence.[6] State Duma Parliamentarian Viktor Sobolev warned that mobilized servicemen who decide to join the ranks of Wagner private military company (PMC) will face 10 to 15 years in prison because Wagner is an illegal armed formation within Russia.[7] It is unclear if Sobolev’s comments were made in response to the allegations, since Sobolev is an avid critic of Prigozhin and the Wagner forces.[8]
Prigozhin’s reported efforts to cooperate with Ukrainian intelligence would have been part of his feud with the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) rather than an attack on Russian President Vladimir Putin. ISW assessed on March 12 that Prigozhin is competing with the Russian MoD for Putin’s favor but had unintentionally alarmed Putin with his military-political ambitions.[9] Prigozhin’s reported outreach to Ukranian intelligence would likely have been part of an effort to win Putin’s favor, in fact, by facilitating a rapid Wagner victory in Bakhmut while harming Russian conventional forces behind the scenes. Prigozhin recently retracted his May 9 comments that indirectly mocked Putin, further indicating that Prigozhin is aware of his dependance on Putin and does not mean to antagonize him.[10]
The allegations are unlikely to cause the Kremlin to remove Prigozhin in the near term but can contribute to efforts to discredit Prigozhin. The Kremlin likely suspects or is aware of Prigozhin’s reported communications with Ukrainian intelligence and likely was not blindsided by The Washington Post report or the leaked US intelligence documents. Russian officials had reportedly threatened Prigozhin with treason if he were to act on his attempt to blackmail the MoD into providing him more ammunition by threatening to withdraw from Bakhmut. The Kremlin is likely preparing mechanisms to discredit Prigozhin as a traitor.[11] Unnamed Kremlin sources revealed that the Russian Presidential Administration is preparing an information operation to publicly discredit Prigozhin but noted that the Kremlin is unlikely to threaten Prigozhin while Wagner forces are on the frontlines.[12] Prigozhin commands the Wagner forces in Donbas, and his removal would disrupt the Russian lines in Bakhmut – a risk that Putin is unlikely to take. The Kremlin is also unable easily to publicly remove and replace Prigozhin as the de facto head of Wagner because Wagner is an independent company and Prigozhin holds no official position in the Russian government. Removing Prigozhin from his control of Wagner would ironically require asserting direct Kremlin control of the mercenary group from which Putin has been at pains to maintain formal distance.
Ukrainian officials acknowledged limited Ukrainian battlefield successes during recent localized counterattacks in and around Bakhmut. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated on May 15 that the Ukrainian forces made unspecified advances in and around Bakhmut in the past several days. Malyar added that Russian forces are deploying airborne (VDV) forces to defend Bakhmut’s flanks, presumably from other areas of the front.[13] Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi characterized the localized Ukrainian counterattacks as the first successes in Ukraine’s overall defense of Bakhmut and noted that this operation must be perceived as only a partial success.[14] Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated on May 14 that Ukrainian forces advanced 150-600 meters in various directions in the Bakhmut area and that Russian forces continue efforts to complete the capture of Bakhmut and defend the occupied territories.[15]
Russian milbloggers uniformly attacked a proposal for “military censorship,” further indicating that the community is highly motivated to defend its privileged position within the Russian information space. State Duma Deputy Viktor Sobolev proposed on May 15 that military correspondents’ reports about the situation in Ukraine should be subject to “military censorship” and that the lack of censorship has led to the spread of false information and panic.[16] Russian milbloggers widely criticized Sobolev for the supposed illegality and impracticality of the proposal, arguing that "military censorship” would be incongruous with Russia’s need to fill the information space with pro-Russian sources against the backdrop of the war in Ukraine.[17] State Duma Deputy Oleg Matveychev amplified an article by Russian political scientist Pavel Danilin on May 14 accusing the Russian milbloggers of promoting panicky false stories about Russian retreats and problems with the Russian MoD.[18] Danilin suggested that the milbloggers‘ actions constitute acts of high treason and stated that “during the Great Patriotic War, those who [sowed] panic … were put against the wall.”[19] Russian milblogger and Human Rights Council member Alexander “Sasha” Kots refuted Danilin's points and launched a series of critiques against Matveychev that other milbloggers amplified.[20] Russian milbloggers in both instances highlighted their alleged achievements and the importance of the “patriotic segment of Telegram” in bringing attention to acute problems and moving Russia closer to victory.[21]
Select Russian officials have previously called for the censorship of Telegram and the milbloggers, although ISW assesses that Putin is unlikely to approve such a measure because the Kremlin is attempting to use the wider ultranationalist community’s established networks to recruit volunteers and generate social support for the war.[22] The rapid and unified response from milbloggers suggests that the community perceives itself as a unitary civil society entity, one interested in defending its increasingly singular privilege in being able to criticize the conduct of the Russian war in Ukraine despite its internal factions and disagreements.
The Russian MoD claimed that it intercepted a Ukrainian Storm Shadow missile for the first time on May 15.[23] The MoD made this claim on the third day of four days of claimed Ukrainian Storm Shadow strikes against the Russian military assets in Luhansk City, roughly 80-100 kilometers behind the frontline.[24] A Russian milblogger expressed concern that Ukraine’s use of the missile can severely impact the situation on the frontlines because the only way Russian forces can counter the Storm Shadows is to destroy the aircraft carrying the missiles.[25]
The Kremlin has reportedly banned high-ranking officials from resigning during the war in Ukraine, likely in an attempt to maintain stability within domestic security organs, government bodies, and the Russian military command. Independent Russian investigative outlet Vazhnye Isotrii (iStories) reported on May 15 that a former Federal Security Service (FSB) officer and sources close to an unnamed regional governor and the presidential administration stated that the Kremlin threatened civil servants in security organs and government bodies with criminal prosecution for trying to defy the ban.[26] The Kremlin reportedly instituted the ban because many officials wanted to leave their positions after Russia's full-scale invasion of Ukraine, although iStories’ sources emphasized that the informal and illegal nature of the ban may allow for exceptions.[27] The Kremlin may be attempting to stop Russian officials from resigning in protest to advance their own objectives. ISW previously reported that former Central Military District (CMD) commander Colonel General Alexander Lapin and Russian Airborne Forces (VDV) commander Colonel General Mikhail Teplinsky reportedly resigned due to intense public criticism and in protest of conditions at the front, respectively.[28] Teplinsky likely used the fallout from his resignation to advocate for a leading military command position in Ukraine, a scenario that the Kremlin may attempt to avoid in the future by applying the reported ban more broadly.[29]
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky met with French President Emmanuel Macron and UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak on May 14 and 15 confirming the provision of more Western military aid. The Ukrainian and French governments issued a joint statement on May 15 announcing that France will train and equip “several” Ukrainian battalions with “tens” of armored vehicles and light tanks, including the AMX-10RC.[30] The joint statement reiterated that the French government would continue providing political, financial, humanitarian, and military aid to Ukraine “for as long as it takes.” The UK government confirmed on May 15 that Sunak will announce another round of military aid to Ukraine, including the provision of unspecified long-range attack drones with ranges of over 200 kilometers, and will deliver them to Ukraine over the coming months.[31] Sunak announced that the UK will begin developing a program to train Ukrainian pilots to fly F-16 fighter jets and will begin training an initial cohort of pilots over the summer.
Key Takeaways
- Leaked US intelligence accessed by The Washington Post indicates that Wagner Group financier Yevgeniy Prigozhin offered to disclose the locations of Russian positions to Ukrainian intelligence in exchange for Bakhmut.
- Ukrainian officials acknowledged limited Ukrainian battlefield successes during recent localized counterattacks in and around Bakhmut.
- Russian milbloggers uniformly attacked a proposal for “military censorship,” further indicating that the community is highly motivated to defend its privileged position within the Russian information space.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that it intercepted a Ukrainian Storm Shadow missile for the first time on May 15.
- The Kremlin has reportedly banned high-ranking officials from resigning during the war in Ukraine, likely in an attempt to maintain stability within domestic security organs, government bodies, and the Russian military command.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky met with French President Emmanuel Macron and UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak on May 14 and 15 confirming the provision of more Western military aid.
- Russian sources claimed that Russian forces captured Masyutivka, Kharkiv Oblast and established a bridgehead on the west bank of the Oskil River, but ISW has observed no visual confirmation of these claims.
- Russian forces continued to launch ground assaults in and around Bakhmut and conducted limited offensive operations near Donetsk City.
- Ukrainian intelligence reported that approximately 152,000 Russian military personnel in southern Ukraine continue defensive efforts ahead of a possible Ukrainian counteroffensive.
- Russian authorities continue efforts to take advantage of migrant labor and incentivize foreigners into contract military service.
- Russian officials and occupation authorities continue to set conditions to forcibly relocate Ukrainians from occupied territories to Russia.
- Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko received a briefing from Belarusian generals on May 15 following recent speculation about his possible illness or death.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 14, 2023
Russian forces conducted another series of drone and missile strikes against Ukraine on the night of May 13 to 14. Ukrainian sources reported that Russian forces launched an unspecified number of drones of varying models at Ukraine and that Ukrainian forces destroyed 25, including 18 Shahed 131/136s.[i] The Ukrainian General Staff noted that Russian forces launched 23 Shahed-136/131 drones in total.[ii] The Ukrainian General Staff also reported that Russian forces launched an unspecified number of Kalibr missiles from the Black Sea as well as an unspecified number of Kh-101/555/55 cruise missiles, and that Ukrainian forces shot down three Kh-101/555/55 missiles.[iii] Ukrainian sources reported that Russian forces struck civilian infrastructure in Ternopil and Mykolaiv cities as well as Kharkiv City and Zolochiv in Kharkiv Oblast with S-300 missiles.[iv] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian forces struck a Ukrainian ammunition depot in Khmelnytskyi City and Ukrainian military facilities and deployment areas near Ternopil and Petropavlivka, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast.[v]
Increasingly regular series of Russian drone and missile strikes are likely a part of a new Russian air campaign in Ukraine aimed at degrading Ukrainian abilities to conduct counteroffensive offensive operations in the near term. Russian forces have conducted at least 10 series of strikes throughout Ukraine, particularly in rear areas, since April 19.[vi] Russian forces have used significantly fewer high precision missiles in these latest series of strikes in comparison to their failed campaign against Ukrainian critical infrastructure from the fall of 2022 through the winter of 2023. ISW previously assessed that Russian forces likely expended a significant proportion of their precision missiles in the previous air campaign, and the current Russian air campaign may be using far fewer of these missiles in an effort to conserve the limited remaining stocks.[vii] Russian forces have instead relied heavily on launching large numbers of Iranian-made Shahed drones to overwhelm Ukrainian air defenses, although Ukrainian forces have been more effective in shooting down Russian precision systems than during the previous Russian air campaign.[viii] The new Russian air campaign appears to be focused on Kyiv and alleged Ukrainian military industrial and logistics facilities in deep rear areas. The more limited air campaign has so far been more regular than the previous wider Russian campaign against critical infrastructure, and ISW has previously assessed that Russian forces may be attempting to conduct almost daily series of strikes to portray themselves as successfully constraining potential upcoming Ukrainian counteroffensive operations.[ix] The alleged targets and limited nature of this campaign indicates that Russian forces are immediately concerned with current Ukrainian capabilities to launch counteroffensive operations, although the diminished effectiveness of these strikes are likely not significantly constraining Ukrainian capabilities writ large.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 13, 2023
Ukrainian forces continue to counterattack in the Bakhmut area amid unconfirmed claims of further marginal Ukrainian gains southwest of the city as of May 13. A Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces established new positions on the outskirts of Kurdyumivka (14km southwest of Bakhmut) and pushed Russian forces behind the Siversky Donets-Donbas canal in the area.[1] The milblogger also claimed that Ukrainian forces advanced towards Klishchiivka (7km southwest of Bakhmut) from the direction of Predtechyne (16km southwest of Bakhmut). ISW has not observed visual confirmation of these additional Ukrainian gains southwest of Bakhmut or elsewhere in the wider Bakhmut area as of May 13. Ukrainian Eastern Grouping of Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi stated on May 13 that Ukrainian forces are advancing in unspecified areas of the front, and the Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian forces are currently conducting active operations in the Bakhmut area.[2] Ukrainian Eastern Grouping of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated on May 13 that Ukrainian forces liberated 17.3 square kilometers of territory in the Bakhmut direction over three days of counterattacks.[3] ISW has assessed as of May 13 that the Ukrainian forces have liberated 16.85 square kilometers in the Bakhmut area during recent counterattacks. Russian sources amplified footage purporting to show the aftermath of a recent Ukrainian counterattack on Russian positions near Mayorsk (20km southwest of Bakhmut) and claimed that the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) 3rd Brigade of the 1st Army Corps repelled the assaults.[4] A prominent Russian milblogger claimed that recent successful limited Ukrainian counterattacks north of Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut) degraded Russian forces’ ability to interdict the O0506 highway between Khromove and Chasiv Yar (13km west of Bakhmut), a significant ground line of communication (GLOC) for Ukrainian forces operating in Bakhmut itself.[5] The milblogger claimed that Russian retreats in response to recent Ukrainian counterattacks have occurred in relatively small areas of the frontline but warned that these “regroupings” could become more significant if Russian forces fail to stabilize the frontline.[6] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed on May 12 that talks of tactical Russian withdrawals are nonsense as Russian forces continue to outright abandon positions in unspecified locations.[7]
Russian forces conducted a Shahed-131/136 drone strike against Ukraine on the night of May 12 to 13. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that shot down 18 of the 22 Shahed-131/136 drones that Russian forces launched from the northern and southern directions.[8] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that drones struck an infrastructure facility in Khmelnytsky Oblast.[9] Footage published on May 13 purportedly shows the aftermath of the strike in Khmelnytsky Oblast.[10]
Russian media reported that two Russian Mi-8 helicopters, a Su-34 bomber, and an Su-35 fighter crashed in Bryansk Oblast on May 13, which some Russian sources claimed was caused by Ukrainian air defenses. Geolocated footage shows the aftermath of crashes near Surestskii Muravei and Klintsy, about 50km from the Ukrainian border.[11] Russian milbloggers speculated that all four aircraft crashed as the result of a coordinated Ukrainian strike using air defense systems pulled to the border area of Chernihiv Oblast.[12] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) has not yet responded to the incident at the time of publication. Ukrainian officials have similarly refrained from commenting on the incidents. However, several Russian milbloggers seized on the incident to criticize aspects of how the Russian aerospace forces conduct air operations and to accuse the leadership responsible for these aircraft of gross negligence and incompetence. Milbloggers warned about Ukrainian capabilities and called for harsh retaliation against Ukraine. Some milbloggers questioned why the two Mi-8 helicopters were flying so close to the border in the first place and called for aerospace commanders to take better steps to move such assets further into the rear.[13] Moscow Duma Deputy Andrey Medvedev warned that Ukrainian counteroffensive actions will not manifest only in mechanized warfare, suggesting that Russian authorities should prepare for further strikes on such aviation assets as part of a wider Ukrainian counteroffensive strategy.[14] Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) Deputy Information Minister Daniil Bezsonov accused the Russian aerospace command of “tyranny” and “fraud.”[15]
Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces struck rear Russian areas in Luhansk Oblast with British Storm Shadow cruise missiles on May 12 and 13, prompting heightened Russian anxiety about potential Ukrainian abilities to target Russian logistics. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed on May 13 that Ukrainian aircraft struck industrial facilities in occupied Luhansk City with a Storm Shadow cruise missile on May 12.[16] Geolocated footage published on May 13 shows the aftermath of Ukrainian strikes on Yuvileyne (7km west of Luhansk City) on May 13, and Russian sources widely claimed that Ukrainian forces also used Storm Shadow cruise missiles in the subsequent strike.[17] A Russian milblogger claimed that a Storm Shadow cruise missile would have caused more damage, however, and the Luhansk People’s Republic (LNR) Internal Ministry claimed that Ukrainian forces used “Hrim-2” missiles to conduct the May 12 strike.[18] United Kingdom Defense Secretary Ben Wallace confirmed on May 12 that the UK is supplying Ukraine with the missiles but did not specify when or even if Ukraine received them.[19] ISW has not observed visual confirmation that Ukrainian forces have used Storm Shadow cruise missiles to strike Russian positions in Ukraine. Russian milbloggers claimed that the strike illustrates that Ukrainian forces may be able to target airfields and rear deployment and logistics centers in areas previously considered to be completely safe.[20] A prominent Russian milblogger compared the alleged use of the cruise missiles to the summer of 2022 when Ukrainian forces began using HIMARS rockets to target Russian logistics in Kherson Oblast and argued that the Russian information space is similarly attempting to downplay the impact that such systems may have.[21]
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s insistence on conducting the war in Ukraine in the style of the “Great Patriotic Special Military Operation” has opened the door for several hardline actors to advocate for the institutionalization of increasingly Stalinist domestic policies. Russian Investigative Committee Head Alexander Bastrykin proposed on May 13 that, in light of the requirements for “economic security in a war,” Russia should take the path of “nationalization of the main sectors” of the economy.[22] A prominent Russian milblogger responded to Bastrykin’s statement and noted that whole-scale nationalization has transcended the rhetoric of the Communist Party and is now being advocated for by one of the largest Russian law enforcement agencies.[23] The milblogger remarked that the Russian elites appear to be increasingly using Bolshevik and Stalinist practices to organize Russian society for war in the absence of other successful historical analogues for wartime economic structuring.[24] ISW has previously assessed that Putin is invested in constructing false historical parallels between the war in Ukraine with the Soviet Great Patriotic War.[25] The emulation of these conditions on the highest levels of Russian government will likely continue to have domestic implications as the war continues and opens the door for increased normalization of Soviet and Stalinist practices in all branches of government.
Former Pacific Fleet Commander Admiral Sergey Avakyants reportedly received an appointment to lead a new Russian force generation organization called “Voin” (“Warrior”), which reportedly replaced Russia’s legacy Russian Volunteer Society for Assistance to the Army, Aviation, and Navy of Russia (DOSAAF). One Russian source claimed on May 13 that the “Voin” organization, which will provide combat training and education to Russians between 14 and 35 years old, has “completely replaced” DOSAAF, which had been active in recruitment efforts.[26] ISW previously reported that the same Russian milblogger claimed that Avakyants will be forming a new “organization” which could cooperate with DOSAAF.[27] It is unclear what DOSAAF’s current status is if this milblogger’s report is accurate. It is also unclear if DOSAAF was disbanded and reformed into “Voin” or if “Voin” had subsumed DOSAAF’s organization into a new vertically integrated organization under Avakyants’ and the Russian Ministry of Defense‘s (MoD’s) control. This report, if accurate, could indicate a Kremlin effort to subordinate DOSAAF — a nominally non-governmental organization — under the MoD. DOSAAF, a Soviet-era youth movement for promoting military skills, has likely supported Russian forces and Wagner Group recruitment and youth education aimed at Russifying youth in occupied Ukraine.[28]
Belarusian President Lukashenko was reportedly hospitalized at a presidential hospital in Minsk on May 13. Independent Belarusian monitors reported that Lukashenko was hospitalized in Minsk around 19:00 local time on May 13 but that Lukashenko’s motorcade had left the hospital by around 21:00.[29] The status of Lukashenko’s health condition remains unclear. Lukashenko has not been seen in public nor has his office updated his weekly schedule with any events since his visit to Moscow on May 9.[30] Lukashenko did not deliver his traditional Victory Day address in Minsk, Belarus, on May 9 although it is not clear why.[31]
Key Takeaways
- Ukrainian forces continue to counterattack in the Bakhmut area amid unconfirmed claims of further marginal Ukrainian gains southwest of the city as of May 13.
- Russian forces conducted a Shahed-131/136 drone strike against Ukraine on the night of May 12 to 13.
- Russian media reported that two Russian Mi-8 helicopters, an Su-34 bomber, and an Su-35 fighter crashed in Bryansk Oblast on May 13, which some Russian sources claimed was caused by Ukrainian air defenses.
- Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces struck rear Russian areas in Luhansk Oblast with British Storm Shadow cruise missiles on May 12 and 13, prompting heightened Russian anxiety about potential Ukrainian abilities to target Russian logistics.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin’s insistence on conducting the war in Ukraine in the style of the “Great Patriotic Special Military Operation” has opened the door for several hardline actors to advocate for the institutionalization of increasingly Stalinist domestic policies.
- Former Pacific Fleet Commander Admiral Sergey Avakyants reportedly received an appointment to lead a new Russian force generation organization called “Voin” (“Warrior”), which reportedly replaced Russia’s legacy Russian Volunteer Society for Assistance to the Army, Aviation, and Navy of Russia (DOSAAF).
- Belarusian President Lukashenko was reportedly hospitalized at a presidential hospital in Minsk on May 13.
- Russian forces continued limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and northwest of Svatove.
- Russian forces made marginal gains within Bakhmut and continued limited offensive operations along the Avdiivka-Donetsk front.
- Russian forces targeted Ukrainian positions in southern Ukraine west of Hulyaipole.
- Russian forces are reportedly replenishing units with mobilized personnel.
- Russian authorities continue efforts to deport Ukrainian children to Russia under the guise of “rest and relaxation” schemes.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 12, 2023
Ukrainian forces have made gains northwest of Bakhmut in localized counterattacks as of May 12. Geolocated footage posted on May 12 shows Russian forces fleeing Ukrainian artillery fire on the southern bank of the Berkhivske Reservoir, about 4km northwest of Bakhmut. This footage visually confirms claims made by a number of Russian milbloggers that Ukrainian forces made gains northwest of Bakhmut in the area between Bohdanivka and Berkhivka. One Russian milblogger claimed that elements of the 200th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (14th Army Corps, Northern Fleet) lost their positions in the area between Hryhorivka and Dubovo-Vasylivka (about 6km northwest of Bakhmut). Several Russian sources warned that Ukrainian forces may be attempting to encircle the Wagner Group within Bakhmut. Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Priogozhin emphasized that Ukrainian forces are approaching Berkhivka and claimed that Ukraine now holds positions within 500m of Bakhmut’s northwestern city limits. Russian milbloggers additionally reported that Ukrainian troops are counterattacking towards Khromove (3km west of Bakhmut), Bohdanivka (6km northwest of Bakhmut), and Klishchiivka (6km southwest of Bakhmut). One Russian milblogger claimed that the situation southwest of Bakhmut near Mayorsk has stabilized following Ukrainian attacks on positions of the 1st Donetsk People’s Republic Army Corps. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) rejected claims made by other Russian sources regarding Ukrainian advances and claimed instead that elements of the 4th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (Luhansk People’s Republic) and 200th Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade (14th Army Corps, Northern Fleet) repelled all attacks in the Berkhivka area ”taking into account the favorable conditions of the Berkhivske Reservoir.”
Russian milbloggers and other prominent voices in the pro-war information space continue to respond to recent Ukrainian counterattacks with varying degrees of caution and anxiety. Many milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian activity around Bakhmut marks the official beginning of the anticipated spring counteroffensive and speculated about where Ukraine’s main effort will take place. Several prominent Russian voices, however, urged caution and restraint in responding to the counteroffensive, suggesting that some milbloggers are advocating for the application of certain lessons they took from the information space meltdown during Ukraine’s successful Kharkiv and Kherson counteroffensives. Some milbloggers warned that reports about Ukrainian success could be a deliberate Ukrainian attempt to sow panic. Another milblogger warned against accepting all reports that Ukrainian activities are “psychological operations” at face value and voiced concern about Russian propaganda responses to the counterattacks. One milblogger suggested that credible reports of Ukrainian counterattacks do not mean that the “everything is on fire,” cautioning the audience against falling into despair. The milblogger remarked that telling the truth about Ukrainian operations does not amount to ”sowing panic.” The overall Russian information space response appears to be focused on the idea of avoiding spreading panic.
Ukrainian and American officials stated that Ukrainian forces have not yet started the planned counteroffensive. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated on May 12 that Ukrainian forces are still conducting defensive operations, which sometimes include counterattacks and other unspecified active actions. A senior US military official and a senior Western official stated on May 12 that Ukrainian forces have started conducting “shaping” operations in advance of the counteroffensive. Western reporting on this subject notably contradicts Russian sources, many of which have claimed the counteroffensive is officially underway.
Senior Russian officials proposed a series of domestic repression and censorship measures during the St. Petersburg International Legal Forum on May 11. The theme of the forum centered on the criminalization of “Russophobia,” a measure that Russian Human Rights Council Chairperson Valery Fadeev proposed and Deputy Minister of Justice Andrey Loginov and Russian Ombudsman Tatyana Moskalkova supported. Moskalkova defined Russophobia as a “misanthropic ideology,” and a State Duma deputy claimed that the International Criminal Court’s arrest warrants for Russian officials for the kidnapping of Ukrainian children to Russia is an example of “Russophobia.” Deputy Minister of Justice Oleg Sviridenko announced an expansion of the law against ”foreign agents” to include a section penalizing ”third parties” for aiding foreign agents in violating Russian law. Russian Investigative Committee Chairperson Alexander Bastrykin asked Russian Constitutional Court Chairperson Valery Zorkin to look into ways of establishing an unspecified state ideology in the Russian Constitution, which Bastrykin claimed would require the Duma to adopt a new constitution rather than pass an amendment. Russian Minister of Justice Konstantin Chuichenko supported Bastrykin’s proposal, but Zorkin noted that the current constitution contains a set of values that can ”allow civil society to connect.” Senior Russian officials’ introduction of such proposals indicates that the Kremlin may be gauging the information space reaction to increased repression measures and setting conditions for long-term strengthening of these measures.
Former Russian officer and ardent nationalist Igor Girkin’s newly formed “Club of Angry Patriots” held a press conference on May 12 to discuss its discontent with the current Russian conduct of the war in Ukraine. Former self-proclaimed Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) “People’s Governor” Pavel Gubarev emphasized that the goal of the “special military operation” should be the “elimination of Ukrainian statehood,” and “Another Russia” political party coordinator Mikhail Aksel accused Russian authorities of not taking the steps needed to realize the goals of the war. Girkin himself reiterated his belief that the Russian military in its current state cannot achieve decisive battlefield results and criticized the inaction of Russian leadership. As ISW has previously assessed, the Club of Angry Patriots is using its platform to launch specific critiques at the inner circles of Russian leadership while protecting a pro-war faction within the Kremlin. The public format of this press conference is additionally noteworthy--Girkin and other members of the club typically use their individual Telegram channels to propagate their talking points, and a public press conference suggests that they have had some success in reaching broader audiences, potentially as domestic pro-war factions are increasingly discontent with the way Russia has been fighting the war thus far. The Club of Angry Patriots notably held the press conference during a period of high information space agitation about a future Ukrainian counteroffensive, which may inflame some factions’ criticisms of senior Russian leadership for poor performance in the war.
U.S. Ambassador to South Africa Reuben Brigety accused South Africa of loading a Russian ship with ammunition and weapons in December 2022, contradicting its proclaimed neutral stance on the war in Ukraine. Brigety stated on May 11 that a sanctioned Russian vessel containing weapons departed the Simon’s Town naval base in Cape Town on December 9, 2022, and arrived in Novorossiysk on February 22, 2023. White House National Security Council spokesperson John Kirby stated on May 12 that these reports are a “serious issue” as the US has consistently and strongly urged other countries not to supply weapons to Russia. South African officials stated that there is no evidence to support US accusations and summoned Brigety on May 12 after criticizing his statements.
Key Takeaways
- Ukrainian forces have made gains northwest of Bakhmut in localized counterattacks as of May 12.
- Russian milbloggers and other prominent voices in the pro-war information space continue to respond to recent Ukrainian counterattacks with varying degrees of caution and anxiety.
- Ukrainian and American officials stated that Ukrainian forces have not yet started the planned counteroffensive.
- Senior Russian officials proposed a series of domestic repression and censorship measures during the St. Petersburg International Legal Forum on May 11.
- Former Russian officer and ardent nationalist Igor Girkin’s newly formed “Club of Angry Patriots” held a press conference on May 12 to discuss its discontent with the current Russian conduct of the war in Ukraine.
- S. Ambassador to South Africa Reuben Brigety accused South Africa of loading a Russian ship with ammunition and weapons in December 2022, contradicting its proclaimed neutral stance on the war in Ukraine.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) attempted to distract from and assuage information space paranoia over a potential Ukrainian counteroffensive on the Kharkiv-Luhansk front.
- Russian forces continue limited ground attacks in and around Bakhmut.
- Russian sources continue to speculate about potential Ukrainian counteroffensive preparations in southern Ukraine.
- Russian forces continue to recruit convicts and establish volunteer battalions as a part of crypto-mobilization efforts.
- Senior Russian officials are claiming that they are taking active measures to return displaced and illegally deported Ukrainian civilians, including Ukrainian children, to occupied Ukraine.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 11, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 2:00 pm ET on May 11. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 12 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Ukrainian forces likely broke through some Russian lines in localized counterattacks near Bakhmut, prompting responses from Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD). Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi stated that Russian forces retreated up to two kilometers behind Russian lines in unspecified sectors of the Bakhmut front.[1] Syrskyi’s confirmation of Ukrainian gains prompted a response from Prigozhin, who claimed that Ukrainian forces have started the counteroffensive and recaptured three kilometers of ground in and around Bakhmut.[2] The Russian MoD acknowledged the Ukrainian counterattacks uncharacteristically quickly, claiming that Russian forces repelled eight ground attacks and three reconnaissance-in-force efforts in the Donetsk direction but denied reports that Ukrainian forces broke through the Russian defensive lines.[3] Prigozhin’s and the MoD’s responses are reflective of increased panic in the Russian information space over speculations about planned Ukrainian counteroffensives and indicate increased concern among Wagner and Russian MoD leadership as well as reflecting Kremlin guidance to avoid downplaying Ukrainian successes.[4]
The deployment of low-quality Russian forces on the flanks around Bakhmut suggests that the Russian MoD has largely abandoned the aim of encircling a significant number of Ukrainian forces there. The Russian MoD likely began a broader deprioritization of the Bakhmut effort by January 2023 when the MoD cut off Wagner Group penal recruitment efforts, which likely prompted Prigozhin to ramp up the Soledar-Bakhmut effort in January and publicly complain about the lack of MoD support for his efforts starting in February 2023.[5] The Russian MoD briefly allocated more resources to the Bakhmut front line in March and April by sending T-90 tanks and Russian Airborne (VDV) forces to the Bakhmut area and assigning mobilized reservists to Wagner, however.[6] Prigozhin claimed on April 24 that the Russian MoD only deployed irregular and degraded units to hold Bakhmut’s flanks, and the inability of these units to fulfill even this limited mission indicates that Russian flanks in Bakhmut and other similarly-manned areas of the front are likely vulnerable to Ukrainian counterattacks.[7] The MoD’s allocation of forces combined with changes in the geometry of the battlespace also suggests that the danger of a Russian encirclement of significant Ukrainian forces in Bakhmut may have passed. Wagner forces will likely continue conducting frontal assaults in Bakhmut, which would allow Ukrainian forces to conduct organized withdrawals from threatened areas in a shallower partial envelopment rather than facing encirclement on a large scale.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky stated that Ukraine needs more time to launch a counteroffensive because it is waiting for the delivery of promised military aid. Zelensky told the BBC that some of the expected military equipment has not arrived in Ukraine and that, although Ukrainian forces are ready for the counteroffensive, Ukraine would suffer too many casualties.[8] Zelensky also stated that the Ukrainian counteroffensive is important to prevent Russia from freezing the war.
Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov contradicted the pre-war Kremlin justifications for the war by asserting that the Russian “special military operation” began as “a conflict between Russia and Ukraine.” He said that Russia has “partially” achieved the goals of “protecting” people in Donbas,[9] but added that Russia is still far from fully achieving these goals. He said that it was ”hard to believe” at the beginning of the war that NATO, the United States, and European countries would ”intervene in this conflict.” ISW previously reported that the Kremlin has begun to shift its domestic narratives to claim that Russia is fighting only against NATO in an effort to set informational conditions for potential Russian military failures during the planned Ukrainian counteroffensive.[10] Peskov’s statement is consistent with the new Russian narrative but contradicts Russian President Vladimir Putin’s statements prior to the February 24, 2022 invasion. Putin stated on February 21, 2022, that Russia is ”not fighting the Ukrainian people” and claimed that Ukraine had become a hostage of its ”Western masters.”[11] The Russian pre-war justification for the invasion relied heavily on portraying a NATO threat to Russia supposedly emanating from Ukraine.[12]
Unnamed Kremlin sources claimed that Wagner Group Yevgeny Prigozhin’s recent rhetoric is “seriously disturbing the top leadership” of Russia. Two Kremlin sources told Russian opposition outlet Meduza that the Kremlin saw Prigozhin’s attempts to blackmail the Russian MoD on May 5 as a “serious threat” and that Prigozhin is not acting in the Kremlin’s interests.[13] One interlocutor stated that Prigozhin is committed to claiming Bakhmut as a personal victory in order to have influence over the Russian MoD. The Kremlin reportedly expressed further concerns over Prigozhin’s May 9 mockery of the “happy grandfather” figure who is responsible for future Russian generations.[14] ISW assessed on May 9 that Prigozhin was likely referring to Putin, and a Kremlin source claims that Prigozhin’s statement was a direct allusion to Putin. The second interlocutor claimed that Prigozhin’s rhetoric cannot be interpreted as a “direct attack” on Putin, however. Prigozhin attempted on May 10 to downplay his original statements, claiming that the “happy grandfather” did not refer to Putin.[15] The sources noted that Prigozhin’s escalating behavior is likely a result of his inability to meet an unspecified deadline for the capture of Bakhmut. One source claimed that Prigozhin is blaming conventional units in order to avoid accepting responsibility for failing to follow through on his “personal promise” to capture Bakhmut.
The interlocutors noted that Prigozhin may have crossed the Kremlin’s “red lines” and may alienate his supporters within the Russian inner circle. Prigozhin reportedly is losing contact with one of his patrons, Russian billionaire and Putin’s “personal banker” Yuriy Kovalchuk. Kovalchuk was reportedly one of the leading voices supporting the full-scale invasion of Ukraine after developing a strong relationship with Putin during the Covid-19 pandemic.[16] The sources noted that Russian propagandists received a directive to discredit Prigozhin as a traitor if he continues to critique the Kremlin – an effort that has previously failed.[17] The sources assessed that Prigozhin is not at risk while Wagner is still on the frontline, which allows Prigozhin to have contact with Putin.
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) denied official Ukrainian and US reports that a Patriot missile defense system shot down a Kinzhal missile on the night of May 4.[18] Kremlin newswire TASS reported on May 11 that a “high-ranking source in the Russian MoD” denied reports that Ukraine intercepted a Kinzhal missile. Ukrainian Air Force Commander Mykola Oleshchuk had reported that Ukrainian forces used the Patriot system to shoot down a Kinzhal missile in the air over Kyiv Oblast at night on May 4.[19] The Russian MoD denied this report only after the US Department of Defense confirmed on May 9 that a Patriot air defense system had shot down a Russian Kinzhal missile.[20]
Russian occupation authorities seized the cathedral of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine in Simferopol as oppression of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church continues in Russian-occupied Crimea. The Commissioner of the Crimean Eparchy of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine, Metropolitan Kliment of Simferopol, and Crimean journalist Andriy Shchekun reported on May 11 that representatives of the Russian State Property Fund of the Republic of Crimea and other occupation authorities broke down the doors of the church and began stealing the property of the cathedral.[21] ISW has previously reported on Russia’s religious repression throughout occupied Ukraine.[22]
Key Takeaways
- Ukrainian forces likely broke through some Russian lines in localized counterattacks near Bakhmut, prompting responses from Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD).
- The deployment of low-quality Russian forces on the flanks around Bakhmut suggests that the Russian MoD has largely abandoned the aim of encircling a significant number of Ukrainian forces there.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky stated that Ukraine needs more time to launch a counteroffensive because it is waiting for the delivery of promised military aid.
- Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov contradicted the pre-war Kremlin justifications for the war by asserting that the Russian “special military operation” began as “a conflict between Russia and Ukraine.”
- Unnamed Kremlin sources claimed that Wagner Group Yevgeny Prigozhin’s recent rhetoric is “seriously disturbing the top leadership” of Russia.
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) denied Ukrainian and US reports that a Patriot missile defense system shot down a Kinzhal missile on the night of May 4.
- Russian occupation authorities seized the cathedral of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine in Simferopol as oppression of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church continues in Russian-occupied Crimea.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Ukrainian forces reportedly continued to conduct localized counterattacks around Bakhmut.
- Russian forces targeted Ukrainian positions west of Hulyaipole and in Kherson Oblast.
- Russia needs to produce over 29 million shells per year to satisfy Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin’s demands for Wagner to use 80,000 shells per day – 13 times more than Russia’s pre-invasion annual production rate.
- Russian officials continue to threaten and seek to manipulate international humanitarian efforts by threatening to dissolve the Black Sea Grain Initiative, which is set to expire on May 18.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 10, 2023
Ukrainian forces conducted successful limited counterattacks around Bakhmut on May 9. Geolocated footage published on May 9 and 10 indicates that Ukrainian forces likely conducted successful limited counterattacks north of Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut) and northwest of Bila Hora (14km southwest of Bakhmut) and made marginal advances in these areas. Ukrainian sources claimed on May 9 that Ukrainian forces destroyed the 6th and 8th companies of the 72nd Motorized Rifle Brigade of the 3rd Army Corps near Bakhmut and advanced 2.6km along a 3km frontline in the area, although ISW has not observed visual confirmation of these reported wider Ukrainian advances. A prominent Russian milblogger claimed on May 10 that the Ukrainian forces tried to advance further in the Luhansk People’s Republic (LNR) 4th Motorized Rifle Brigade’s zone of responsibility in the Bakhmut area following Ukrainian counterattacks on May 9 but that formations of an unspecified Russian paramilitary company (PMC) prevented a Ukrainian breakthrough. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian Airborne Forces (VDV) are constraining the actions of Ukrainian forces on the flanks around Bakhmut. ISW has previously assessed that reports of Ukrainian counterattacks throughout Donetsk Oblast appear to be a part of an ongoing pattern of localized and limited counterattacks.
Pervasive issues with Russian combat capability, exacerbated by continued attritional assaults in the Bakhmut area, are likely considerably constraining the ability of Russian forces in this area to defend against localized Ukrainian counterattacks. The 72nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade itself is emblematic of many of the endemic force generation issues constantly faced by the Russian military. ISW reported on August 7, 2022, that the 72nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade was forming in Orenburg Oblast as part of the 3rd Army Corps, a new formation created in 2022 and largely comprised of volunteer battalions. Forbes reported in September of 2022 that the 3rd Army Corps deployed to Kharkiv Oblast and that the Ukrainian Kharkiv Oblast counteroffensive largely destroyed the corps’ constituent elements, likely including the 72nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade. Ukrainian media suggested that the surviving elements of the 72nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade may have redeployed to Mykolaiv Oblast following the Kharkiv Oblast counteroffensive, where they once against suffered losses during Ukraine’s southern counteroffensive in October 2022. ISW cannot confirm where the 72nd Brigade deployed to following the withdrawal of Russian forces from the west (right) bank of the Dnipro River, but it is highly likely that whatever elements of the 72nd Brigade that deployed to the Bakhmut area more recently are not operating at anywhere near full strength. The Russian military command’s apparent commitment of elements of a formation that has suffered two successive defeats to the Bakhmut axis alongside already attrited Wagner elements likely offer Ukrainian forces opportunities to exploit with limited counterattacks. A Russian milblogger, citing a Wagner commander active in the Bakhmut area, additionally reported that the alleged withdrawal of the 72nd Brigade was the result of severe miscommunication between command of the 72nd Brigade and the Wagner Group. Issues with the ad hoc commitment of various depleted force groupings to the Bakhmut axis, alongside apparent command and control failures, are likely preventing Russian forces in the area from conducting sound defensive operations.
Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian forces struck a command center where high-ranking Ukrainian military commanders and officials were located, likely to support an ongoing effort to frame Russian operations as constraining Ukrainian capabilities to launch a counteroffensive. Russian milbloggers claimed on May 10 that Russian forces struck the command post near Chasiv Yar (12km west of Bakhmut), killing Ukrainian Chief Advisor to the Directorate for Domestic and Humanitarian Policy Alexei Titarenko. Russian milbloggers speculated that the strike may have killed other high-ranking Ukrainian commanders and officials and stated that the strike has prompted completely unsubstantiated rumors, which Ukrainian officials have explicitly denied, that it killed Commander-in-Chief of the Ukrainian Armed Forces General Valery Zaluzhnyi. Milbloggers acknowledged that the strike likely did not kill Zaluzhnyi but argued that it may be affecting his decisions to attend certain events. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated that all the Ukrainian commanders in question are alive and that claims about the killing of Ukrainian commanders are a part of a Russian information operation aimed at degrading Ukrainian morale. ISW assessed that Russian ultranationalists recently claimed that Russian forces struck a vehicle carrying Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces Commander General Ihor Tantsyura to frame Russian operations as limiting Ukrainian abilities to conduct counterattacks in the Bakhmut area. Russian sources have also largely framed increasingly routine series of Russian air and missile strikes as similarly constraining potential upcoming Ukrainian counteroffensive operations. There is no evidence to support these Russian claims.
The US Department of Defense (DoD) confirmed on May 9 that Ukrainian forces successfully used the Patriot missile defense system to shoot down a Russian missile for the first time. Ukrainian Air Force Commander Mykola Oleshchuk had reported that Ukrainian forces used the Patriot system to shoot down a missile in the air over Kyiv Oblast at night on May 4. The Biden administration also announced a new $1.2 billion military aid package to Ukraine on May 9. The package includes additional air defense systems, 155-mm artillery rounds, and equipment to integrate Ukrainian air defense systems with Western-supplied equipment.
Key Takeaways
- Ukrainian forces conducted successful limited counterattacks around Bakhmut on May 9.
- Pervasive issues with Russian combat capabilities, exacerbated by continued attritional assaults in the Bakhmut area, are likely considerably constraining the ability of Russian forces in this area to defend against localized Ukrainian counterattacks.
- Russian milbloggers claimed that Russian forces struck a command center where Ukrainian military commanders and officials were located, likely to support an ongoing effort to frame Russian operations as constraining Ukrainian capabilities to launch a counteroffensive.
- The US Department of Defense (DoD) confirmed that Ukrainian forces successfully shot down a Russian missile using the Patriot missile defense system. The Biden administration also announced a new $1.2 billion military aid package to Ukraine.
- Russian forces conducted ground attacks in the Kupyansk and Kreminna areas.
- Russian and Wagner Group forces continued offensive operations in and around Bakhmut on May 10, despite Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin’s previous threat that Wagner would withdraw from the area at midnight.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations along the Avdiivka-Donetsk front.
- Russian forces conducted airstrikes on Ukrainian positions in Kherson and Zaporizhia oblasts.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin signed an annual decree calling up citizens from reserves for military training.
- Russian occupation authorities are continuing the removal of Ukrainian residents from their homes in occupied areas under the guise of humanitarian evacuations.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 9, 2023
Russian President Vladimir Putin declined to use his Victory Day address to make any significant rhetorical changes and reiterated existing narratives, preparing for a protracted war and framing Russia as successfully resisting the entire West. Putin stated in his annual address marking the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany on May 9 that “a real war has been unleashed against Russia” and that Russia has repelled international terrorism and will continue to “defend” residents in Donbas.[i] Putin has previously claimed the West is waging a global “war” against Russia.”[ii] Putin has previously referred to the Russian military campaign in Ukraine as a “war” but this rhetoric, whether an intentional acknowledgement of the scale of the fighting or not, has not corresponded with any changes in the Kremlin’s approach to the “special military operation.”[iii] Putin similarly declined to use recent notable events such as his annual New Year’s Eve address or his February 2023 address to the Federal Assembly to offer any concrete vision on how to reverse the Russian military’s setbacks in Ukraine or reframe the war.[iv] Putin has instead used these events to reinforce long-standing rhetorical lines aimed at preparing the Russian public for a protracted war in Ukraine by evoking the memory of World War Two without calling on Russian society to support full mobilization.[v]
Putin additionally attempted to use Victory Day celebrations to rally Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) partners, many of which have sought to reduce their reliance on the Kremlin since February 2022. Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan, Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko, Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, Kyrgyz President Sadyr Japarov, Tajik President Emomali Rahmon, Turkmen President Serdar Berdimuhamedov, and Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev joined Putin at the Moscow Victory Day parade in Red Square.[vi] Putin emphasized the importance of CIS leaders attending the event and repeated boilerplate Kremlin rhetoric that Russia is pursuing a multi-polar world order.[vii] Putin’s latest efforts to rally CIS countries was muted by the reluctance of several Central Asian leaders initially expressed towards attending the Victory Day event, and Lukashenko did not join the rest of the leaders at an earlier wreath laying ceremony.[viii] Lukashenko also did not deliver his traditional Victory Day address in Minsk, Belarus, although it is not immediately clear why.[ix] Other non-Western states have largely rebuffed the Kremlin’s attempts to coalesce a potential anti-Western coalition, most notably China through its increasing rhetorical distancing from Russia.[x] ISW has previously assessed that the degradation of Russian military power in Ukraine has likely made this Russian effort even less attractive to other states.[xi] The Victory Day events showcased far less military equipment than usual (including only a single World War Two–era T-34/85 and no modern tanks, which Russia badly needs in Ukraine) and demonstrated the further degradation of the Russian military, despite the Kremlin’s attempts in previous weeks to downplay Victory Day by downsizing parades and outright canceling events.[xii]
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin seized the Victory Day holiday as an opportunity to mock Putin and question his judgement. Prigozhin referred to a “happy grandfather” figure who “thinks that he is good” during a discussion of ammunition shortages and Russia’s future prospects in Ukraine.[xiii] Prigozhin then rhetorically asked what Russia and future generations should do and how Russia can win if the “grandfather” turns out to be a “complete asshole.” Prigozhin also noted that unnamed figures (likely referring to Putin and the senior Russian MoD figures) should stop showing off on Red Square. Prigozhin is likely referring to Putin, who is often referred to as “grandfather” (or more specifically
“Bunkernyi ded” or “bunker grandfather”), and Prigozhin has previously attacked other senior Russian officials and officers by name — but has not done so against Putin. Prigozhin has previously attempted to upstage Putin’s authority through similar rhetorical stunts.[xiv] Prigozhin’s escalating attacks on Putin may — if the Kremlin does not respond to Prigozhin’s thinly veiled criticism of Putin on Victory Day — further erode the norm in Putin’s system in which individual actors can jockey for position and influence (and drop in and out of Putin’s favor) but cannot directly criticize Putin.
Prigozhin announced that Wagner forces will not withdraw from Bakhmut by his previously stated deadline of May 10, despite the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) failing to provide Wagner with additional shells. Prigozhin stated on May 9 that Wagner will continue to fight for Bakhmut and will continue to uphold its demands in the next few days.[xv] Prigozhin stated that Wagner did not receive the total ammunition the Russian MoD allegedly promised it in a May 7 order, and claimed Wagner only received 10 percent of the requested ammunition on May 8. Prigozhin added that the Russian MoD order threatened Wagner with treason if Prigozhin withdrew his forces from Bakhmut, likely one of the reasons why Prigozhin is not following through on his May 5 threat to withdraw from Bakhmut if the Russian MoD failed to fully supply Wagner with ammunition by May 10, a threat he dropped on May 7.[xvi] Prigozhin also noted that he has not been able to contact deputy theater commander in Ukraine and intermediary between the Russian MoD and Wagner, Army General Sergey Surovikin.
Prigozhin’s failure to follow through on his May 5 withdrawal threat indicates his cognizance of his dependence on the Russian MoD. Prigozhin attempted to blackmail the Russian MoD into reprioritizing the Bakhmut offensive so he could independently claim victory in the city at the expense of the Russian military’s likely preparations ahead of the planned Ukrainian counteroffensive.[xvii] Prigozhin criticized officials in charge of allocating ammunition of pointlessly conserving shells and allowing Russian servicemen to die in battle, though the Russian MoD is likely (smartly) conserving limited ammunition to repel a Ukrainian counteroffensive.[xviii] Prigozhin likely expected the Russian MoD to entirely cave to his demands at the risk of abandoning their own objectives for regular Russian forces but likely realized he cannot follow through with his ultimatum at this time. Prigozhin also likely anticipated that Surovikin would be able to coerce the Russian MoD into satisfying Wagner demands; but his inability to reach Surovikin, if true, indicates that Prigozhin does not have as much leverage within the Russian MoD as he imagined.
Prigozhin continued to blame high casualties and the slow pace of advances in Bakhmut on other Russian irregular formations to frame Wagner as the only competent force operating in the area. Prigozhin accused the 72nd Motorized Rifle Brigade of the 3rd Army Corps of abandoning a strategic position in Bakhmut which resulted in 500 Wagner casualties on May 9.[xix] Prigozhin accused the Russian MoD (which he nicknamed “the Russian Ministry of Drama”) of focusing on internal conflicts instead of fighting, which he claimed leads forces to “run away.” Prigozhin also criticized the Russian “Potok” battalion — which is affiliated with Russian state energy company Gazprom — for fleeing. Wagner-affiliated Telegram channels previously accused “Potok” of abandoning Wagner’s flanks in Bakhmut, and ISW assessed that Prigozhin launched a campaign to undermine Russian state-affiliated private military companies (PMCs).[xx]
Russian forces conducted another large-scale series of missile strikes against Ukraine on the night of May 8 to 9. The Ukrainian General Staff reported on May 9 that Ukrainian air defenses shot down all 8 Kalibr cruise missiles and 15 of the 17 Kh-101/Kh-555 missiles that Russian forces launched.[xxi] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that three S-300 missiles struck civilian infrastructure in Kramatorsk and Kostyantynivka in Donetsk Oblast.[xxii] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Russian forces conducted a concentrated strike on Ukrainian temporary deployment points and ammunition depots, successfully striking all targets.[xxiii] The continuation of Russian missile strikes at a smaller scale than the daily strikes during the failed Russian campaign against Ukrainian critical infrastructure likely indicates that Russian forces are more focused on sustaining a regular series of missile strikes than the actual effectiveness of the strikes.[xxiv] Russian forces may be attempting to conduct an almost daily series of missile strikes in order to portray themselves as constraining potential upcoming Ukrainian counteroffensive operations, although the diminished effectiveness of the strikes is likely not significantly constraining Ukrainian actions.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 8, 2023
Russian forces conducted another large-scale missile and drone strike against Ukraine on the night of May 7 to 8. The Ukrainian General Staff reported on May 8 that Russian forces launched 16 missiles at Kharkiv, Kherson, Mykolaiv, and Odesa oblasts, and that Ukrainian forces shot down all 35 launched Shahed drones.[i] Kyiv Mayor Vitaly Klitschko stated that Ukrainian forces shot down 36 Russian drones targeting Kyiv out of 60 total launched against Ukraine, however.[ii] Klitschko did not specify how many total drones Ukrainian forces shot down elsewhere in Ukraine. Klitschko’s report is more likely accurate as it was posted nearly four hours after the initial round of Ukrainian reporting on the Shahed strike. The Ukrainian Red Cross stated that one Russian missile destroyed an entire Red Cross warehouse in Odesa Oblast.[iii] Russian milbloggers celebrated claims that Russian forces intensified strikes against Kyiv, with one milblogger claiming that Russian forces conducted the largest strike campaign against Kyiv since the start of the war.[iv] Russian sources are likely overcompensating for the ineffectiveness of the drone strikes by playing up the size and scale of the effort.
Senior Ukrainian officials indicated that Ukrainian forces may be preparing to conduct counteroffensive operations in May or June. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky stated on May 7 that Ukrainian forces are preparing for “new events” in May or June 2023.[v] Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Volodymyr Havrylov stated in a May 8 interview that the timing and location of a Ukrainian counteroffensive are not significant because Russian forces and leadership will panic regardless, but that he would not be surprised if “something,” possibly alluding to Ukrainian counteroffensive operations, occurred in May or June.[vi] The Ukrainian Defense Forces Military Media Center stated that Russian forces continue to transfer military equipment, ammunition, and supplies to Ukraine to prepare for a defensive operation against a Ukrainian counteroffensive push.[vii]
Russian-occupied Transnistria asked Russia to increase its peacekeeping contingent in the region, likely to support the Kremlin’s efforts to destabilize Moldova. A Transnistrian occupation representative to Moscow, Leonid Manakov, asked Russia to increase the number of peacekeepers in Transnistria due to claims of increasing security and terrorist risks.[viii] Manakov proposed that Transnistria increase the number of peacekeepers by involving the Russians living in Transnistria in the peacekeeping operations. Manakov’s statement follows reports of Moldovan prosecutors detaining and cracking down on the members of the pro-Russian ”Shor” party in mid-April and May.[ix] Chisinau detained 27 protestors from the ”Shor” party on May 7.[x] Kremlin’s Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov did not comment on Manakov’s proposals.[xi] White House officials warned in March that individuals linked with Russian intelligence were planning to stage protests against the Moldovan government in order to install a pro-Russian administration. Manakov’s statements are likely a continuation of the Kremlin’s effort to destabilize Moldova.[xii] Russia remains unlikely to deploy additional forces to Transnistria given its ongoing need for forces in Ukraine.
Russian President Vladimir Putin is attempting to use the Moscow Victory Day parade to show Russia’s continued influence in Central Asia. Kazakh President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, Kyrgyz President Sadyr Japarov, Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev, and Tajik President Emomali Rakhmon are reportedly attending the Victory Day parade in Moscow on May 9.[xiii] Kremlin-affiliated news outlet Vedemosti reported Japarov’s visit to Moscow for Victory Day on April 23, while Russian media reported Tokayev’s, Mirziyoyev’s, and Rakhmon’s visits on May 8, only one day before the Victory Day parade in Moscow.[xiv] Russian independent news outlet SOTA reported that Rakhmon’s press service initially announced that Rakhmon would celebrate in Dushanbe, but later stated that Rakhmon had arrived in Moscow for Victory Day.[xv] Kremlin newswire TASS reported that Putin also invited Turkmen President Serdar Berdymukhamedov but he did not confirm his attendance.[xvi] No foreign leader attended Moscow Victory Day in 2022, and Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan did not hold Victory Day parades in 2022 with some citing health risks from the coronavirus pandemic.[xvii] The late announcement of Central Asian leaders’ attendance likely indicates their reticence to show direct and public support of the war despite Kremlin efforts to project power. Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko and Armenian President Nikol Pashinyan reportedly also flew to Moscow to attend the Victory Day parade.[xviii]
Key Takeaways
- Russian forces conducted another large-scale missile and drone strike against Ukraine on the night of May 7 to 8.
- Senior Ukrainian officials indicated that Ukrainian forces may be preparing to conduct counteroffensive operations in May or June.
- Russian-occupied Transnistria called on Russia to increase its peacekeepers in the region likely to support the Kremlin’s efforts to destabilize Moldova.
- Russian President Vladimir Putin is attempting to use the Victory Day parade to show Russia’s continued influence in Central Asia.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks on the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces have made marginal advances within Bakhmut as of May 8 amid reports of intensified Wagner Group forces offensive operations and continued ground attacks along the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Russian forces continued defensive operations in southern Ukraine.
- Russian authorities have reportedly escalated their campaign targeting ethnic minorities for contract service in the Russian military.
- Russian occupation authorities continued to forcibly evacuate civilians in rear areas in Kherson and Zaporizhia oblasts.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 7, 2023
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov may have compelled the Russian theater commander in Ukraine, Army General Valery Gerasimov, to resume artillery ammunition distribution to the Wagner forces in Bakhmut despite Gerasimov’s desired de-prioritization of that effort. Prigozhin announced on May 7 that he had obtained a document from the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) that promised to supply Wagner forces with the ammunition and weapons necessary to maintain offensive operations in Bakhmut. Prigozhin has not published the official document and ISW cannot verify Prigozhin’s claims at this time. The Russian MoD likely has not fundamentally changed its intention of deprioritizing offensive operations and conserving munitions across the theater, as ISW has recently assessed. Prigozhin and Kadyrov likely effectively blackmailed the Russian MoD into allocating resources to Wagner forces in Bakhmut by threatening to pull Kadyrov’s Chechen forces from other parts of the theater to relieve Wagner forces in Bakhmut. Prigozhin also claimed that the MoD gave Wagner complete freedom of operations in Bakhmut and appointed Army General Sergey Surovikin as an intermediary between the MoD and Wagner, actions that would indicate that Gerasimov and possibly Minister of Defense Sergei Shoigu lack the ability to command Prigozhin and Kadyrov as subordinates but must instead negotiate with them as peers. This assessment assumes that Prigozhin’s claims that the MoD was withholding shells but has now agreed to supply them are true—the MoD has made no official statements regarding those claims—and Ukrainian officials report that they have not observed a decline in Wagner shelling during this period (see below).
Kadyrov’s threats to transfer his forces to Bakhmut may have blackmailed the Russian military command into allocating ammunition to Wagner mercenaries. Kadyrov published a letter on May 6 asking Russian President Vladimir Putin to order Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu and Director of the Russian National Guard (Rosgvadia) Viktor Zolotov to authorize the transfer of Chechen “Akhmat” units from “other directions” to assume Wagner’s positions in the Bakhmut direction. Kadyrov’s letter to Putin bypassed the Russian chain of command, and the withdrawal of Chechen forces from other parts of the theater likely posed a risk to Russian defensive lines, a risk that Gerasimov and Shoigu, or Putin, appear to have been unwilling to take. ISW previously observed Akhmat units operating in the Bilohorivka area on the Svatove-Kreminna line and in Zaporizhia Oblast, and their withdrawal from those positions might undermine Russia’s defensive preparations ahead of the planned Ukrainian counteroffensives. Shoigu and Gerasimov, who have been consistently loyal to Putin’s orders, may alternatively have decided to allocate ammunition to Wagner at Putin’s direction. Kadyrov’s and Prigozhin’s apparently successful joint blackmail efforts further indicate that Gerasimov does not actually control all the Russian forces in Ukraine, despite being the nominal theater commander. Gerasimov likely attempted to assume control over all Russian irregular forces over the winter of 2023 but had failed in that endeavor even before losing favor with Putin in the spring.
Kadyrov likely supported Wagner’s blackmail efforts against the Russian military command in order to reestablish his position within the circle of power in the Kremlin. Kadyrov had previously held an influential position within the Putin's close circle in until apparently losing favor recently, likely because his forces played a limited role in active combat operations in Ukraine throughout late fall of 2022 and winter of 2023. Putin belittled Kadyrov during their meeting on March 13 where Kadyrov appeared visibly nervous when reporting on the Chechen fighters’ role in Ukraine. Kadyrov likely saw Prigozhin’s threats to withdraw from Bakhmut as an opportunity to play up the effectiveness of his forces against the backdrop of Gerasimov‘s and Shoigu’s failures to deliver decisive victories during the winter-spring offensive.
Gerasimov's apparent need to negotiate with subordinate commanders and those commanders’ ability to force his hand suggests that chain of command problems are significantly impacting the Russian military’s ability to conduct coherent theater-wide operations. The position of overall theater commander should in principle allow Gerasimov to command any Russian unit or ground forces commander in Ukraine, even those in charge of irregular formations such as Wagner and Akhmat. Prigozhin and Kadyrov appear to be able to largely make independent decisions concerning their forces, however, a phenomenon that appears to have become more pronounced the longer these forces have had de facto control over certain sectors of the frontline. Wagner and the Russian MoD appeared to have recently reached an agreement about the delineation of responsibilities between conventional and irregular forces. The Russian military command deployed Russian Airborne Forces (VDV) to defend the flanks around Bakhmut around when Wagner began advancing in the city itself, for example. ISW previously assessed that the Russian military command had likely recently decided to reprioritize efforts and resource allocation to prepare to receive potential Ukrainian counteroffensive operations but did not set conditions to appease Prigozhin or offset Wagner’s likely degradation in the Bakhmut area. The subsequent upheaval over the de-prioritization of Bakhmut and the Russian military command's reversal on supplying Wagner is likely to undermine this theater-wide effort.
These events raise questions about Russia’s ability to coordinate a coherent theater-wide defensive campaign. The Russian military command appears to be increasingly delegating responsibilities for different sectors of the front in Ukraine to various Russian commanders while the power of the theater commander continues to wane. Gerasimov’s degraded abilities to control his commanders will likely further limit the Russian military’s ability to conduct coherent operations involving different areas of responsibility. ISW has previously assessed that factional dynamics within the Russian military are shaping decision making to an unusual degree, and the increasing erosion of the Russian chain of command is likely caught in a self-reinforcing feedback loop with the Russian military’s growing factionalism. ISW assesses that Putin is unlikely to remove Gerasimov as overall theater commander for reputational reasons, and therefore Prigozhin’s and Kadyrov’s public undermining of Gerasimov may have lasting impacts on the power of the overall theater commander’s position. Putin may seek to reward commanders he favors with responsibility beyond their official positions instead of outright appointing them to a higher position. The Russian military is highly unlikely to solve these chain of command issues in the near term, and these problems will likely influence how Russian forces on different axes respond to potential Ukrainian counteroffensive operations.
Prigozhin’s and Kadyrov’s ability to significantly influence the Russian military command decisions relies on Putin’s willingness to appease them and his reliance on their forces, both of which will likely degrade after further blackmail efforts. Both Prigozhin and Kadyrov retain likely differing amounts of favor and personal contact with Putin despite their individual tensions with the Russian military command. The decision to blackmail and subsequently humiliate the Russian military command may have expended a fair amount of Prigozhin‘s and Kadyrov’s political capital to influence operational and strategic level military decision-making. Such high-profile blackmailing is likely not a feasible long-term strategy for Prigozhin and Kadyrov given their reliance on Putin’s favor to bend the MoD to their demands. Prigozhin has already lost favor with Putin in recent months, with recent events appearing to demonstrate that he needed Kadyrov’s own capital to successfully blackmail the Russian military command into additional ammunition provision. Putin notably avoids firing members of his inner circle, however, instead rotating them into and out of favor, influence, and resources. Prigozhin and Kadyrov are unlikely to generate such extreme effects again without damaging their relationships with Putin.
Prigozhin’s continued fight to complete the capture of Bakhmut contradicts his consistent narrative that capturing Bakhmut lacks strategic value. Prigozhin released a 41-point letter on May 6 (prior to his announcement about the provision of additional ammunition) criticizing the Russian MoD for intentionally refusing to support Wagner in Bakhmut. Prigozhin claimed that he and Surovikin organized “Operation Bakhmut Meatgrinder” in October 2022 to provoke Kyiv into throwing Ukrainian forces into Bakhmut en masse. Prigozhin reiterated that Wagner’s main task in Bakhmut has always been to exhaust Ukrainian forces in a meat-grinder, and not to capture the settlement. Prigozhin claimed that completing the capture of Bakhmut is not operationally significant, rejecting Shoigu’s March 7 claim that taking Bakhmut would open the way for further Russian offensive efforts in Donbas, a narrative that Prigozhin has consistently maintained since November 2022. Prigozhin’s long-standing claims that Bakhmut is not of strategic importance contradict his demands that the Russian MoD provide Wagner the necessary ammunition to allow it to complete the capture of Bakhmut, suggesting that Prigozhin continues to prioritize his own personal aims over those of the Russian military command and good of the overall Russian war effort.
Key Takeaways
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov may have compelled the Russian theater commander in Ukraine, Army General Valery Gerasimov, to resume artillery ammunition distribution to Wagner forces in Bakhmut despite Gerasimov’s desired de-prioritization of that effort.
- Kadyrov’s threats to transfer his forces to Bakhmut may have blackmailed the Russian military command into allocating ammunition to Wagner mercenaries.
- Kadyrov likely supported Wagner’s blackmail efforts against the Russian military command to reestablish his position within the circle of power of the Kremlin.
- Gerasimov's apparent need to negotiate with subordinate commanders and those commanders’ ability to force his hand suggests that chain of command problems are significantly impacting the Russian military's ability to conduct coherent theater-wide operations.
- These events raise questions about Russia’s ability to coordinate a coherent theater-wide defensive campaign.
- Prigozhin’s and Kadyrov’s ability to significantly influence Russian military command decisions relies on Putin’s willingness to appease them and his reliance on their forces – both of which will likely degrade after further blackmail efforts.
- Prigozhin’s continued fight to complete the capture of Bakhmut contradicts his consistent narrative that capturing Bakhmut lacks strategic value.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations northeast of Kupyansk and south of Kreminna.
- Russian forces made some territorial gains in Bakhmut as of May 7 and continued limited offensive operations on the Avdiivka-Donetsk front.
- Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces launched up to 23 drones at Crimea on the night of May 6 to 7.
- Russian federal subjects are continuing to recruit and form regional armed formations and volunteer battalions.
- Russian occupation authorities continue to plan and carry out forced evacuations from Zaporizhia Oblast.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 6, 2023
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov stated their intent on May 6 for Chechen “Akhmat” troops to replace Wagner Group forces in Bakhmut on May 10. Prigozhin published a letter to Russian Minister of Defense Sergei Shoigu on May 6 declaring that Wagner will hand over its positions to Akhmat units at exactly midnight on May 10, when Prigozhin claims Wagner will have entirely run out of combat potential.[i] Prigozhin expressed his confidence that Akhmat forces can capture the remaining 2.5 square kilometers of Bakhmut that remain under Ukrainian control.[ii] Kadyrov responded to Prigozhin by stating he has addressed a letter to Russian President Vladimir Putin signaling his readiness to take Bakhmut and claimed that Chechen units are already working on a strategy with the Russian MoD for the Chechens to take over Wagner‘s positions.[iii]
Prigozhin and Kadyrov likely aim to frame the Russian MoD and regular Russian troops as ineffective and set conditions to blame the MoD for any Russian setbacks in the Bakhmut area. Prigozhin’s decision to hand responsibility for Bakhmut over to the forces of a fellow silovik deliberately excludes the conventional Russian airborne (VDV) troops already operating on Wagner’s northern and southern flanks around Bakhmut, framing the battle of Bakhmut strictly as a Wagner – and now Akhmat – concern. This decision reflects Prigozhin’s ongoing distrust of the Russian military command, and postures himself as independent from the Russian military establishment and allows him to save face if Wagner forces cannot capture Bakhmut and avoiding a repeat of the capture of Soledar – where the Russian MoD took credit for what Prigozhin claimed was a Wagner success.[iv] Kadyrov, in turn, could benefit from the positive reputational effect of entering such a high-profile operation with the backing of Prigozhin’s personal notoriety. Kadyrov recently met with several high-ranking Russian officials in Russia, likely to ameliorate his own reputation within Russian political circles.[v] The switch from Wagner to Akhmat troops may also set conditions to blame the Russian MoD for future failures down the line — if Akhmat forces experience similar difficulties to Wagner and are unable to completely capture Bakhmut, Prigozhin and Kadyrov may feasibly blame the MoD for failing to adequately support their efforts. Alternatively, if the Russian MoD prevents Akhmat forces from relieving Wagner (as it is unclear if Prigozhin and Kadyrov can execute this maneuver without any Russian MoD support as they claim), the two siloviki and their allies will likely brandish the hypothetical that if only the Russian MoD had supported the maneuver, Chechen forces would have captured Bakhmut quickly.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 5, 2023
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) appears to have deprioritized the Bakhmut offensive in favor of preparing to defend against an anticipated Ukrainian counteroffensive, putting the Wagner Group and Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin in a potentially difficult position. Prigozhin released a series of videos on May 4 and 5 announcing that Wagner will withdraw from Bakhmut on May 10 unless Wagner receives necessary supplies and launched particularly acerbic and emotional attacks against Chief of the Russian General Staff Army General Valery Gerasimov, Russian Minister of Defense Sergei Shoigu, and the Russian MoD establishment writ large.[1] Prigozhin’s palpable desperation in the videos, one of which shows the corpses of recently deceased Wagner fighters, marks a significant rhetorical inflection in his continued pleas for increased Russian MoD support for Wagner in Bakhmut. His visible and visceral anger suggests that the Russian MoD has likely deprioritized Bakhmut and shifted operational focus elsewhere in the theater in ways that may seriously compromise Wagner’s ability to operate effectively. Wagner has not ceased efforts to completely capture Bakhmut despite reduced access to ammunition and other necessary supplies, however. Prigozhin has shown no willingness to switch to the defensive within the city.
Wagner’s continued persistence within Bakhmut is incongruent with the overall slow-down in the pace of Russian offensive operations elsewhere in Ukraine as conventional Russian forces appear to be largely shifting focus to prepare to receive the much-anticipated Ukrainian counteroffensive.[2] Aside from very limited and localized attacks in the Kreminna area and near Donetsk City, Russian forces have largely ceased offensive operations throughout the theater, likely signifying a transition to the defensive.[3] It would be an operationally sound decision for the Russian MoD to begin withholding and stockpiling ammunition and supplies in order to prepare for any Ukrainian counteroffensive actions, and Prigozhin’s desperate statements indicate that the Russian MoD is likely doing so. ISW has recently reported that Prigozhin began appealing to the Russian MoD to provide Wagner with necessary ammunition once again after a brief period during which it seemed that relations between Prigozhin and Russian military leadership had improved.[4] Prigozhin’s renewed anger reached its peak in the May 4 video of Prigozhin essentially screaming at Gerasimov and Shoigu and accusing them of the deaths of Wagner fighters.[5]
The losses suffered by Wagner in Bakhmut, alongside the likely de-prioritization of the Bakhmut effort by the Russian MoD, may leave Prigozhin and Wagner in a particularly bad spot. It is not immediately clear whether Prigozhin actually intends to withdraw from Bakhmut on May 10 or whether he made the announcement in a last-ditch attempt to secure MoD support. If Wagner does withdraw, then it will likely need Russian MoD equipment to protect and facilitate the retrograde. The Russian military lacks the reserves needed to man positions Wagner might abandon in Bakhmut, moreover. The massive losses suffered by Wagner in Bakhmut for the sake of tactical gains, as well as the overall shift of the Russian military towards a more cautious posture preparing for defensive operations, appears to be offering Ukrainian forces opportunities for fruitful counterattacks in various areas of the front. Ukrainian forces appear to be seizing some of these opportunities, as noted below, but ISW does not assess that these counterattacks are necessarily part of the anticipated counteroffensive. NB: ISW uses the term “counterattack” to describe tactical actions by Ukrainian forces to make limited gains in local areas. It uses the term “counteroffensive” to describe operational-level undertakings composed of many distinct tactical actions intended to achieve operationally or strategically significant gains. ISW has so far observed reporting only of Ukrainian counterattacks.
Recently dismissed former Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev is reportedly serving as deputy commander of the Wagner Group, likely as part of Wagner’s campaign to retain access to Russian military supplies. A Wagner-affiliated Russian milblogger published footage on May 4 and 5 purporting to show Mizintsev acting as Wagner deputy commander and discussing logistical and tactical issues with Wagner fighters in the Bakhmut area.[6] Prigozhin publicly offered the command position to Mizintsev following his dismissal on April 27, and Prigozhin claimed on May 5 that Mizintsev in his capacity as head of logistics supplied Wagner with low quality ammunition.[7] Prigozhin may have appointed Mizintsev as Wagner deputy commander in an effort to leverage Mizintsev‘s understanding of and relationships within the Russian military’s logistics apparatus to retain access to ammunition and supplies amid an apparent reprioritization away from Wagner’s area of responsibility. Mizintsev was reportedly dismissed after Commander of the Russian Airborne Forces (VDV) Mikhail Teplinsky, a likely anti-Gerasimov figure, conducted readiness checks that revealed that the Russian Northern Fleet lacked supplies, possibly indicating that Mizintsev fell out of favor with both factions within the MoD and joined Wagner to retain a command role in Ukraine.[8] The changes likely occurring within the Russian military’s logistics apparatus associated with the reprioritization of supplies for defensive operations will likely impede Mizintsev‘s presumed efforts to retain Wagner’s access to supplies.
Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu ordered newly-appointed Deputy Minister for Logistics Alexei Kuzmenkov to control the supply of weapons and equipment to Russian forces in Ukraine. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) reported on May 5 that Shoigu gave Kuzmenkov the order during an inspection of forces and military equipment in the Southern Military District.[9] The Russian MoD reported that Kuzmenkov presented Shoigu with new tanks, armored fighting vehicles, and other equipment and claimed that Russian military industrial enterprises have repaired equipment at a rate faster than that of equipment losses. Shoigu likely met with Kuzmenkov to accelerate the conservation and reprioritization of logistics and sustainment processes ahead of expected upcoming Ukrainian counteroffensive operations. Shoigu’s meeting with the new head for logistics amid Wagner’s attempt to retain access to the Russian military’s logistics apparatus further suggests that Wagner will struggle to maintain its current level of provisions from the MoD.
Russian occupation authorities announced the forced removal of 70,000 civilians in occupied Zaporizhia Oblast to areas deeper in the Russian-occupied rear under the guise of evacuations. Zaporizhia Oblast occupation Head Yevgeny Balitsky and Deputy Head Andriy Kozenko announced on May 5 that Russian authorities will conduct a partial evacuation of 70,000 Ukrainian civilians of vulnerable populations, including families with children, the disabled, and the elderly, from 18 settlements along the southern bank of the Kakhovka Reservoir and along Russian ground lines of communications (GLOCs) roughly 20-40 kilometers from the front line.[10] Kozenko claimed that authorities have already begun evacuating civilians from the Polohy Raion to Berdyansk.[11] The locations of these settlements so far from the current front lines suggests that Russian forces plan to conduct a controlled, fighting withdrawal from their current positions to a prepared line of defense rather than trying hold the current line of contact in the event of a possible Ukrainian counteroffensive. Kherson Oblast occupation authorities had similarly used the guise of evacuation to justify the forced relocation of Ukrainians from the frontlines in Kherson Oblast during Ukraine’s counteroffensive in October and November 2022, citing threats of Ukrainian strikes and frontline hostilities.[12] These Russian preparations do not necessarily indicate that Ukrainian forces will attack in or prioritize this area. Russian and occupation authorities will likely capitalize on growing Russian fear over a prospective Ukrainian counteroffensive to justify further mass relocations of Ukrainian civilians.
The Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) proposed a draft bill aimed at appealing to growing anti-migrant sentiments in Russia and supporting the Russian military’s efforts to recruit migrants. The MVD submitted a draft bill on May 5 that would allow employers to deprive migrant employees of their work permits and create expanded administrative supervision over the residence of foreign citizens in Russia.[13] The draft bill states that the administrative supervision regime is aimed at establishing the whereabouts of foreign citizens illegally staying in Russia, although a Russian source claimed that the measure will allow Russian officials and police to freely enter the homes of migrants.[14] The MVD added an explanatory note to the bill in which it argued that ”illegal migration is closely related to such negative phenomena as terrorism, extremism, human trafficking, [and] drug trafficking.”[15] The reasoning offered for the bill is similar to Russian Investigative Committee Head Alexander Bastrykin’s recent accusation that migrants destabilize Russia by importing terrorism and extremist ideologies.[16] The bill is reflective of growing domestic ramifications from the wide acceptance of the Kremlin’s ”Russification” ideology, which ISW previously assessed is increasingly manifesting itself in how Russian authorities and ultranationalist negatively portray ethnic minorities and migrants in Russia.[17] Russian officials also disproportionally focus recruitment efforts on migrant communities, and the bill could set conditions for Russian officials to leverage jeopardized migration statuses to coerce migrants into signing contracts with the Russian military.[18]
Russian Human Rights Council head Valery Fadeev reportedly stated that Russian authorities should regulate Telegram channels similarly to how Russia censors state-controlled media. Kremlin newswire TASS reported on May 5 that Fadeev called for Russian authorities to “analyze the activities of Telegram channels” to consider introducing legislation to regulate Telegram.[19] Russian First Deputy Chairman of the Civic Chamber on Media and Mass Communication Alexander Malkevich supported the regulation of Telegram channels claiming that traditional forms of media and “new media” should be on an equal footing because ”new media” has ”only rights, and no obligations.“ Fadeev’s support of Telegram censorship is also notable because prominent Russian milblogger Alexander Kots also serves on the Russian Human Rights Council. ISW has previously reported on efforts on the part of Russian authorities to stimulate self-censorship in the information space.[20]
Key Takeaways
- The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) appears to have deprioritized the Bakhmut offensive in favor of preparing to defend against an anticipated Ukrainian counteroffensive, putting the Wagner Group and Wagner financier Yevgeny Prigozhin in a potentially difficult position.
- Wagner’s continued persistence within Bakhmut is incongruent with the overall slow-down in the pace of Russian operations elsewhere in Ukraine as conventional Russian forces appear to largely be shifting focus to prepare to receive the much-anticipated Ukrainian counteroffensive.
- Recently dismissed former Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev is reportedly serving as deputy commander of the Wagner Group, likely as part of Wagner’s campaign to retain access to Russian military supplies.
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu ordered newly-appointed Deputy Minister for Logistics Alexei Kuzmenkov to control the supply of weapons and equipment to Russian forces in Ukraine.
- Russian occupation authorities announced the forced removal of 70,000 civilians in occupied Zaporizhia Oblast to areas deeper in the Russian-occupied rear under the guise of evacuations.
- The Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) proposed a draft bill aimed at appealing to growing anti-migrant sentiments in Russia and supporting the Russian military’s efforts to recruit migrants.
- Russian Human Rights Council head Valery Fadeev reportedly stated that Russian authorities should regulate Telegram channels similarly to how Russia censors state-controlled media.
- Russian forces conducted ground attacks near Kreminna and Avdiivka and made marginal gains within Bakhmut.
- Russian milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted limited counterattacks near Bakhmut.
- The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) claimed it prevented a Ukrainian assassination attempt against an occupation deputy of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) on May 5.
- Chechen Republic Head Ramzan Kadyrov continues his own personal force generation efforts aimed at securing Russian President Vladimir Putin’s favor.
- Russian occupation authorities continue measures to strengthen social control of occupied territories.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 4, 2023
Russia conducted another Shahed-131/136 strike against Ukraine on May 4. Ukrainian military sources reported that Russian forces launched 24 Shahed-131/136s at Ukraine from the direction of Bryansk Oblast and the eastern coast of the Sea of Azov and that Ukrainian air defense destroyed 18 of the drones above northern, central, and southern regions of Ukraine. Ukraine’s Southern Operational Command noted that Russian forces launched 15 of the Shaheds at Odesa Oblast, 3 of which struck an educational institution. Russian milbloggers claimed that the drones struck military facilities throughout Ukraine. The Kyiv City Military Administration reported that Russian forces attacked Kyiv overnight with Shaheds and unidentified missiles for the third time in the last four days, noting that Kyiv has not experienced such a high intensity of air attacks since the beginning of 2023.
Russian sources continued to respond to the May 3 drone strike on the Kremlin. The Russian Investigative Committee announced that it opened a criminal case “on the fact of a terrorist attack in connection with an attempt to strike the Kremlin” and further amplified the claim that Kyiv is to blame for the strike. Russian President Vladimir Putin will reportedly hold a Security Council meeting to discuss the incident on May 5. Russian Security Council Deputy Chairman Dmitry Medvedev called for the “physical elimination” of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky in retaliation for the strike. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov baselessly claimed that the US is behind the attack. Several Russian authorities, including the heads of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Leningrad, and Pskov oblasts introduced bans on drone launches and flights. State Duma Deputy Aleksandr Khinshtein sent an appeal to the Russian Ministry of Transport and Federal Air Transport Agency to introduce a total temporary moratorium on drone use due to the increased threat of drones associated with the “special military operation.” Russian media aggregator Baza, citing unidentified internal sources, claimed that residents of Moscow suburbs noticed the drones flying at very low altitudes well in advance of the moment of contact with the Kremlin Senate Palace building on May 3 but that authorities ignored their reports as “drone hysteria.” Another Russian source amplified this report and noted that if it is true, it demonstrates how impenetrable the Russian bureaucratic apparatus is. The milblogger praised the Kremlin’s response as being thoughtful and logical and dismissed other voices in the information space for being irrational and hysterical.
Russian officials are likely using the May 3 drone strike on the Kremlin to expand cancellations of parades for the May 9 Victory Day holiday. Russian sources reported that Russian officials have canceled May 9 parades in 21 cities in Russia and occupied Crimea either without offering official justification or citing security reasons. Russian officials in several cities claimed that they were canceling May 9 events and parades out of concern for participants of the “special military operation.” ISW has previously assessed that the Kremlin will use the May 3 strike to cancel May 9 events and augment its informational effort to frame the war in Ukraine as an existential threat to Russia. The Kremlin likely hopes to limit typical May 9 events to conceal the degradation of the Russian military because such events demonstratively showcase advanced Russian military equipment, much of which is either critical to Russian operations in Ukraine or has been destroyed in 14 months of attritional fighting. The Kremlin also likely hopes to curb May 9 events out of fears that celebrations honoring deceased servicemembers could become a potential source of domestic backlash for Russia’s high casualty figures in Ukraine. Russian officials have canceled immortal regiment memorial events in recent weeks likely for such reasons.
The Kremlin is reportedly continuing its overhaul of domestic security organs. Russian media aggregator Baza reported that Russian authorities expanded prior mass investigations into the Moscow Central District Internal Affairs Directorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) to other district MVD directorates in Moscow. Baza reported that Russian authorities detained the Bibirevo Raion’s deputy chief of police on allegations of leaking information as well as two other employees at unspecified MVD departments. The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) and the MVD Security Service reportedly started mass checks of MVD departments in Moscow due to the “leakage of data from Russian security forces at the request of Ukrainian citizens.” The Kremlin appears to be also overhauling elements of the Rosgvardia (Russian National Guard) amid a series of recent arrests and dismissals of prominent Rosgvardia officials. The Kremlin likely intends to use these investigations and arrests to oust officials who have fallen out of favor and to consolidate control of internal security organs. ISW has previously assessed that Russian authorities may use a series of new laws expanding punishments for discrediting the Russian Armed Forces, the misappropriation of military assets, and trespassing at facilities operated by security organs to support these efforts.
US Director of National Intelligence Avril Haines stated that Russian forces are likely unable to conduct a “significant offensive” in 2023 due to munitions and manpower shortages regardless of the success of the Ukrainian counteroffensive. Haines testified on May 4 to the Senate Armed Services Committee that it will be increasingly challenging for Russia to sustain “even modest offensive operations” if the Kremlin does not initiate mandatory mobilization or obtain third-party ammunition supplies in addition to existing deliveries from Iran and other unspecified countries. Haines stated that Putin has “probably” reduced his short-term goals in Ukraine to consolidate control over occupied territories and is unlikely to consider negotiations with Ukraine. Haines’ statements support and expand on ISW’s prior assessments that Russian forces are unable to conduct large-scale, simultaneous offensive campaigns on multiple axes.
Russia and India reportedly suspended efforts to trade in rupees. Reuters reported on May 4 that Russia and India suspended months of negotiations because Moscow does not want to accumulate over $40 billion in rupees by the end of 2023. Russia reportedly views rupees as not convertible. An unnamed Indian government official stated Russia would prefer to settle bilateral trade with India in Chinese yuan or another currency and that Russia is increasingly trading in United Arab Emirate dirhams. The suspended negotiations likely concern India’s payment to Russia for spare parts and two S-400 air defense systems.
Key Takeaways
- Russia conducted another Shahed-131/136 strike against Ukraine on May 4.
- Russian officials are likely using the May 3 drone strike on the Kremlin to expand cancellations of parades for the May 9 Victory Day holiday.
- The Kremlin is reportedly continuing its overhaul of domestic security organs.
- US Director of National Intelligence Avril Haines stated that Russian forces are likely unable to conduct a “significant offensive” in 2023 due to munitions and manpower shortages regardless of the success of the Ukrainian counteroffensive.
- Russia and India reportedly suspended efforts to trade in rupees.
- Russian sources claimed that Russian forces made territorial gains south of Kreminna.
- Ukrainian forces likely conducted a limited counterattack southwest of Bakhmut.
- Russian forces continued ground attacks in and around Bakhmut and along the Avdiivka–Donetsk City line.
- Russian sources claimed that Russian forces repelled Ukrainian forces in Zaporizhia Oblast.
- The Kremlin is attempting to increase the production quotas of military supplies despite reportedly lacking the necessary manpower.
- Russian occupation authorities continue to announce new security measures in an effort to prevent partisan attacks in occupied territories.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 2, 2023
Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu claimed that the Russian defense industrial base (DIB) is increasing its production of precision missiles for use against Ukraine. Shoigu highlighted the state-owned Tactical Missiles Corporation as a model defense enterprise, stating that is successfully beginning mass production of missiles and will develop plans to double its current production output in the near term.[1] Shoigu’s focus on precision missile production aligns with a shift in Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD)’s rhetoric focusing on Russia‘s use of precision missiles to strike military infrastructure targets in Ukrainian rear areas, likely aiming to similarly appear proactive and demonstrative positive Russian actions amid growing concerns in the Russian information space about a potential Ukrainian counteroffensive.[2]
Shoigu likely seeks to deflect intensifying accusations that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) cannot provide sufficient ammunition to Russian forces. Shoigu stated that the Russian defense industrial base (DIB) increased its production pace and output volumes, and claimed that Russian forces have received enough ammunition to date in 2023 to inflict extensive damage on Ukrainian forces.[3] ISW previously reported that the Russian military command is reshuffling the leadership of command organs associated with logistics and force generation efforts after commanders that oppose Gerasimov and the core of the Russian MoD partially regained Russian President Vladimir Putin’s favor in late March.[4] Russian milbloggers also began naming specific Russian MoD officials in their accusations of poor supply provisions to Russian forces in this period.[5] Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin continues to claim that the Russian MoD is deliberately setting Wagner mercenaries up for failure in Bakhmut by refusing to provide their requested number of shells, which his commanders claim is leading to high casualties and slow progress on the battlefield.[6] A Wagner serviceman also claimed that he delivered 39 boxes with complaints from Wagner servicemen about lack of ammunition to the Russian State Duma’s Defense Committee on May 2.[7]
Russian reactions to a claimed strike against a vehicle carrying Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces Commander Major General Ihor Tantsyura suggest Russian ultranationalists seek to frame any Russian operations as delaying potential Ukrainian counteroffensive actions. Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin claimed on May 2 that Wagner forces struck a Ukrainian armored vehicle carrying Tantsyura enroute to Bakhmut, and published a video purporting to show the strike.[8] Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces Spokesperson Denys Zelinskyi denied Prigozhin’s claim and stated that “everyone is alive and well.”[9] Prigozhin responded that Wagner will continue to operate in the area.[10] Milbloggers widely circulated Prigozhin’s claims and framed the strike as an informational victory.[11] A prominent milblogger claimed that Tantsyura received an order to transfer reserves to Bakhmut and prepare Ukrainian forces to conduct counterattacks in the area, likely to frame the Russian strike as an operationally significant event which delayed potential upcoming Ukrainian counteroffensive actions.[12] Russian milbloggers claimed that the Russian strike on Pavlohrad on May 1 impacted a critical Ukrainian logistics and accumulation hub and similarly suggested that the strike would delay Ukrainian counteroffensive operations.[13]
The Kremlin reportedly distributed a new manual instructing Russian state media on how to cover an upcoming potential Ukrainian counteroffensive that, if real, indicates the Kremlin is setting informational conditions both for an effective Russian defense and to mitigate shocks in the Russian information space from Ukrainian successes. Russian opposition outlet Meduza reported on May 2 that it attained the manual, which reportedly instructs Russian state media to “not lower the expectations of the announced Ukrainian counteroffensive” Or claim that Ukraine is not ready to conduct a counteroffensive – instead treating the possibility of a Ukrainian offensive as a given[14] The manual instead reportedly stresses that Russian media should focus on Western security assistance and support for Ukraine.[15] Meduza reported that sources close to the Russian presidential administration stated that the coverage aims to allow the Kremlin to announce a military victory in the event of an unsuccessful Ukrainian counteroffensive and establish justifications for a successful counteroffensive by claiming that Russian losses will be understandable because “the entire West has concentrated huge efforts on the front.”[16] The alleged document suggests the Kremlin is preparing for – if not expecting – Ukrainian successes and is planning to mitigate demoralization in the Russian information space. This is an important Russian adaptation from previous Ukrainian counteroffensives in Kherson and Kharkiv, which produced dramatic shocks and demoralization in both the Russian military and the Russian information space that the Kremlin likely seeks to mitigate[17]
UN member states, including key Russian partners like China, India, and Brazil, voted to adopt a resolution on April 26 acknowledging Russia as the aggressor in the war in Ukraine.[18] The resolution preamble states that the UN aims to more closely align with the Council of Europe amid “unprecedented challenges now facing Europe following the aggression by the Russian Federation against Ukraine, and against Georgia prior to that.” This resolution is reportedly the first such resolution in which China recognized Russia as the aggressor in the war in Ukraine.[19] Voting in favor of this resolution by itself does not likely reflect the broader opinion of Russian allies towards Russia, however.
Correction: ISW reported on May 1 that US officials assessed that Russian forces have suffered 100,000 casualties – 80,000 wounded and 20,000 dead– in fighting for Bakhmut since January 2023 based on statements from National Security Council spokesperson John Kirby.[20] National Security Council deputy spokesperson Sean Savett later clarified on May 1 that the figures account for Russian casualties throughout Ukraine since January 2023.[21]
Key Takeaways
- Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu claimed that the Russian defense industrial base (DIB) is increasing its production of precision missiles for use against Ukraine.
- Shoigu likely seeks to deflect intensifying accusations that the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) cannot provide sufficient ammunition to Russian forces.
- Russian reactions to a claimed strike against Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces Commander Major General Ihor Tantsyura suggest Russian ultranationalists are attempting to frame any Russian operations as delaying potential Ukrainian counteroffensive actions.
- The Kremlin reportedly distributed a new manual instructing Russian state media on how to cover an upcoming potential Ukrainian counteroffensive that, if real, indicates the Kremlin is setting informational conditions both for an effective Russian defense and to mitigate shocks in the Russian information space from Ukrainian successes.
- UN member states, including key Russian partners like China, India, and Brazil, voted to adopt a resolution on April 26 that acknowledges Russia as the aggressor of the war in Ukraine.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks on the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces made marginal gains near Bakhmut but did not advance within the city itself.
- Russian forces continued limited offensive operations along the Avdiivka-Donetsk front, and Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted limited and local counterattacks in the Avdiivka area.
- Ukrainian forces continue to operate on and around islands in the Dnipro River delta in Kherson Oblast.
- Russian government officials are continuing to introduce new social benefits to veterans and their families to incentivize further military recruitment efforts in Russia.
- Likely Ukrainian partisans targeted an unspecified Zaporizhia Oblast occupation Ministry of Internal Affairs deputy head in Melitopol.
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 1, 2023
Russian forces conducted another large-scale missile strike against Ukraine on the night of April 30 to May 1. Ukrainian sources reported that nine Tu-95 and two Tu-160 strategic bombers took off from Murmansk Oblast and near the Caspian Sea and launched 18 Kh-101/555 cruise missiles at Ukraine.[1] Ukrainian air defense shot down 15 of the missiles.[2] Geolocated footage from Pavlohrad, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, shows that one of the missiles struck the Pavlohrad Chemical Plant and caused a massive explosion on impact.[3] The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed on May 1 that the strikes targeted Ukrainian military-industrial objects and successfully disrupted the production of military resources.[4] The Russian MoD has recently shifted its rhetoric and is actively describing strike campaigns, likely in an effort to portray a proactive approach to growing concerns in the Russian information space regarding a Ukrainian counteroffensive. Russian milbloggers claimed that the missiles struck Ukrainian air defense systems and a transportation hub in Pavlohrad.[5] Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Yuriy Ihnat noted that the fact that both the Tu-95 and Tu-160s carried far fewer missiles than their maximum load suggests that Russia continues to struggle with adequate production of such munitions.[6]
The White House assessed on May 1 that Russian forces have suffered 100,000 causalities—80,000 wounded and 20,000 killed—in fighting for Bakhmut since January 2023.[7] US National Security Council Spokesperson John Kirby announced that half of the 20,000 killed in action were Wagner Group fighters. Kirby also assessed that Russia’s offensive on Bakhmut has failed.[8]
Ukrainian officials continue to signal Ukraine’s readiness for potential counteroffensive operations. Ukrainian Defense Minister Oleksii Reznikov stated on May 1 that Ukraine is “reaching the finish line” in terms of when it will be ready to launch counteroffensive actions.[9] Reznikov noted that the ratio of available ammunition still does not favor Ukraine but stated that Russian capabilities continue to be limited.[10] Ukrainian Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) Head Kyrylo Budanov emphasized on April 30 that the main goal of the Ukrainian counteroffensive remains the liberation of all Ukrainian territory and stated that he hopes Ukraine will be able to improve its positions along the entire frontline in order to effectively threaten Russian logistics in occupied Crimea and Donbas.[11]
Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin is likely using his rehabilitated standing with Russian leadership to amplify his self-promotion efforts and his longstanding issues with the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD). Russian sources began circulating an alleged letter from the MoD to Prigozhin on April 30 responding to Prigozhin's Apil 29 interview wherein he threatened to withdraw Wagner forces from Bakhmut if the Russian military fails to provide more ammunition to Wagner.[12] The letter, dated April 23, lists all the artillery ammunition and equipment that the Russian MoD provides to Wagner.[13] A Russian official may have released the letter to stop Prigozhin from using the issue of artillery shortages to criticize the MoD as he has done in the past.[14] Prigozhin responded by stating that the figures provided by the unverified document are still not sufficient for what Wagner needs to complete its assigned tasks.[15] Prigozhin then claimed on May 1 that Wagner is in possession of large stocks of weapons it captured from Ukrainian forces during the seizure of Soledar in January 2023, and Prigozhin rhetorically boasted that he has enough arms to support a million-strong army.[16] Prigozhin suggested that he would offer to exchange these stocks of weapons for the resources that Wagner requires.[17] Prigozhin will likely continue to rely on his existing informational lines of attack to promote himself and seek further privileges from the Russian military as he retains a rehabilitated standing with Russian leadership.[18]
The Russian MoD confirmed on April 30 the replacement of Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev with Colonel General Aleksey Kuzmenkov. The MoD provided no justification for the replacement nor did it specify whether Mizintsev has a new role. Russian milbloggers began speculating about the replacement of Mizintsev with Kuzmenkov, who was then Deputy Head of the Russian National Guard (Rosgvardia), on April 27.[19] Regular changes to the Russian military command have resulted in increasingly factionalized Russian military and disorganized command structures that degrade Russia’s military capability, as ISW has recently assessed.[20]
The Russian MoD opposition faction is likely attempting to remove select MoD officials by publicly criticizing their war efforts. Russian milbloggers complained that Deputy Defense Minister Colonel General Yunus-bek Yevkurov visited the Kherson direction months ago and did not fulfill his promise to allocate 140 to 150 boats to Russian forces to defend the islands in the Dnipro River Delta.[21] One milblogger claimed that the lack of watercraft prompted Kherson Oblast occupation head Vladimir Saldo to order his administration in mid-April to start commandeering civilian boats for Russian military use.[22] Milbloggers’ criticism of Yevkurov follows the dismissal of the Russian Deputy Defense Minister for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev on April 27.[23] Mizintsev was reportedly dismissed after Commander of the Russian Airborne (VDV) forces and Wagner affiliate Colonel General Mikhail Teplinsky’s inspection of the Northern Fleet troops revealed significant issues with supply provisions.[24] Teplinsky reportedly assumed command of Russian forces in southern Ukraine in mid-April and may be using his new appointment to remove Russian MoD officials with the justification that they are failing to adequately supply troops. ISW assessed on April 30 that Teplinsky likely gained Russian President Vladimir Putin’s favor in late March, and the milbloggers’ criticisms against Yevkurov is likely an ongoing effort to weaken or remove a group of Russian military commanders and officials who are loyal to Russian Chief of General Staff Army General Valery Gerasimov.[25]
Key Takeaways
- Russian forces conducted another large-scale missile strike against Ukraine on the night of April 30 to May 1.
- The White House assessed on May 1 that the Russian offensive against Bakhmut has failed.
- Ukrainian officials continue to signal Ukraine’s readiness for potential counteroffensive operations.
- Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin is likely using his rehabilitated standing with Russian leadership to amplify his self-promotion efforts and his longstanding issues with the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD).
- The Russian MoD confirmed the replacement of Russian Deputy Minister of Defense for Logistics Colonel General Mikhail Mizintsev with Colonel General Aleksey Kuzmenkov.
- The Russian MoD opposition faction is likely attempting to remove select MoD officials by publicly criticizing their war efforts.
- Russian forces conducted ground attacks along the Svatove-Kremmina line.
- Russian forces continued ground attacks in and around Bakhmut and on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
- Ukrainian officials indicated that Wagner Group and other Russian forces are struggling to maintain their pace of offensive operations in Bakhmut.
- Russian sources continue to claim that Ukrainian forces are conducting raids across the Dnipro River.
- The recent increased prevalence of Russian private military companies (PMCs) operating in Ukraine may be necessitating certain changes in the overall command structure.
- Russian officials and occupation authorities continue efforts to integrate occupied territories into the Russian socio-economic system.